new superbug found
advertisement

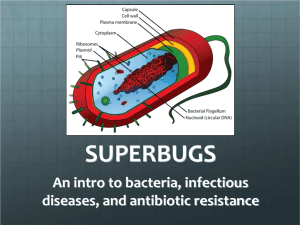
NEW SUPERBUG FOUND NDM-1, or New Delhi Metallo-betalactamase, is a newly found mutation in bacteria that causes bacteria to become super resistant to antibiotics. This means that we cannot fight the disease, and there is no known way of killing it. NDM-1 is extremely dangerous for this reason. If an outbreak of NDM-1 occurred, there may be no stopping it. NDM-1 is only a mutation of bacteria. It is not actually its own disease, but a variation of diseases. So far, NDM-1 has only been found in E. Coli and Klebsiella pneumonia. It causes the affected bacteria to become super resistant to antibiotics and also makes them more lethal. E. Coli is a bacteria that often causes urinary tract infections. Antibioticresistant E. Coli may also be responsible for fatal cases of pneumonia and other infections. The other affected disease, Klebsiella pneumonia, has symptoms that include sudden onset of high fever, and hemoptysis. Klebsiella pneumonia is also known for causing urinary tract infections, intraabdominal infections, and nosocomial pneumonia. If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms be sure to contact your doctor immediately. NDM-1 was widespread in India before scientists discovered much about it. It wasn’t until Dr.Timothy Walsh observed a case in America that real research was conducted. Walsh’s team concluded that NDM1 (New-Delhi-metallo-betalactamase) was a mutation that occurred on many different types of bacteria. This mutation made an enzyme that counteracted the effects of carbapenems. Carbapenems are a type of antibiotic that inhibits the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. This effectively kills the bacteria because this organelle is necessary for their survival. Carbapenems were considered one of the strongest classes of antibiotics and NDM-1 is making Bacteria completely immune to it as well as a wide variation of other antibiotics. NDM-1 spreads easily between Bacteria species because it travels on a plasmid or a loop of DNA that can be copied and traded easily during conjunction. In order to fight NDM-1 and other superbugs there a few steps that need to be taken. One is to stop unnecessarily pumping antibiotics into our livestock. 80% of all antibiotics in the United States are being given to livestock. Farmers are giving their animals antibiotics in mass before they are infected instead of waiting until the animal is infected and administering the appropriate dosage. Another reason that farmers are administering large amounts of antibiotics to animals is because they often raise the animal’s growth rate causing them to mature faster which is good for business. This causes an enormous demand on bacteria to mutate and develop new strains that are resistant to these drugs. So by lowering this rate of distribution it is possible to slow the development of new superbugs. A second space age seeming method is called phage therapy, this is the engineering of new viruses that would prey on bacteria and kill them within infected humans. This method has not received the necessary funding for it to make any real progress yet. By not feeding our livestock so many antibiotics, and the funding of phage therapy we can fight these mutations and superbugs. NDM-1 is found on a on the plasmids of DNA, on an extra chromosomal loop. This allows the mutation to be traded easily among other DNA. It is passed freely from one strain to the next. Due to the mutation producing an enzyme that will counteract with an antibiotic, it is found to spread on people who are receiving antibiotic treatments. In order to stop the spread of the mutation, tests need to be ran in order to find out which antibiotics NDM-1 is not resistant to. Looking at the antibiotic resistant patterns can help to determine this. Scientists perform tests growing isolated bacteria strains of NDM-1 with the presence of disks containing the antibiotic. Bacteria that are resistant to the antibacterial will continue to grow up to the edge of the disk, but if the antibiotic is susceptible to the bacteria a clear white space is left around the disk, showing the stop of growth. Some common susceptible antibiotics to NDM-1 are Colistin, and Tigecycline, Aztreonam. Colistin specifically helps fight NDM-1 because of its toxicity, as well as it has not been used in the past few decades. There has been a new antibiotic made to help stop the replication of NDM-1, but it has not been clinically tested, and has yet to be found in drug stores.