1. D [1] 2. B [1] 3. C [1] 4. B [1] 5. A [1] 6. A [1] 7. C [1] 8. C [1] 9. A [1
advertisement
![1. D [1] 2. B [1] 3. C [1] 4. B [1] 5. A [1] 6. A [1] 7. C [1] 8. C [1] 9. A [1](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006589960_1-5376af4ffd182ddab56a5a434b7f3bc0-768x994.png)
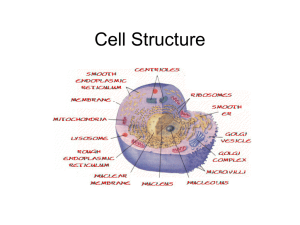
1. D [1] 2. B [1] 3. C [1] 4. B [1] 5. A [1] 6. A [1] 7. C [1] 8. C [1] 9. A [1] IB Questionbank Biology 1 10. (a) Award marks for any of the following clearly drawn and correctly labelled. cristae; inner membrane; outer membrane; intermembrane space; matrix; ribosomes; DNA; 4 max (b) cristae provide surface area for oxidative phosphorylation; inner membrane contains electron transport chains/ATP synthase (which carry out oxidative phosphorylation); outer membrane separates the mitochondrion from the rest of the cell; mitrochondrial DNA/ribosomes make (mitochondrial) proteins; small volume intermembrane space allows for higher concentration of protons; matrix has enzymes for the Krebs cycle; 3 max [7] 11. pyruvate (from glycolysis) enters a mitochondrion; enzymes in the matrix remove one carbon dioxide and hydrogen from the pyruvate; hydrogen is accepted by NAD/forms NADH; removal of hydrogen is oxidation; removal of carbon dioxide is decarboxylation; the whole process/link reaction is oxidative decarboxylation; the product is an acetyl group which reacts with CoA/coenzyme A; acetyl CoA enters Krebs cycle; Accept any of the above points in the form of a clearly drawn and correctly labelled diagram. 4 max [4] 12. (a) Award [1] for each structure clearly drawn and correctly labelled. Whole cells not necessary. (plasma) membrane—single line surrounding cytoplasm; nucleus — with a double membrane and pore(s) shown; mitochondria(ion) — with a double membrane, the inner one folded into internal projections, shown no larger than half the nucleus; rough endoplasmic reticulum—multi-folded membrane with dots/ small circles on surface; Golgi apparatus—shown as a series of enclosed sacs with evidence of vesicle formation; ribosomes — dots/small circles in cytoplasm/ribosomes on rER; lysosome; Award [0] if plant cell is drawn. Award [2 max] if any plant cell structure (e.g. cell wall) is present. IB Questionbank Biology 4 max 2 (b) prokaryotic eukaryotic naked DNA protein associated with DNA; DNA in cytoplasm / nucleoid / no nucleus DNA in nucleus / nucleus present; circular DNA linear chromosomes/DNA molecules; no mitochondria mitochondria; 70S ribosomes present 80S ribosomes present; no membrane bound organelles internal membranes form organelles; pili present pili absent; plasmids (sometimes) present plasmids absent; cell wall present cell wall only present in plants/fungi; Do not accept cell wall sometimes present. flagella solid flagella flexible/membrane-bound; 6 max (c) DNA replication is semi-conservative / each strand of DNA acts as template; (DNA) helicase separates two strands/forms a replication fork; new strand built / nucleotides added in a 5´ to 3´ direction; (deoxy)nucleoside triphosphates hydrolysed to provide energy for nucleotide formation/base pairing; on one strand DNA polymerase III builds continuous strand; on other strand short chains of DNA/Okazaki fragments are formed; each short chain starts with RNA primer; added by RNA primase; then remainder of chain of DNA built by DNA polymerase III; DNA polymerase I removes RNA primer and replaces it by DNA; DNA ligase joins DNA fragments together forming complete strand; replication only occurs at a single replication fork; Award credit for any of the above points clearly drawn and accurately labelled. 8 max (Plus up to [2] for quality) [20] 13. (a) Award [1] for each of the following clearly drawn and labelled correctly. a double layer of lipid / phospholipid molecules — with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails; an integral protein —passing completely through the lipid bilayer; a peripheral protein — shown on the surface and not penetrating the lipid bilayer; an integral protein with a pore passing through its entire length / a glycoprotein with the carbohydrate components shown / cholesterol as component in bilayer; 4 IB Questionbank Biology 3 (b) chlorophyll is composed of a number of pigments; absorb different colours of light; mainly red and blue absorbed; green light reflected; temperature increases rate; up to a point where enzymes denature; light intensity increases rate; up to a point where maximum absorbance can occur; carbon dioxide increases rate; up to a point where fixation is at a maximum; (c) 6 max Krebs cycle:[3 max] in matrix of mitochondrion; decarboxylation; oxidation / removal of hydrogen by NAD and FAD; substrate level phosphorylation; Electron transport chain:[5 max] transfer of hydrogen to inner membrane carriers; hydrogen ion pumped across inner membrane; creates a concentration gradient; electron transferred between carriers; chemiosmosis; hydrogen ion passes down concentration gradient; through ATPase complex; oxygen is final acceptor forming water; 8 max (Plus up to [2] for quality) [20] IB Questionbank Biology 4