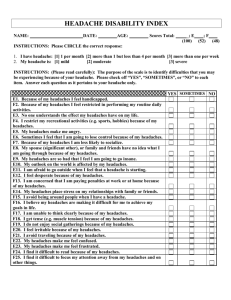
Headache
advertisement
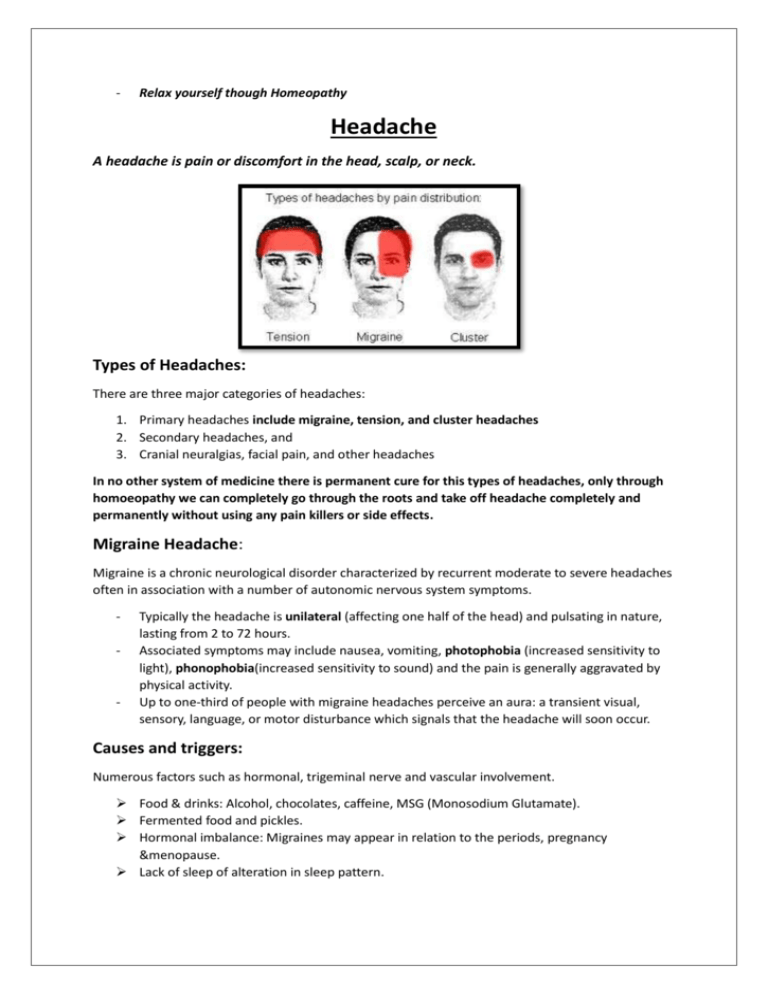
- Relax yourself though Homeopathy Headache A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Types of Headaches: There are three major categories of headaches: 1. Primary headaches include migraine, tension, and cluster headaches 2. Secondary headaches, and 3. Cranial neuralgias, facial pain, and other headaches In no other system of medicine there is permanent cure for this types of headaches, only through homoeopathy we can completely go through the roots and take off headache completely and permanently without using any pain killers or side effects. Migraine Headache: Migraine is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent moderate to severe headaches often in association with a number of autonomic nervous system symptoms. - - Typically the headache is unilateral (affecting one half of the head) and pulsating in nature, lasting from 2 to 72 hours. Associated symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, photophobia (increased sensitivity to light), phonophobia(increased sensitivity to sound) and the pain is generally aggravated by physical activity. Up to one-third of people with migraine headaches perceive an aura: a transient visual, sensory, language, or motor disturbance which signals that the headache will soon occur. Causes and triggers: Numerous factors such as hormonal, trigeminal nerve and vascular involvement. Food & drinks: Alcohol, chocolates, caffeine, MSG (Monosodium Glutamate). Fermented food and pickles. Hormonal imbalance: Migraines may appear in relation to the periods, pregnancy &menopause. Lack of sleep of alteration in sleep pattern. Medications: Contraceptive pills, Excessive use of migraine relieving pain-killers, HRT(Hormone replacement therapy) etc. Sensory Stimuli: Sunlight, bright or fluorescent light, glare and loud noises and unusual or strong smells. Skipping or delaying a meal. Stress: Excessive mental & physical stress, depression and insomnia. Watching movies or moving objects may trigger an attack. Signs and symptoms: Migraine attacks typically have the following stages: 1. 2. 3. 4. Prodrome Aura Headache Postdrome Prodromal Stage: Less than half of Migraineurs experience prodromal symptoms which appear a few hours or days prior to an attack. These symptoms, if recognized early, can help one avoid the actual attack. A general feeling of elation, irritability or an unusually, sudden desire for sweets, water etc appears during this stage. Headaches with auras Approximately I/5 of individuals suffering from migraine experience an aura or warning symptoms 15-20 minutes prior to an attack. The aura comprise of: Visual: Wavy, flashing or sparkling light or blind spots in the field of vision. Olfactory: Smelling odors that are actually not there. Tingling or needle like sensation in their arms, face etc. Difficulty in speaking or weakness in articulation. Headaches without aura Individuals experiencing such attacks primarily suffer from the pain and do not experience any other associated symptom or symptoms before the attack. Symptoms during this attack are: Pain confined to one side of the head or may affect both sides. Pain may also affect the eyes, temple area and may radiate to the face and jaws. Nature of pain is usually moderate to severe and pulsating or throbbing. Pain associated with nausea and/or vomiting. Sensitivity to light and noises during the pain. Sensitive to anything touching the head during attack. Pain may typically last for up to 72 hours. Postdrome Following the attack most individuals experience the following symptoms which last for a few hours to day: Tiredness or Fatigue. Depression or mood elation. Poor comprehension. Lack of concentration. Tension Headache: Tension-type headache pain is often described as a constant pressure, as if the head were being squeezed in a vice. The pain is frequently bilateral which means it is present on both sides of the head at once.This headache is due to constant stress and tension in once mind. Triggers: Stress: usually occurs in the afternoon after long stressful work hours or after an exam. Sleep deprivation. Uncomfortable stressful position and/or bad posture. Irregular meal time (hunger). Eyestrain. Tension headaches may be caused by muscle tension around the head and neck. Cluster Headaches: The term "cluster headache" refers to a type of headache that recurs over a period of time. People who have cluster headaches experience an episode one to three times per day during a period of time (the cluster period), which may last from two weeks to three months. People who suffer from cluster headaches get them at the same time each year, such as the spring or fall. Causes: Tend to run in families and this suggests that there may be a genetic role. May be triggered by changes in sleep patterns. May be triggered by medications (for example, nitroglycerin, used for heart disease). If an individual is in a susceptible period for cluster headache, cigarette smoking, alcohol, and some foods (for example, chocolate). Symptoms: During the period in which the cluster headaches occur, pain typically occurs once or twice daily, but some patients may experience pain more than twice daily. Each episode of pain lasts from 30 to 90 minutes. Attacks tend to occur at about the same time every day and often awaken the patient at night from a sound sleep. The pain typically is excruciating and located around or behind one eye. The affected eye may become red, inflamed, and watery. The nose on the affected side may become congested and runny. What are secondary headaches? Secondary headaches are those that are due to an underlying structural problem in the head or neck. There are numerous causes of this type of headache ranging from bleeding in the brain, tumor, or meningitis and encephalitis. Homoeopathic Treatment: Homeopathic remedies for headaches are very popular due to their effectiveness and safety. Homeopathic medicines when carefully chosen have the ability to cure migraine headaches and also other types of headaches and also lower the frequency and intensity of attacks. Relapses of the headache can be stopped. Better pain management without the use of pain killers. Better long-term prognosis without any side effects. Significant reduction in the Migraine episodes. Better tolerance to stimuli or triggers of the headaches. Complete cure or long-term relief undeniably achievable.