Fill in Student Notes
advertisement

1
Pre-AP Chemistry Notes: Solutions
I. Types of Mixtures (p. 395 – 399) Ch. 13 Solutions
A. Solution– ____________________________ of 2 or more substances in a
single phase
1. Components of Solutions
a. __________________ - substance being dissolved --usually
________________ amount
b. ______________- dissolving medium --usually present in
________________ amount
c. Examples:
2.Types of Solutions
air
O2 gas and N2 gas
_____________________
soda
CO2 gas in water
_____________________
seawater
NaCl in water
_____________________
brass
copper and zinc
_____________________
3. Characteristics of Solutions
a. Have ________________________________ (ions or molecules)
b. Are ____________________________
c. __________________________________________
d. ____________________________________________
e. ______________________________________________
4. Electrolytes
a.Substance that dissolves in water to produce a ______________
that _____________________________________________
1) _______________________ separation of an ionic solid into
aqueous ________________
b. Ionic compounds (NaCl)
c. Polar cmpds (HCl & other acids)
1) ______________________ - breaking apart of some
_____________________________________ into
aqueous ions
5. Nonelectrolytes
a. Substance that dissolves in water to produce a solution that
______________________________________________________
1) Molecular Solvation - ________________________________
b. Molecular cmpds (sugar)
B. ____________________________ (_____________________________)
1. Characteristics
a. Have very ___________________________ (1000x larger than
atoms)
2
b. 1000+ nm
c. Settle out
d. ______________________________________
e. ___________________________________________________
2. Examples of Suspensions
Whole ______________ (with platelets, rbc’s, wbc’s & plasma)
Muddy water
Calamine lotion (for poison ivy)
C. _____________________________ (not solutions)
1. Characteristics
a. Have ______________________ size particles
b. 1nm to 1000 nanometers
c. _____________________________________________
d. Separated with semi-permeable membranes
e.Scatter light (______________________________________)
2. Examples of Colloids
______________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
II. The Solution Process (dissolution = dissolving)
A. _________________________ – what effects how ________________
something dissolves?
1. _______________ of solute
a. Increase surface area of solute – crush the solute – dissolution (the
process of dissolving) occurs on the surface of the solute
2. _______________ of solvent
a. Agitate the solution – stir it- helps to disperse the solute particles
b. opposite for a gas!
3. ____________________________________________
a. Heat the solvent – ______________________ & helps to separate
solute particles from each other
b. opposite for a gas!
4. ________________________________________
a. _____________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________
b. Gas in contact w/ surface of liquid & some gas is dissolved into the
liquid while some gas also escapes the liquid until equilibrium is
reached
c. If you change the pressure a new _________________ is reached
3
d. __________________________ on the gas (solute) causes more
molecules to collide w/ the surface of the liquid so more gas
molecules become dissolved in the solvent until a new EQ is reached
at the new pressure----____________________ (Le Who?) Principal
(apply a stress to a system in EQ & it will eventually reach a new EQ)
e. _____________________ (of gas dissolved in a liquid)
1) The solubility of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to its
pressure above the liquid (temp remains constant)
SOOOOOOOOOOO… if the pressure of the gas above
the liquid increases then the solubility of the gas increases
Partial pressure blah, blah, blah
B. _____________________________aka dissolution – the process of
dissolving
1. _________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________
2. solute particles are _______________________ and pulled into solution
C. __________________________
1. Amt of substance required to form a saturated solution w/ a specific amt
of solvent at a specific temp
2. __________________________________ is the opposite of dissoluton!
3. Solution equilibrium – state where the
__________________________ = ________________________________
4. p. 404 Chart shows amt of g of solute that can be dissolve in 100 g water
at different temps.
5. Liquids that aren’t soluble in each other are considered
___________________
Liquids that are soluble in each other are considered
___________________
D. Saturated solution
1. A saturated solution contains the ______________________________
___________________________________________________________
a. If you add any more solute at that temp it will not dissolve but {sink}
to the bottom
E. Unsaturated
1. An unsaturated solution contains ____________________________
________________________________________________________________
a. All the solute you put in has dissolved & there is still room in the
solution for more solute
F. Supersaturated
1. A solution that contains __________________________________
saturated solution can hold under the same conditions!
4
a. Usually prepared by ________________________ &
_________________ it, filtering out any excess solute, then letting the
solution cool while being careful not to disturb it in any way – if you
bump it etc…crystallization begins because it is ______________
__________________!
II. Solute-solvent interactions- ____________________________________!
A. Ionic compounds dissolve in ____________________________ but not in
nonpolar molecular solvents & _____________ substances dissolve in
____________________ substances
1. ___________________ – forming a solution with water as the solvent
2. Some hydrated ionic solutions when crystallized incorporate some of the
water molecules in their crystals & are then called _______________
B. Soap/Detergent why does it work on everything?
1______________________ with long ____________________________
2. dissolves nonpolar grease in polar water
C. Heats of Solution
1. ____________________________ goes hand-in-hand w/ an
______________, E can either be absorbed or released dependent on the
solute & solvent (can be a really small amount)
2. The ________________________________ is the heat of solution (it’s
different for each solute/solvent combo)
a. + if heat is absorbed (it gets cold to the touch) endothermic
b. - if heat is released (it gets hot to the touch) exothermic
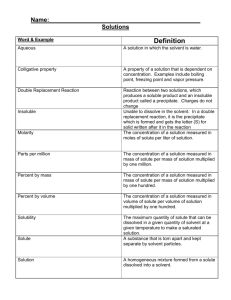
III. Concentration of Solutions--The __________________________________.
A. Describing Concentration
1. __________________________ - medicated creams
2. __________________________ - rubbing alcohol used by bio
3. ____________________ - water contaminants
4. _________________________- used by chemists
5. _________________________ - used by chemists
B. Molarity = ___________________________________________ (not liter
of solvent)
C. molality = ___________________________________________
D. ______________________________- Preparation of a desired solution by
adding water to a concentrate.
Moles of solute remain the same. M1V1 = M2V2