SI Figure legends Fig. S1. Crossing for recombination analysis
advertisement

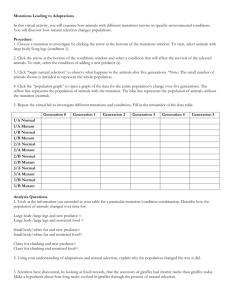
1 SI Figure legends 2 Fig. S1. Crossing for recombination analysis between Bm and Ws. Wild type 3 females and F1 offspring (Bm × Ws) were crossed to obtain individuals with 4 recombination between the Bm and Ws mutations. 5 6 Fig. S2. Phenotypes of Bm and Ws mutations in pupae. Wild type (p50T), 7 Bm mutant (No. 908), and Ws mutant (u42). The panels show the three 8 different pupal stages: day 0, eye-pigmented stage, and 1 day before 9 emergence. The phenotypes of both mutations were observed clearly from 1 10 day before emergence. The arrowheads indicate the spot at the apex of the 11 wing. 12 13 Fig. S3. RT-PCR analysis of the candidate genes of Bm and Ws in the 14 overlapping region. Twenty-four candidate genes were predicted based on 15 the overlapping region (Fig. 4 and Table 3). The letters correspond to the 1 16 numbers in Table 3. 18S ribosomal RNA was used as an internal control. 17 18 Fig. S4. RT-PCR analysis of the candidate genes for Bm and Ws. RT-PCR 19 was performed using primer sets based on the 5′- and 3′-UTRs using the 20 sequences of full-length cDNA or EST clones that corresponded to the 21 predicted genes: BGIBMGA005550 (I), 005522 (M), 005557 (S), and 22 005656 (R) (Table 3). cDNA was prepared from the wing on pupal day 0. 1, 23 p50T (wild type); 2, No. 908 (Bm mutant); 3, u42 (Ws mutant). The 24 numbers on the right represent the fragment sizes of . 174 DNAs were 25 digested separately with Hind III and Hae III. 18S ribosomal RNA was used 26 as an internal control. 2