Technical Description
advertisement

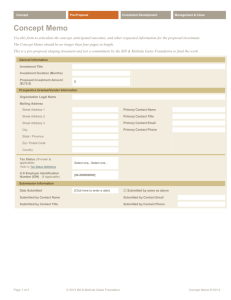
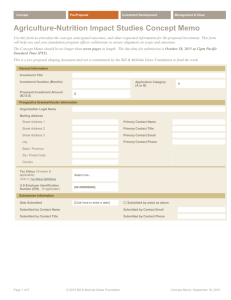
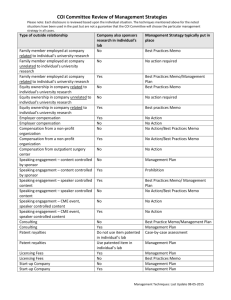
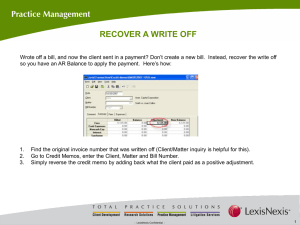
English 314: Technical Communication Technical Description (10%) Due: Thurs, 2/7/08 We all use the word description loosely to refer to practically any discussion or explanation. The biggest hurdle you may face in writing a technical description is remembering what the term means as it is used in this context. “Descriptions, like definitions, help define an idea. In addition, descriptions use words and visuals to create a picture of the produce or process, such as the structure of a bicycle frame or the process of nuclear fission.” (G&L, 257). That means discussing things like color, shape, size, weight, height, width, thickness, texture, density, contents, materials of construction, process, procedures, timeline, and so on. It also means discussing any quantifiable details such as numbers. For example, the sentence "A computer diskette is a device used for storing electronic data" is not really description in our sense of the word. It explains the function or purpose but provides little or no physical detail. However, the sentence "The common computer diskette is 3.5 inches by 3.5 inches and approximately 1/8 inch thick" is very definitely description. Descriptions are common element in technical writing. Descriptions appear more often as a sentence or two here, a paragraph there, or a whole section there. There are certain kinds of technical writing that feature description. You can imagine accident reports requiring plenty of description. Product specifications--documents that describe design and feature of a new or changed product--have plenty of description. Also instructions typically require description as an important supplement: readers need to be able to visualize what they are doing and what they are working with. Description Select a technical item or process for your field of study. Ensure that the item or process is sufficiently technical as to require explanation to field-outsiders. Also ensure that you select a small enough concept to be explainable within the frame work of this assignment. For example, you could explain a technical item like a vacuum picker wheel in a planter or a technical procedure like restriction fragment length polymorphism isolation. Explain this item or process to a lay audience using an appropriate combination of the following strategies: Physical Description Process Description Etymology History and Background Operating Principle Life Cycle Visual Representation Analogy Cause and Effect Troubleshooting English 314 Sec 16 Spring 2008 Page 2 Description of Description Your technical description should be confined to two sides of a 1 page handout on 8 ½ x 11 in paper. It should include roughly 50% written and 50% visual content. It should be printed in color. The design, layout, and orientation of the document are at your discretion. Explanatory Memo Additionally, you should compose a 2-3 page memo report explaining your technical description. The memo should specify the audience, purpose, and context of your technical description, and explain your rationale behind selecting chosen descriptive strategies. You may choose to situate your technical description within a rhetorical context appropriate to your anticipated career. Therefore it may be addressed to bosses, non-technical coworkers, clients, government regulators, or another appropriate audience. Additionally, you will need to specify the document purpose, and context of use. These details will be critical in explaining your selected rhetorical strategies. Some Evaluation Criteria Description includes adequately explains technical item/process. Description is appropriate for the specified rhetorical situation. Description is well-organized and coherent. Description is clear and easy to understand. Description is visually informative. Description is visually engaging. Memo includes rhetorical situation. Memo clearly explains selected description strategies. Memo clearly details why strategies are appropriate for rhetorical situation. Memo is well organized with clear introduction, thesis, and conclusion. Memo contains few or no errors in correctness.