CHEMISTRY I
advertisement

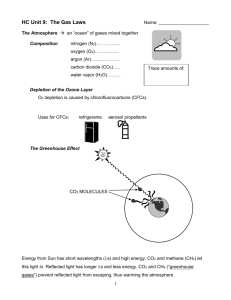
CHEMISTRY I Kinetic Theory Review Matching: 1. _____ Energy of movement in an object. 2. _____ Force of billions of collisions between gas molecules and the surface of an object. 3. _____ Piece of equipment that measures atmospheric pressure. 4. _____ A measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in matter. 5. _____ Temperature at which all molecular motion stops. 6. _____ State of matter with no definite shape but definite volume. 7. _____ State of matter with highest kinetic energy 8. _____ State of matter with definite shape and definite volume. 9._____ State of matter with no definite shape and no definite volume; particles have random motion. A. B. C. D. Absolute Zero Barometer Gas Gas Pressure G. Kinetic Energy H. Liquid I. Plasma J. Solid K. Temperature Pressure Conversions: 18. 216.5 kPa = ________ atm 19. 2.65 atm = ________ mm Hg 20. 842.2 mm Hg = _______ kPa 21. 1.65 atm = ________ kPa 22. 812.5 mm Hg = _______ atm 23. 176.4 kPa = ________ mm Hg Kinetic Energy: 24. What is the equation for kinetic energy? _____________________ 25. As mass increases, velocity will (increase/decrease). This is a(n) (direct/inverse) relationship. 26. As kinetic energy decreases, velocity of the object will (increase/decrease). This is a(n) (direct/inverse) relationship. 27. A larger gas molecule will have a (high/low) kinetic energy. This is a(n) (direct/inverse) relationship. Temperature Conversions: 28. 35 °C = ________ K 32. 52 °C = _______ K 29. 100 °C = _______ K 33. -22 °C = ______ K 30. 298 K = _______°C 34. 317 K = ______ °C 31. 286 K = _______ °C 35. 356 K = ______ °C 36. Heat always flows from ________ to ________. States of Matter: Kinetic Energy Motion of Particles Shape Volume Solids Liquids Gases Plasma 1. _____________________ forces hold particles together in ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. 2. _____________________ forces are the forces of attraction between particles. 3. The three main types of intermolecular forces are: 1) ___________________________, 2) ____________________________, and 3) ______________________________. 4. _______________________ are the weakest of all molecular attractions. 5. ______________________ result from temporary shifts in the density of electrons in electron clouds. 6. Dispersion forces exist between all particles, but are the dominant force of attraction between identical ________________ molecules. 7. ______________________ is the attraction between oppositely charged regions of polar molecules. 8. Liquids take the ______________ of their container while their ______________ is fixed. 9. The higher density of liquids than gases is due to their __________________ forces. 10. ________________ is the ability to flow. 11. ________________ is a measure of the resistance of a liquid to flow. 12. Viscosity of a liquid is determined by 1) _______________________________, 2) _________________________________, and 3) _____________________ of the particles. 13. Viscosity decreases with _________________. 14. Solids have a/n ______________ shape and volume. 15. Ice floats because it is less ___________ than water. 16. Atoms such as carbon and silicon, which can form, multiple covalent bonds, are able to form ________________________________ solids. Examples are ________________, ________________, and __________________. 17. The term _______________ is used when the three states of matter coexist as physically distinct parts of a mixture. 18. The _________________ of a crystalline solid is the temp. at which the forces holding its crystalline lattice together are broken and it becomes a liquid. 19. _________________ is the process from which a liquid changes to a gas or vapor. 20. _________________ is the method by which your body controls its temp. 21. Evaporation is when vaporization occurs only at the ________________ of a liquid. 22. _______________ pressure is exerted by a vapor over a liquid. 23. ___________________ is the temp. at which the vapor pres. of a liquid equals the external pres. 24. __________________ is the process in which a solid changes directly to a gas without first becoming a liquid. 25. Examples of sublimation are _______________________ and ______________________________, 26. ___________________ is the process by which a substance changes from a gas to a solid without first becoming a liquid. An example is ____________________________________________. 27. ________________________ is the temp. at which a liquid is converted into a crystalline solid. 28. A ________________________ is a graph of pres. vs. temp. at which three phases of a substance can coexist. 29. _____________________________ indicates the critical pres. and critical temp. above which water cannot exist as a liquid. 30. ____________________ on a phase diagram represents the temp. and pres. at which 3 phases of a substance can coexist. 31. How does the lowering of atmospheric pressure affect boiling point?__________________________ Pressure (mm Hg) USE THE PHASE DIAGRAM BELOW TO ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS 55,327 Liquid Solid 3885 Gas 760 Vapor -78 -57 31 Temperature (C) 32. What is the triple point of the substance depicted in the phase diagram above? 33. What is the melting point at 55,327 mmHg? _________ sublimation point at 760 mmHg? ____________ 34. What phase is this substance in at –67C and 3900 mm Hg of pressure? 35. At what temperature and pressure is triple point? ________________ 36. At what temperature and pressure is critical point? _________________