Evolution Notes
advertisement

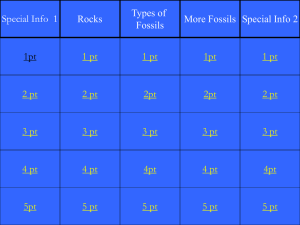
Evolution Notes 1. Species = group of organisms that can reproduce with each other and have babies. - Only two organisms of the same species can mate and produce fertile offspring. 2. Evolution = change in genetics of a species over time. 3. Theory of acquired characteristics = species evolve by keeping traits their parents developed & used in their lives & loosing traits their parents didn’t use or develop. THEORY PROVEN WRONG - According to their theory by Jean Baptiste de Lamarck, giraffes got longer & longer necks with each generation because their parents were always trying to reach higher in the trees for food. 4. Charles Darwin came up with the theory of evolution. - Darwin was a ship’s naturalist on the HMS Beagle. His job was to record information about all the plants and animals they saw while on their journey. - Darwin found many different plants & animals that were never seen before – especially on the Galapagos Islands. 5. Natural selection = organisms with traits best suited to their environments are more likely to survive. Factors controlling natural selection: - Organisms make more offspring than can survive. - Variations are found among individuals of a species. - Some variations allow members of a population to survive longer and reproduce more. - Over time, offspring with more helpful variations make up more and more of a population. 6. Mutation = a natural change, or mistake, in the DNA occurring during cell division (mitosis or meiosis) 7. Variation = appearance of an inherited traits that makes an individual different from other members of the same species. Ex: blonde, brown, black, & red hair are all natural variations of human hair color. - Mutations in DNA are what cause variations to happen. 8. Population = group of organisms of one species that live in an area. 9. If enough variations occur in a population as it makes more offspring, a new species can be formed from the existing species. This takes a very long time to happen. 10. Adaptation = any variation that makes an organism better suited to its environment. 11. When new individuals come into a population from outside the area, they bring in new genes and variations. If a population is cut off geographically (mountain range, deep valley or canyon, ocean, sea, etc) from the rest, it can create a new species from the original species. 13. Gradualism = theory of evolution by slow changes of a species over time to create a new species. - This takes place over many thousands or millions of years. - There are many small changes in the fossils of a species over a long period of time. - Example: horse from Eohippus slowly changes over time to today’s Equus. 13. Punctuated Equilibrium = theory of evolution by rapid changes in the DNA due to mutations. - New species are created within a few generations. - There are no intermediary fossils to show small changes. The fossils are one thing, then all of a sudden they are a new species. - Examples: elephant from Primelephas to today’s Asian and African elephants; bacteria becoming resistant to penicillin within the last 50 years 14. Branching tree diagram used to show how organisms evolve over time. 15. Evolution is gradual and slow with many small changes until a mutation in the DNA makes a sudden change in the species. Then evolution goes back to being small changes over a long time again. - Species unable to evolve and adapt to their environments will die out and become extinct. 16. Fossils = remains of life from an earlier time. Examples: - Imprint of a leaf, feather, or organism in a rock 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. - Cast made of minerals that filled in the hollows of an animal track, shell, etc - Piece of wood or bone replaced by minerals - Organism frozen in ice - Organism trapped in plant resin (tree sap) Sedimentary rock = type of rock formed by mud, sand, etc that build up layer by layer over years. - Fossils are found in sedimentary rock. Igneous rock is cooled magma and would burn up the fossil. Metamorphic rock is heated sedimentary rock. It would also burn up the fossil. Geologic Time Scale = shows Earth’s history divided into eras and periods. Fossils are placed into this to show how old they are and how long they were on Earth. Relative dating = dating fossils that gives an estimate of the fossils age. Older fossils are found at the bottom of a pile and younger fossils are found at the top. Radioactive dating = dating fossils by comparing the amount of rock that is still radioactive to the amount of rock that has lost some electrons and is now stable. - Rocks give off radiation, in the form of electrons, at a constant rate and each element has a different rate of losing electrons. This allows scientists to accurately date the age of each rock on Earth. - Example: Radioactive element uranium changes to lead as it ages. The more lead in the rock, the older the rock is. The more uranium still in the rock, the younger the rock is. Fossil Record = all the fossils found on Earth organized by date they were on Earth. - Fossil record can be broken down into smaller records. You can have the fossil record of the horse to see how the horse has changed from its earliest time to the horse we know today. - An organism found in the fossil record that is not on Earth today is extinct. - Fossil record shows that simple organisms existed on Earth early on and became more complex over time. - Only information needed to place a fossil in the fossil record is the name of the organism it belongs to & age of the fossil. A complete fossil is not needed. Fossil record is not complete because: - Not all organisms become a fossil. Most dead organisms will decompose long before they turn into a fossil or only small bits and pieces will be left behind. - We’ve not found all the fossils that have been created so far. - Many fossils have been destroyed through earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and human interactions like digging or pit mining. Homologous Structure = body parts that are similar in origin and structure from one species to another. - Used to show a common ancestor. - Example: Bat’s wing, bird’s wing, dolphin’s flipper, human’s arm all have same number of bones, muscles, and blood vessels in the same place. Vestigial Structure = body part that is reduced in size and doesn’t seem to have a function any more. - Used to show a common ancestor. - Examples: 4 toes on a horse, back legs of a whale, front and back legs of a snake, human’s appendix Embryology = study of the development of embryos (unborn babies in an egg or mommy’s tummy). - Used to show a common ancestor. - Example: fish, lizard, chicken, & rabbit all develop at about the same way and at about the same rate while they are an embryo. - Embryos show that all vertebrates, including humans, have tails & gills or gill slits before born. DNA = molecule that controls heredity or the passing down on traits from one generation to the next. - Used to show a common ancestor. - Organisms that are more closely related have DNA that is similar. - Example: a dog is a bear’s closest living relative today.