LES of Reacting Flows Summer School Schedule
advertisement
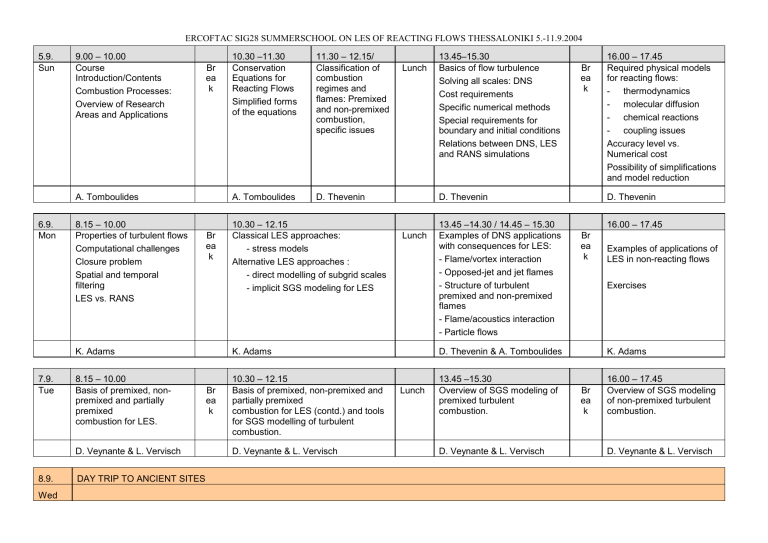
ERCOFTAC SIG28 SUMMERSCHOOL ON LES OF REACTING FLOWS THESSALONIKI 5.-11.9.2004 5.9. Sun 9.00 – 10.00 Course Introduction/Contents Combustion Processes: Overview of Research Areas and Applications Br ea k A. Tomboulides 6.9. Mon 8.15 – 10.00 Properties of turbulent flows Computational challenges Closure problem Spatial and temporal filtering LES vs. RANS Br ea k K. Adams 7.9. Tue 8.15 – 10.00 Basis of premixed, nonpremixed and partially premixed combustion for LES. D. Veynante & L. Vervisch 8.9. Wed DAY TRIP TO ANCIENT SITES 10.30 –11.30 Conservation Equations for Reacting Flows Simplified forms of the equations 11.30 – 12.15/ Classification of combustion regimes and flames: Premixed and non-premixed combustion, specific issues A. Tomboulides D. Thevenin 10.30 – 12.15 Classical LES approaches: - stress models Alternative LES approaches : - direct modelling of subgrid scales - implicit SGS modeling for LES Lunch 10.30 – 12.15 Basis of premixed, non-premixed and partially premixed combustion for LES (contd.) and tools for SGS modelling of turbulent combustion. D. Veynante & L. Vervisch Br ea k D. Thevenin Lunch K. Adams Br ea k 13.45–15.30 Basics of flow turbulence Solving all scales: DNS Cost requirements Specific numerical methods Special requirements for boundary and initial conditions Relations between DNS, LES and RANS simulations 13.45 –14.30 / 14.45 – 15.30 Examples of DNS applications with consequences for LES: - Flame/vortex interaction - Opposed-jet and jet flames - Structure of turbulent premixed and non-premixed flames - Flame/acoustics interaction - Particle flows D. Thevenin 16.00 – 17.45 Br ea k 13.45 –15.30 Overview of SGS modeling of premixed turbulent combustion. D. Veynante & L. Vervisch Examples of applications of LES in non-reacting flows Exercises D. Thevenin & A. Tomboulides Lunch 16.00 – 17.45 Required physical models for reacting flows: - thermodynamics - molecular diffusion - chemical reactions - coupling issues Accuracy level vs. Numerical cost Possibility of simplifications and model reduction K. Adams Br ea k 16.00 – 17.45 Overview of SGS modeling of non-premixed turbulent combustion. D. Veynante & L. Vervisch ERCOFTAC SIG28 SUMMERSCHOOL ON LES OF REACTING FLOWS THESSALONIKI 5.-11.9.2004 9.9. Thu 8.15 – 10.00 SGS turbulent transport in flames. Br ea k D. Veynante & L. Vervisch 10.9. Fri 8.15 – 10.00 Review of reactive LES Filtering and closure Terms SGS Closure for Momentum Transport Algebraic, 1- and 2equation dynamic models Two-Level Simulation S. Menon 11.9. Sat DAY TRIP TO CHALKIDIKI 10.30 – 12.15 Refined SGS modelling for premixed turbulent combustion. Lunch D. Veynante & L. Vervisch Br ea k 10.30 – 12.15 SGS Closure for Scalar Transport: Scale Similarity Models Linear-Eddy Models Thin-Flame Models, PDF Models Critical Analysis of SGS Models Numerical and unresolved issues Limitations, practical needs and implications RANS vs LES and DES S. Menon 13.45 –15.30 Refined SGS modelling for non-premixed and spray turbulent combustion. Br ea k D. Veynante & L. Vervisch Lunch 13.45 –14.30 Using LES to understand industrial flame stabilization mechanisms in swirling flows 14.30-16.00 Laboratory Flames Gas Turbine, and other turbulent reacting flow applications 16.00 – 17.45 Comparison between LES and experiments LES of real combustion systems D. Veynante & L. Vervisch Br ea k 16.30 – 17.15 Close up: - Reacting LES as a Design Tool? F. Biagioli (Alstom) S. Menon all Feedback Course Evaluation Suggestions/ Outlook