the process of water vapor in the air turning into liquid water
advertisement

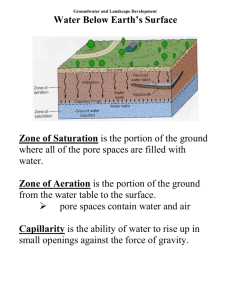
The Water Cycle Glossary aquifers--When a water-bearing rock readily transmits water to wells and springs, they are called aquifers. Wells can be drilled into the aquifers and water can be pumped out. Precipitation eventually adds water (recharge) into the porous rock of the aquifer. The rate of recharge is not the same for all aquifers, though, and that must be considered when pumping water from a well. Pumping too much water too fast draws down the water in the aquifer and eventually causes a well to yield less and less water and even run dry. In fact, pumping your well too fast can even cause your neighbor's well to run dry if you both are pumping from the same aquifer. condensation--the process of water vapor in the air turning into liquid water. Water drops on the outside of a cold glass of water are condensed water. Condensation is the opposite process of evaporation. evaporation--the process of liquid water becoming water vapor, including vaporization from water surfaces, land surfaces, and snow fields, but not from leaf surfaces. See transpiration ground water--(1) water that flows or seeps downward and saturates soil or rock, supplying springs and wells. The upper surface of the saturate zone is called the water table. (2) Water stored underground in rock crevices and in the pores of geologic materials that make up the Earth's crust. headwater(s)--(1) the source and upper reaches of a stream; also the upper reaches of a reservoir. (2) the water upstream from a structure or point on a stream. (3) the small streams that come together to form a river. Also may be thought of as any and all parts of a river basin except the mainstream river and main tributaries. hydrologic cycle--(scientific name for water cycle) -- the cyclic transfer of water vapor from the Earth's surface via evapotranspiration into the atmosphere, from the atmosphere via precipitation back to earth, and through runoff into streams, rivers, and lakes, and ultimately into the oceans. precipitation--rain, snow, hail, sleet, dew, and frost. runoff -- (1) That part of the precipitation, snow melt, or irrigation water that appears in uncontrolled surface streams, rivers, drains or sewers. Runoff may be classified according to speed of appearance after rainfall or melting snow as direct runoff or base runoff, and according to source as surface runoff, storm interflow, or ground-water runoff. (2) The total discharge described in (1), above, during a specified period of time. (3) Also defined as the depth to which a drainage area would be covered if all of the runoff for a given period of time were uniformly distributed over it. water cycle -- See Hydrologic Cycle above.