PROTOTYPE DRUG: Ranitidine (Zantac)
advertisement

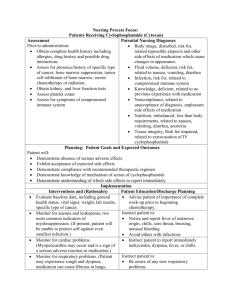
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Ranitidine (Zantac) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration Injury, Risk for (falls) related to drowsiness secondary to drug therapy Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Nutrition, Risk for Imbalanced: Less interactions than body requirements related to adverse effects of drug therapy Assess for presence/history gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastric Pain, related to gastric irritation ulcer secondary to ineffective response to Obtain vital signs drug therapy Assess liver and kidney function, Knowledge, Deficient related to drug pregnancy status and complete blood therapy and side effects count. Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Remain free of side effects including abdominal pain, heartburn, jaundice, hematemesis, and respiratory difficulty. Demonstrate understanding of risks and benefits of drug therapy. Remain free of physical injury Maintain balanced nutrition, and weight within expected levels Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Monitor serum creatinine, AST, ALT alkaline phosphatase and total bilirubin. Patient Education/Discharge Planning Advise patient to: Report symptoms of liver dysfunction including jaundice, pruritus, fatigue Stop smoking while on drug therapy Abstain from alcohol while taking this medication, as it may potentiate drowsiness Monitor for bleeding, bruising, including Instruct patient to report signs of unusual complete blood count. (Drug may cause bleeding such as petechiae or excessive thrombocytopenia.) bruising Institute safety procedures to protect the Advise patient not to drive or operate heavy patient who experiences dizziness. machinery until the response to drug therapy can be evaluated. Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Omeprazole (Prilosec) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration Injury, Risk for (fall) related to drowsiness secondary to drug therapy Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Pain, Risk for related to gastric irritation interactions Nutrition, Risk for Imblance: less than Assess for presence/history body requirements related to ineffective Gastrointestinal distress, gastrointestinal response to drug therapy bleeding Assess alcohol use, complete blood count, renal function, and stool for occult blood. Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Remain free of signs of side effects including headache, dizziness, diarrhea, abdominal pain, hematuria and rash Demonstrate understanding of the risks and benefits of drug therapy. Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Monitor the smoking and food habits of the patient. (Smoking increases stomach acid production.) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Advise patient to: Abstain from alcohol use while taking this medication Refrain from spicy foods, caffeine and smoking which may increase gastric irritation Monitor elimination pattern. (Drug may Advise patient to keep a food diary to help cause diarrhea.) correlate symptoms with foods eaten. Periodically monitor urine for the Instruct patient to report change in urine presence of blood and/or protein. color to health care provider. Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Diphenoxylate with Atropine (Lomotil) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration: Fluid volume, Risk for Imbalance: less than body requirements related to fluid Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history and possible drug loss secondary to diarrhea interactions IMpaired skin integrity, Risk for related to diarrhea stools Assess for presence/history of diarrhea, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance Injury, Risk for (falls) related to Assess sodium level, chloride level, drowsiness secondary to drug therapy potassium level, stool culture, presence of Knowledge, Deficient related to drug dehydration, vital signs and EKG. action and side effects Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Demonstrate understanding of instructions necessary for drug therapy. Immediately report persistent diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, blood in stool, confusion, dizziness or fever. Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Monitor abdomen for distention and degree and location of abdominal pain. (This may be sign of toxic megacolon.) Monitor frequency, volume, characteristics, and consistency of stools. Offer ice, gum or sour candy. May swab lips with a glycerine-based emollient. (The medication may cause dry mucous membranes.) Initiate safety measures to prevent falls. (The medication may cause drowsiness.) Monitor electrolyte levels. Patient Education/Discharge Planning Advise patient to: Record the frequency of stools. Instruct patient to note if any blood is present. Report any abdominal pain or abdominal distention to the health care provider immediately Instruct patient to: Report worsening of diarrhea to health care provider Report occurrence of bloody stools to health care provider Increase fluid intake and to drink electrolyte enriched fluids. Advise patient to suck on sour candy or chew gum to relieve sensations of dry mouth. Advise patient to: Not drive or operate heavy machinery due to drowsiness. Abstain from the use of alcohol while using this medication Advise patient to keep all laboratory appointments. Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Prochlorperazine (Compazine) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration: Injury, Risk for (fall) related to dizziness secondary to drug therapy Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history and possible drug Fluid volume, Risk for Imbalance: interactions deficit related to ineffective response to drug therapy Assess for presence/history severe nausea, vomiting Nutrition, Risk for Imbalanced: less Obtain vital signs than body requirements related to nausea and vomiting Assess for presence of dehydration, sodium level, chloride level, potassium Knowledge, Deficient, related to drug level, and temperature. therapy and side effects Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Demonstrate understanding of need for drug therapy and will comply with all instruction given Remain free of drug side effects including rash, blurred vision, jaundice, tremor and changes in vision. Maintain adequate fluid balance Maintain adequate nutrition Remain free of physical injury Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Monitor neurological status (Seizure threshold is decreased. May need to increase seizure medication.) Monitor intake and output (to evaluate drug effectiveness), Monitor elimination pattern. (Medication may cause urinary retention.) Institute safety procedures to prevent patient falls or injuries. Monitor changes in skin integrity. (Medication may cause gray–blue discoloration of skin.) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Advise patient with a seizure disorder that there is an increased risk for seizures with this medication. Advise patient: To report continue nausea and vomiting That medication may cause urine to appear reddish brown Instruct patient to report difficult urination to health care provider. Advise patient to avoid driving or operating heavy machinery due to sedating effects of medication. Advise patient: To protect skin from direct sunlight and to use sunscreen That medication may cause sun exposed skin to turn gray blue Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluste the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”). Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Sibutramine (Meridia) Assessment Potential Nursing Diagnoses Prior to administration: Nutrition, Risk for Imbalanced: more than body requirements related to Obtain complete health history including allergies, drug history and possible drug ineffective response to drug therapy interactions Tissue perfusion, Risk for Ineffective related to adverse effects of drug Assess for presence/history obesity, desire to lose weight therapy Assess weight, blood pressure, pulse, EKG, Gas exchange, Risk for Impaired liver function and kidney function related to respiratory difficulty secondary to adverse effects of drug therapy Injury, Risk for (anaphylaxis) related to adverse effects of drug therapy Knowledge, Deficient related to drug action and side effects Planning: Patient Goals and Expected Outcomes The patient will: Remain free of adverse reaction to drug including severe headache, fever, muscle aches, tachycardia, rash, nausea, vomiting, profuse sweating, tremor, irritability and respiratory difficulty. Demonstrate weight loss within expected range Maintain adequate tissue perfusion Demonstrate knowledge of drug action and side effects Implementation Interventions and (Rationales) Obtain medication history for concurrent use of SSRIs. (Medication may cause serotonin syndrome.) Monitor weight pattern (to evaluate effectiveness of drug therapy). Monitor intake and output (to evaluate compliance with treatment regimen.) Monitor liver function, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase and lipid profile. (There is an increased risk of liver dysfunction.) Patient Education/Discharge Planning Instruct patient to immediately report the development of any rash, fever or difficulty breathing. Advise patient to: Keep weight record Report weight increase to health care provider Encourage patient to: Remain compliant with prescribed dietary and lifestyle modifications Take medication as prescribed by the health care provider Advise patient to keep all laboratory appointments. Monitor patients with narrow angle Advise patient to report any vision glaucoma for increased intraocular changes to the health care provider pressure (Medication may worsen immediately. condition.) Evaluation of Outcome Criteria Evaluate the effectiveness of drug therapy by confirming that patient goals and expected outcomes have been met (see “Planning”).