Bundle 1
advertisement
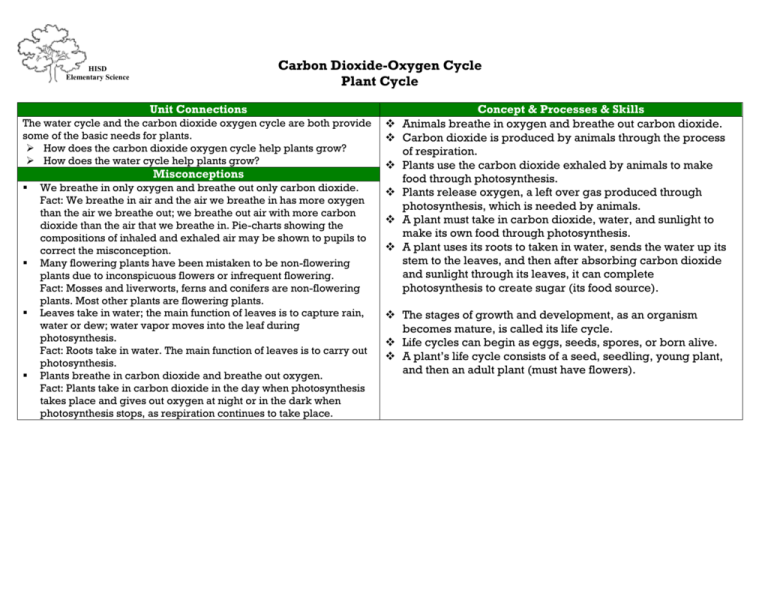
Carbon Dioxide-Oxygen Cycle Plant Cycle HISD Elementary Science Unit Connections The water cycle and the carbon dioxide oxygen cycle are both provide some of the basic needs for plants. How does the carbon dioxide oxygen cycle help plants grow? How does the water cycle help plants grow? Misconceptions We breathe in only oxygen and breathe out only carbon dioxide. Fact: We breathe in air and the air we breathe in has more oxygen than the air we breathe out; we breathe out air with more carbon dioxide than the air that we breathe in. Pie-charts showing the compositions of inhaled and exhaled air may be shown to pupils to correct the misconception. Many flowering plants have been mistaken to be non-flowering plants due to inconspicuous flowers or infrequent flowering. Fact: Mosses and liverworts, ferns and conifers are non-flowering plants. Most other plants are flowering plants. Leaves take in water; the main function of leaves is to capture rain, water or dew; water vapor moves into the leaf during photosynthesis. Fact: Roots take in water. The main function of leaves is to carry out photosynthesis. Plants breathe in carbon dioxide and breathe out oxygen. Fact: Plants take in carbon dioxide in the day when photosynthesis takes place and gives out oxygen at night or in the dark when photosynthesis stops, as respiration continues to take place. Concept & Processes & Skills Animals breathe in oxygen and breathe out carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is produced by animals through the process of respiration. Plants use the carbon dioxide exhaled by animals to make food through photosynthesis. Plants release oxygen, a left over gas produced through photosynthesis, which is needed by animals. A plant must take in carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight to make its own food through photosynthesis. A plant uses its roots to taken in water, sends the water up its stem to the leaves, and then after absorbing carbon dioxide and sunlight through its leaves, it can complete photosynthesis to create sugar (its food source). The stages of growth and development, as an organism becomes mature, is called its life cycle. Life cycles can begin as eggs, seeds, spores, or born alive. A plant’s life cycle consists of a seed, seedling, young plant, and then an adult plant (must have flowers). Graphic Cues Seeds are planted or scattered. Plant sprouts Seeds form on plant Roots, stem, and leaves continue to develop Flower blooms on plant Student Outcomes Identify parts of a plant and their function and describe a plant’s basic needs. What are the structures that make up a plant? What are the functions of these structures? How do the structures of a plant help keep them alive? Describe how plants produce oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. Why is photosynthesis important? What do plants require for photosynthesis? What do plants produce during the process of photosynthesis? Explain how animals produce carbon dioxide. What do animals need from the air? How do animals get oxygen from the air? What do animals breathe out? Describe how the carbon dioxide/oxygen cycle is significant to the survival of plant and animals. How do plants and animals interact within the carbon dioxide-oxygen cycle? What would happen to the Earth’s atmosphere if the rainforest was destroyed? Would plants survive if all the animals were gone? Identify and describe the stages in a plant’s life cycle. What is the role of an adult plant? What is the role of the seedling and young plant? Carbon dioxide Oxygen Photosynthesis Vocabulary Focus Key Vocabulary for the Week Respiration







