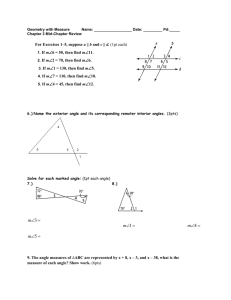
Unit 8 Geometry and Angle Measurement
advertisement

MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 4 Unit Description Big Idea(s) What enduring understandings are essential for application to new situations within or beyond this content? Essential Question(s) What questions will provoke and sustain student engagement while focusing learning? Standards Curriculum and Instruction Unit 8 Geometry and Angle Measurement Suggested Length: 6 weeks Enduring Understanding Describe, Analyze, Compare, and Classify Geometric Shapes Enduring Skills Rubric measures competency of the following skills: Can identify all types of angles. Can recognize both parallel and perpendicular lines. Consistently generate a pattern (number or shape) following a given rule. Consistently apply the area and perimeter formulas to solve mathematical or real world problems. Can measure and draw angles accurately. Solves addition and subtraction problems to find unknown angles accurately. Can draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles, perpendicular or parallel lines accurately. Can recognize and draw a line of symmetry accurately. How are two-dimensional objects different from one another? How can shapes be classified by their angles and sides? How can I determine the lines of symmetry in a figure? How are the units used to measure perimeter different from the units used to measure area? How is perimeter different from area? What is the relationship between an angle and a circle? How can I construct an angle of a given measure? What are benchmark angles and how can they be useful in estimating angle measures? How can I decompose/compose angles to solve geometric problems? Standards for Mathematical Practice 1. Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. Students make sense of problems and persevere in solving them by exploring and investigating properties of geometric figures and lines of symmetry. Students solve problems involving measurement and the conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit. 2. Reason abstractly and quantitatively. Students reason abstractly and quantitatively by comparing, contrasting, and classifying two-dimensional shapes and determining their lines of symmetry. Students recognize angle measure as additive in relation to the reference to a circle. 3. Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. Students construct viable arguments and critique reasoning when determining the properties of geometric shapes and determining their lines of symmetry. Students construct and critique arguments regarding the relative size of measurement units and relating them to everyday objects. 2015-2016 Page 1 of 9 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 4 4. Model with mathematics. Students model with mathematics by drawing, folding, tracing, and constructing lines of symmetry and categorizing twodimensional shapes based on their properties. Students use line plots to display data of measurements in fractions of a unit. 5. Use appropriate tools strategically. Students use appropriate tools such as geometric shapes, corners of paper, tiles, rulers, protractors, and/or graphic organizers to determine angles, classify two-dimensional shapes, and draw lines of symmetry. Students select and use tools such as a ruler, balance, graduated cylinder, angle ruler, and protractor to measure. 6. Attend to precision. Students attend to precision when observing and determining the attributes of sides and degree of angles within geometric shapes. Students carefully specify unit measure and state the meaning of the symbols they choose. 7. Look for and make use of structure. Students look for and make sense of structure when exploring properties of geometric shapes and determining how to fold them to show lines of symmetry. Students use the structure of a two-column table to generate a conversion table for measurement equivalence. 8. Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Students look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning while exploring the geometric properties of two-dimensional shapes by comparing, contrasting, classifying, and identifying lines of symmetry. Students notice repetitive actions in computations to make generalizations about conversion of measurements from a larger unit to a smaller unit. Standards for Mathematical Content 4.G.1 Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures. 4.G.2 Classify two-dimensional figures based on the presence or absence of parallel or perpendicular lines, or the presence or absence of angles of a specified size. Recognize right triangles as a category, and identify right triangles. 4.G.3 Recognize a line of symmetry for a two-dimensional figure as a line across the figure such that the figure can be folded along the line into matching parts. Identify line-symmetric figures and draw lines of symmetry. 4.MD.3 Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems. For example, find the width of a rectangular room given the area of the flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor. 4.MD.5 Recognize angles as geometric shapes that are formed wherever two rays share a common endpoint, and understand concepts of angle measurement: a. An angle is measured with reference to a circle with its center at the common endpoint of the rays, by considering the fraction of Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 2 of 9 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 4 Supporting Standard(s) Which related standards will be incorporated to support and enhance the enduring standards? Instructional Outcomes What must students learn and be able to do by the end of the unit to demonstrate mastery? Curriculum and Instruction the circular arc between the points where the two rays intersect the circle. An angle that turns through 1/360 of a circle is called a “one-degree angle,” and can be used to measure angles. b. An angle that turns through n one-degree angles is said to have an angle measure of n degrees. 4.MD.6 Measure angles in whole-number degrees using a protractor. Sketch angles of specified measure. 4.MD.7 Recognize angle measure as additive. When an angle is decomposed into non-overlapping parts, the angle measure of the whole is the sum of the angle measures of the parts. Solve addition and subtraction problems to find unknown angles on a diagram in real world and mathematical problems, e.g., by using an equation with a symbol for the unknown angle measure. 4.OA.3 Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. 4.MD.2 Use the four operations to solve word problems involving distances, intervals of time, liquid volumes, masses of objects, and money, including problems involving simple fractions or decimals, and problems that require expressing measurements given in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Represent measurement quantities using diagrams such as number line diagrams that feature a measurement scale. I am learning to…. 4.G.1 1. classify angles as acute, right, obtuse 2. analyze two-dimensional figures to identify points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines 3. construct examples of a point, ray, line segment, line, ray, angle (right, acute, obtuse), perpendicular lines, and parallel lines 4.G.2 1. classify triangles as “right triangles” or “not right triangles” 2. recognize a right triangle in any setting no matter its position 3. classify two-dimensional figures based on the size of the angles 4. classify two-dimensional figures based on parallel or perpendicular lines 4.G.3 1. recognize a line of symmetry as a line across a figure that when folded on the line it creates matching parts 2. identify line-symmetric figures 3. distinguish between symmetrical and asymmetrical figures 4. draw lines of symmetry in two-dimensional figures 2015-2016 Page 3 of 9 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 4 Vocabulary What vocabulary must students know to understand and communicate effectively about this content? Resources/Activities What resources could we use to best teach this unit? Curriculum and Instruction 4.MD.3 1. determine the area of a rectangle using a formula 2. determine the perimeter of a rectangle using a formula 3. determine the length or width of a rectangle using an area formula 4. solve area and perimeter problems in which there is an unknown factor (n) 5. apply area and perimeter formulas to real world and mathematical problems 4.MD.5 1. recognize angles as geometric shapes that are formed by two rays with a common endpoint 2. recognize a circle as a geometric figure that has 360 degrees 3. recognize that an angle is a fraction of a 360 degree circle 4. explain the angle measurement in terms of degrees 5. calculate angle measurement using the 360 degrees of a circle 6. compare angles to circles with the angles pointing at the center of the circle to determine the measure of the angle 4.MD.6 1. determine which scale on the protractor to use, based on the direction the angle is open 2. use a protractor to measure angles to the nearest whole-number degree 3. construct an angle with a given measurement 4.MD.7 1. decompose an angle into smaller parts 2. determine the sum of an angle by adding the degree of its parts 3. use addition and/or subtraction to find unknown angle measurements on a diagram Essential Vocabulary acute endpoint perimeter additive formula perpendicular plane figures angle fractions point arc length protractor area line ray circle line of symmetry right angle compose line plot right triangle line segment congruent scale obtuse data two-dimensional parallel decompose width degrees Stepping Stones (www.origoeducation.com) 4.MD.3 o Module 9: Lessons 1-4 4.MD.5 o Module 5: Lessons 9,10 2015-2016 Page 4 of 9 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 4 4.MD.6 o Module 5: Lessons 10-12 4.MD.7 o Module 5: Lesson 12 4.G.1 o Module 5: Lessons 10,11 o Module 10: Lessons 9,10 4.G.2 o Module 5: Lesson 11 o Module 10: Lesson 10 4.G.3 o Module 10: Lessons 11,12 Engage NY (https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-4-mathematics) o Module 8, all Topics From Howard County website https://grade4commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/Assessing+4.MD .5 https://grade4commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/Assessing+4.MD .6 https://grade4commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/Assessing+4.MD .7 https://grade4commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/Assessing+4.G.1 https://grade4commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/Assessing+4.G.2 https://grade4commoncoremath.wikispaces.hcpss.org/Assessing+4.G.3 From K-5 Math Teaching Resources 4.MD.3 o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/howmany-tables.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/fencing-agarden.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/designinga-zoo-enclosure.pdf 4.MD.5 o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/estimating-angle-measures.pdf.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/angles-incircles.pdf 4.MD.6 o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/predicting-and-measuring-angles.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/anglebarrier-game.pdf Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 5 of 9 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 4 http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/howmany-degrees.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/anglesintriangles.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/anglesinquadrilaterals.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/angles-ina-right-triangle.pdf 4.MD.7 o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/additiveangles.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/unknownangle-word-problems.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/patternblock-angles.pdf 4.G.1 o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/alphabetlines.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/geoboard-line-segments.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/angleson-the-geoboard.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/anglebarrier-game.pdf 4.G.2 o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/classifying-2d-figures.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/righttriangles-on-the-geoboard.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/isoscelestriangles-on-the-geoboard.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/constructing-quadrilaterals.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/quadrilateral-criteria.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/triangleson-the-geoboard.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/classifying-triangles-v1.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/classifying-triangles-v2.pdf 4.G.3 o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/symmetryon-the-geoboard.pdf o http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/support-files/symmetryo Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 6 of 9 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 4 o in-regular-polygons.pdf http://www.k-5mathteachingresources.com/supportfiles/symmetrical-coin-design.pdf Illustrative Mathematics 4.MD.3 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/MD/A/3/tasks/876 4.MD.6 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/MD/C/6/tasks/909 4.MD.7 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/MD/C/7/tasks/1168 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/MD/C/7/tasks/909 4.G.1 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/1/tasks/1263 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/1/tasks/1272 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/1/tasks/909 4.G.2 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/2/tasks/1273 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/2/tasks/1275 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/2/tasks/1504 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/2/tasks/1274 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/2/tasks/1168 4.G.3 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/3/tasks/676 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/3/tasks/1060 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/3/tasks/1058 o https://www.illustrativemathematics.org/contentstandards/4/G/A/3/tasks/1059 Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 7 of 9 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 4 Illuminations o http://illuminations.nctm.org/Search.aspx?view=search&cc=1973_2 005 o http://illuminations.nctm.org/Search.aspx?view=search&cc=1973_2 010 Making Math Magic (http://www.makingmathmagic.net/files/101948420.pdf) Remember there are other sources in your school that may not be listed on this common resources list due to variation in each individual school. Examples of other great resources your school may have access to include: Everyday Math Games, Investigations, Everyday Partner Games, AVMR file folders, Ongoing Assessment Project, etc. The Kentucky Numeracy Project is also a great resource that can be searched by AVMR strand, CCSS, and grade level. Find this resource at http://knp.kentuckymathematics.org/#!/page_knphome. Kentucky teachers can use it for free. Just put in your school email address and the username “bluegrass”, and password is “math”. Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 8 of 9 Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 9 of 9