Atmosphere Notes
advertisement

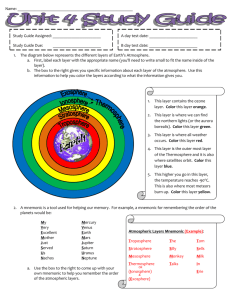
Atmosphere Notes Facts: 1. Mostly composed of __________________________ 2. ________________ 78%, ____________________ 21%, __________________ 9%, and _____________________ is .036% 3. Trace elements: hydrogen, helium, and neon. 4. Elements vary through the seasons – C02 is greatest in the ___________________due to photosynthesis. Water vapor decreases with altitude. 1. There are five layers to the atmosphere: a. _______________________ b. _______________________ c. _______________________ d. _______________________ e. _______________________ 2. Troposphere a. This is the atmospheric layer ______________ to the planet and contains the largest percentage of the mass of the total atmosphere. It is characterized by the density of its air and an average vertical temperature change of 6 degrees Celsius (C) per kilometer. b. Temperature and water vapor content in the troposphere decrease rapidly with altitude. c. Most of the suns radiation is absorbed at the earth’s surface, which then transfers hear into the atmosphere – making it the warmest close to the surface. i. Water vapor plays a major role in regulating air temperature because it absorbs solar energy and thermal radiation from the planet's surface. c. Contains _________________________________ in the atmosphere. i. Water vapor concentrations vary with latitudinal position. They are greatest above the tropics, where they may be as high as 3%, and decrease toward the polar regions. d. All __________________________________ occurs within the troposphere, although turbulence may extend into the lower portion of the stratosphere. Troposphere means "region of mixing" and is so named because of vigorous convective air currents within the layer. e. The upper boundary of the layer ranges in height from 8 km in high latitudes, to 18 km above the equator. Its height also varies with the seasons; highest in the summer and lowest in the winter. 3. A narrow zone called the _______________________ separates the troposphere from the next highest layer called the stratosphere. Air temperature within the tropopause remains constant with increasing altitude. 4. Stratosphere a. Stratosphere i. The ______________________ strata of the atmosphere ii. It resides between 10 and 50 km above the planet's surface. iii. Because the air temperature in the stratosphere increases with altitude, it does not cause convection and has a stabilizing effect on atmospheric conditions in the region. iv. Air temperature in the stratosphere remains relatively constant up to an altitude of 25 km. Then it increases gradually to 200-220 degrees Kelvin (K) at the lower boundary of the stratopause (~50 km), which is marked by a decrease in temperature v. _________________________________in regulating the thermal regime of the stratosphere, as water vapor content within the layer is very low. a. Temperature increases with ozone concentration. Solar energy is converted to kinetic energy when ozone molecules absorb ultraviolet radiation, resulting in heating of the stratosphere. b. The ozone layer is located at an altitude between 20-30 km. c. Ozone absorbs the bulk of solar ultraviolet radiation in wavelengths from 290-320 nm. d. Increased penetration of ultraviolet radiation to the planet's surface would damage plant life and have harmful environmental consequences. Appreciably large amounts of solar ultraviolet radiation would result in a host of biological effects, such as a dramatic increase in cancers. Meteorological conditions strongly affect the distribution of ozone. Most ozone production and destruction occurs in the tropical upper stratosphere, where the largest amounts of ultraviolet radiation are present. Dissociation takes place in lower regions of the stratosphere and occurs at higher latitudes than does production. 5. Mesosphere A. Layer extending from approximately 50 km to 80 km. B. Characterized by _________________________________. c. With increasing distance from Earth's surface the chemical composition of air becomes strongly dependent on altitude and the atmosphere becomes enriched with lighter gases. 6. Thermosphere A. Located above the mesosphere and is separated from it by the mesopause transition layer. B. The temperature in the thermosphere generally increases with altitude C. This increase in temperature is due to the absorption of intense solar radiation by the limited amount of remaining molecular oxygen. D. At an altitude of 100-200 km, the major atmospheric components are still nitrogen and oxygen. At this extreme altitude gas molecules are widely separated. 7. Exosphere A. Outermost region of the Earth's atmosphere. B. The exosphere begins at approximately 500 km and extends outward until it transitions with interplanetary space (at roughly 10,000 km).