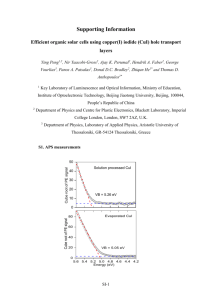
Dependence of deposition parameter on the Structural properties of
advertisement

Wide Band Gap CuI Thin Film through SILAR Technique: Optimization of Deposition Technique P.K.Sheela Department of Physics, Sree Narayana College, Chelannur, Kerala Abstract Deposition parameters play an important role in determining the properties of semiconducting thin films. Copper iodide thin films were deposited at room temperature on the glass substrates by a simple SILAR method under different dipping intervals in cationic and anionic precursors. X-ray diffraction studies of as-deposited CuI thin films indicates that the as-prepared samples were polycrystalline with continuously increasing intensity peak on enhancing dipping time. The preferential orientation was along (111) direction. The experimentally observed d- values were compared with JCPDS data for various samples. These were in good agreement with the standard‘d’ values. The grain size calculations were also done. 1. Introduction Cuprous iodide (CuI) has attracted a great attention, as it is a versatile candidate in optoelectronic devices. Depending on synthesis method and the deposition parameters, there is variation in the physico-chemical properties of the material. The most interesting nature of this compound is that, it is an inorganic semiconductor and its coordination chemistry lets it readily couple with many inorganic and organic ligands as well. CuI belongs to the I–VII semiconductors with Zinc-blende structure,mainly used in electronic devicessuch as liquid crystal displays, photovoltaic devices, photothermalcollectors and so on [1-2]. Deposition of CuI on Cu-tape/n-CuInS2 at roomtemperature by the successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction(SILAR) technique and study of the influence of wet chemicaliodine treatment is reported by Sankapal et al. [3]. Further, thechemical bath deposition and SILAR method is employed bySankpal et al. to obtain the CuI and CuSCN thin films for solar cell windows application [4]. Thin film preparation by successiveionic layer adsorption and reaction (SILAR) is simple, lessexpensive, room temperature synthesis and is convenient forlarge area deposition. Also, SILAR can be used to deposit compound materials on a variety of substrates such as insulators,semiconductors, metals [5]. In the present research work, we report the synthesis and characterization of copper iodide thin film deposited on glass substrate by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction(SILAR) method at room temperature by changing the dipping time and keeping rinsing time constant and vice versa. The obtained results regarding crystal structure, crystallographic orientation,crystallinity etc.for the CuI films under different dipping times were compared 2. Experimental Prior to the deposition of CuI thin films, the substrates were cleaned in order to get uniform deposition. All the reagents used were of analytical grade. We used CuSO4 (0.1 mol/dm3) solution complexed by Na2S2O3 (0.1 mol/dm3 )as a cationic precursor. These two solutions form a complex thiosulphato cuprate. The release of Cu++ ions is possible via the following reaction CuS2O3Cu++ + S2O3--. In the first set of samples, The rinsing time in water was fixed as 5 sec and number of SILAR cycles was fixed as 150.The dipping time in solution was varied from 4 sec to 10sec.Water was replaced after each 10 cycles. The frequency of replacement of water was increased as dipping time in solution was increased. The samples were named as Cu4s 5w,CuI 5s 5w,CuI 6s 5w, CuI 7s 5w,CuI 8s 5W,CuI 9s 5w, CuI 10s 5w and CuI 15s 5w. In another set of samples dipping time in solution was fixed as 10 sec and rinsing time in water was varied from 4 sec to 8sec.In this also water was replaced after each 10 cycles. The samples were named as CuI 10s 4w,CuI 10s 5w,CuI 10s 6w, CuI 10s 7w, andCuI 10s 8w. .The samples were further characterized for structural properties. Structural studies were carried out using an X- ray diffractometer (Bruker AXS-8 advance) with CuK radiation of wavelength 1.5406 Å as the source. 3. Results and discussion 3.1. Structural studies In Fig. 3.1 and 3.2 the XRD spectra of CuI deposited on glass substrate under different dipping time is presented. In Figure 3.3, XRD pattern of CuI 10S 5W for which the most intense peak (2500 arb. Unit) obtained is separately shown. The observed inter-planer distance ‘d’, is compared with JCPDS data which is in good agreement with the standard ‘d’ values. The lattice parameter is found to be 6.034A˚ . Different peaks of g-CuI corresponding to planes (1 1 1), (2 2 0) and(3 1 1) of face-centered cubic structure have been identified with a preferential orientation of (111plane). The presence of a number of peaks in XRD pattern is the indication of polycrystalline nature of the CuI. The intensity peak increases with increase in dipping time in solution. The grains size obtained were in the range of 11.75nm to 16.77nm. comparatively high grain size were obtained for samples having greater dipping time in solution and lower rinsing time in water. FIGURE Fig.1. The XRD pattern of CuI thin films—(a)---sample name—(b)-------- and-------- 4. Conclusions A very simplistic method, SILAR, is used for deposition of CuI thin films on glass substrates. The enhancement in the properties of CuI like adhesion,thickness,crystallinity etc. is observed on enhancing the dipping time. From XRD pattern the material is confirmed to be polycrystalline gamma phase CuI with face-centered cubic structure Acknowledgements [1] M. Katayama, H. Morimoto, S. Yasuda, T. Takamura, H. Tanaka, M. Hijigawa, SID 88Digest (1998) 310. [2] K. Sato, Y. Gotoh, Y. Hayashi, K. Adachi, H. Nishimura, Tech. Dig. Int. PVSEC5,Kyoto, (1990), p. 1032. [3] B.R. Sankapal, A. Ennaoui, T. Guminskaya, Th. Dittrich, W. Bohne, J. Rfhrich, E.Strub, M.Ch. Lux-Steiner, Thin Solid Films 480 (2005) 142. [4] B.R. Sankapal, E. Goncalves, A. Ennaoui, M.Ch. Lux-Steiner, Thin Solid Films 451(2004) 128. [5] H.M. Pathan, C.D. Lokhande, Bull. Mater. Sci. 27 (2004) 85.