Physical Properties of Matter
advertisement

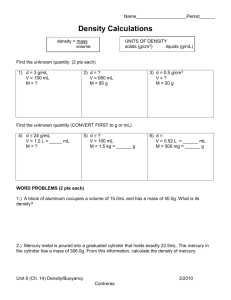
Physical Properties of Matter Unit 1 Review/Notes 1. The word dense refers to the “compactness” of the particles in matter 2. Density is defined as a measurement of the mass of one (1) unit of volume of matter The one (1 ) unit of volume most commonly used in science is the cm3 3. Density is a physical property of matter just like color and hardness – its stays the same for a material unlike mass, weight and volume. 4. The unit most commonly used to list densities is grams/centimeter3 (g/cm3) – Sometimes you will see it listed as kilograms/meter3 (kg/cm3). 5. To calculate density divide the object’s mass by its volume. Math formula: Density = mass/volume or d=m/v 6. To find the density of liquids you must find the mass of the liquid in a graduated cylinder (GC). 1. Remember to subtract the mass of the empty GC from the filled GC (g) 2. The volume of the liquid is the number of ml poured into the graduated cylinder 3. Divide the mass of the liquid by its volume – record as density with correct units (g/mL or g/cm3) Remember for solids 1. To find the volume of a regular-shaped object use a ruler and mathematical formula 2. To find the volume of an irregular-shaped object use the displacement method. Displacement is what happens when a solid is placed in water. The amount of water displaced is equal to the volume of the object. 7. The Densities of some Common Substances Substance Density (g/cm3) air Wood (varies) Oil (corn) water lead mercury gold 0.0013 0.65 0.91 1.0 11.3 13.5 19.3 8. Displacement Method of Finding Volume Remember Archimedes! The meniscus is the upwards curving surface of the liquid in a GC. Where do you read it and what causes it? 9. The most important density (and easiest) to remember is that of water = 1.0 g/cm3! Substances with densities greater than water will sink, if it’s less than water it will float! 10. An object that has the same density as the liquid it is placed in will “flink” or more scientifically speaking it has neutral buoyancy and neither floats or sinks! Buoyancy – the upward force in water that opposes gravity negative buoyancy – a characteristic of things that sink positive buoyancy – a characteristic of things float neutral buoyancy – a characteristic of things that neither sink nor float - “flink” Floating or sinking in water can be predicted by looking at the difference between the volume (in cm3) and the mass (g) of an object. If the number for the volume is greater than the number for its mass, the object will float. The opposite is true for sinking. Remember that density is equal to the mass divided by the volume. d=m/v 11. A 555,000 ton ship will float because its average density is less than 1.0 g/cm3 – The average density includes the density of all the steel, machinery and all the air inside the boat! 12. Explain how each of the following things – submarine, scuba diver and a fish - can alter their density to operate, function or survive in the ocean depths. A submarine can alter its average density by flooding compartments called ballast tanks with water in order to sink and pumping them dry in order to float. In this case the mass is altered but the volume remains the same. A scuba diver can change his/her average density with the use of an inflatable life vest and weights. The buoyancy of the scuba tank and wetsuit is offset by the weights enabling the diver to sink. In order to maintain neutral buoyancy the diver has a life vest that can be filled with air from the scuba tank. By filling or emptying this life vest the buoyancy, or average density, can be changed as needed. This changes the total volume of the diver while mass remains the same. In divers’ terms this system is called a buoyancy compensator device or a bcd. A submerged object will weigh A fish has a swim bladder that allows it to less underwater maintain a state of neutral buoyancy. By adding because the force or subtracting air from the bladder the fish changes of buoyancy is its overall volume – like we do when we pushing up against deeply inhale. the force of gravity. 10. Other facts about density and water Heating matter will change its density – heat causes particles to move apart thereby decreasing its density. Therefore hot water is less dense than cold water. Pure water has a density of 1.0 g/cm3 when measured at 40C (39.20F). Tap water and bottled water are not pure – only distilled water is pure. A floating object displaces an amount of water that is equal in volume to the submerged portion of that object. The weight of that water is equal to the weight of the object. A submerged object will weigh less underwater because the force of buoyancy is pushing up against the force of gravity. It will weigh less by an amount equal to the weight of the water it displaces. Vocabulary See 3 sets of vocabulary at quizlet.com for vocabulary. listed under “hornets7science” password is “hornets” 1. Physical Properties of Matter 2. Metric Prefixes 3. Floating, Sinking and Flinking Websites See my website for links to 1. Math/science format (how to show your work in science), 2. “Fun links for Measurement” to review use of a triple-beam balance and GC Important Things to Know, Remember and Be Able to Do! 1. Explain the difference between mass and weight ( one changes and one remains the same). 2. Use of a balance scale, ruler and graduated cylinder to measure mass and volume. 3. How to calculate the density of solids, liquids and gases. 4. How to predict if an object will float or sink in any given fluid – liquid or gas. 5. Explain the mathematical relationship between density, mass and volume. 6. The density of water, lead, gold and wood (pine about- 0.65 g/cm3). 7. The six (6) metric prefixes (kilo – milli), their values and symbols. 8. The basic metric units for the measurement of liquid volume, mass and length. 9. How submarines, fish and scuba divers maintain neutral buoyancy. 10. How to show your math work in science – math/science format!