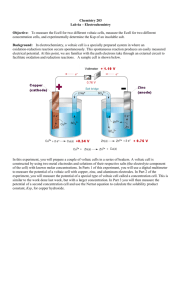
Equations from 1st Semester
advertisement

Practice Exam #2 Spring 2011 Circle the Correct Response 1. If the equivalence pt. of a titration occurs at a pH above 7, then the titration involved a. a strong acid titrated by a strong base b. a weak base titrated by a strong acid c. a weak acid titrated by a strong base d. a strong acid titrated by a weak base e. both a and d 2. The solubility product expression for Cd(OH)2 is: a. Ksp = [Cd2 + ][2OH- ]2 b. Ksp = [Cd2 + ] [2OH- ]1 / 2 2+ 2 d. Ksp = [Cd ] [2OH ] e. Ksp = [Cd2 + ] [OH- ] 3. Which of the following is not a type of equilibrium constant: a. Ka b. Kb c. Ksp d. Kf c. Ksp = [Cd2 + ] [OH- ]2 e. all are equilibrium constants 4. The presence of ligands bound to a transition metal causes the “d” orbitals to split into two groups with different energies. The energy difference between the two groups is the a. ionization energy b. crystal field splitting energy c. electrochemical potential d. Helmholtz free energy e. complex formation constant 5. A gas is heated gaining 75J of heat, and it expands such that the work out to the surroundings is 22J. The internal energy change of the gas is: a. 97J b. -97J c. 53J d. 22J e. 75J 6. For a reaction to be spontaneous at constant temp. and pressure then a. Grxn < 0 b. Srxn < 0 c. rxn > 0 d. Keq<1 e. both a and d In a spontaneous electrochemical cell a. Ecell must be negative. b. Ecell must be positive c. Ecell must be equal to zero b. Ecell can be either positive of negative e. cell must be equal to S 8. A precipitation will occur in an aqueous solution if: b. the Ksp is less than the Kw. b. the cation is not sodium. d. the calculated reaction quotient is greater than the Ksp. e. the calculated reaction quotient is less than the Ksp c. the anion is not acetate. 9. With regard to the Standard Electrode Potential Table, the elements in the half rxns. at the top of the table: a. are most easily reduced. b. are the best oxidizing agents. c. are most easily oxidized. d. are in alphabetical order. e. can’t cause reduction of elements below them in the table. 10. In which of the following would the S value be positive? a. 2KClO3(s) + O2(g) -> 2KClO4(s) b. CH4(g) + 2H2S(g) -> CS2(g) + 4H2(g) c. H2O (g) -> H2O(l) d. 2LiOH(aq)+CO2(g)->Li2CO3(aq)+H2O(l) e. S is positive for all of these. Answer the following problems. Show your work for maximal credit. 1. The Ksp value for Zn(OH)2 is 4.0 x 10- 1 7 . a. Calculate the molar solubility of Zn(OH)2. 1 b. If an acid was added to the a saturated solution containing Zn(OH) 2 would its solubility change? You must explain. 2. Consider the two complex ions, Co(NH3)63 + , and CoF63 a. What is the charge on the cobalt in these complex ions? b. Write down the abbreviated atomic electronic configuration for the Co ion in these complexes. c. Explain how the Co(NH3)63 + ion can be diamagnetic while the CoF63 - is paramagnetic. 3. It was suggested that one way to remove SO 2(g) from power plant emissions is react it with H2S(g) based on the following reaction: 2H2S(g) + SO2(g) - > <- 3 S(s) + 2H2O(g) a. What is the oxidation number of the S in the H2S? b. What is the oxidation number of the S in the SO2? c. Is this an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction? How do you know? 2 d. Calculate the Go for this reaction at 25o C. e. What is the value of the equilibrium constant for the reaction at 25 o C? f. Based on this information, is this a feasible method for removing SO 2(g)? Explain g. Do you expect S to be positive or negative for this rxn? Would this reaction be more or less effective at a higher temperature? Explain. 4. A galvanic cell consists of a Ag electrode in contact with a AgNO 3 solution in one compartment and another compartment a Mg electrode in contact with a Mg(NO3)2 soln. The compartments are connected together by a salt bridge (assume 25o C). a. Is the redox reaction corresponding to this voltaic cell given by? 1. Ag + Mg2 + (aq) - > <- Ag+ (aq) + Mg(s) or 2. Mg(s) + Ag+ (aq) - > <- Ag(s) + Mg2 + (aq) Decide which one it is and write the balanced redox reaction below. b. Write out the cell notation for this cell. Label the anode and the cathode. (It may help to sketch it.) c. Give the Eo cell, for this galvanic cell. 3 d. If the concentration of the AgNO3 soln. is 0.100M and the Mg(NO3)2 solution is also 0.100M, what is the Ecell under these conditions? e. Current is allowed to flow in the cell for a time of 330s until 1.20g of silver was deposited at the silver electrode. What was the current flow in the circuit? (Molar mass Ag = 107.9g/mol) Equations and Constants pH = -log[H+ ] = pKw -pOH Kw(25o C) = 1.0 x 10- 1 4 M1V1 = M2V2 S = q/T G = -nFEcell = C T Ecell = Eocell -(0.0257/n)*ln Q Ecell = Eocell -(RT/nF)*ln K Ecell = Eocell -(0.0592/n)*log Q G0 = -RTlnK Eocell = (0.0592/n)*log K Go = -nFEo Eocell = (0.0257/n)*ln K G = H - TS Go = o - TSo Eo cell = Eo red(red) - Eo red(oxid) Eo cell = Eo red(red) + Eo ox(oxid) current = charge/time (C/s) F = 96500 or 9.65 x 104 C / mole e- R = 0.0821 L atm/(mol K) R = 8.314 J/(mol K) G = Go + RT lnQ * Note that eqns with constants 0.0257 and 0.0592 correspond to values in volts at 25oC CN- > NO2- > en > NH3 > NCS- > H2O > F- > ClStrong Field Weak Field 4