Industrial Revolution Factory Conditions and City Life
advertisement

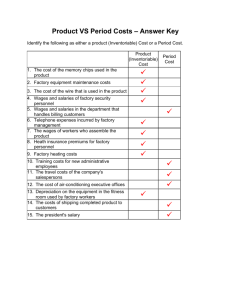
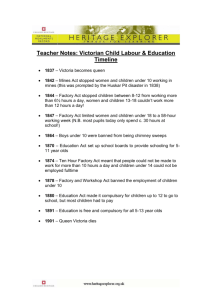
Industrial Revolution Factory Conditions and City Life Chapter 9, Sections 2 and 3 Urbanization • • • For centuries most Europeans lived in rural areas. Because of the _______________, people began to move to the cities. This period of city building and the movement of people to the cities is known as __________. Hardships for Factory Workers Factory owners wanted to keep machines running as many hours as possible as a result, the average worker spent 14 hours a day on the job, 6 days a week! ___________ generally low • • • • Employment was never secure During business slumps, employers lowered wages and laid off workers Sick workers received ___________ and were often fired Elderly workers faced cuts in pay and loss of jobs ____________ earned less than men, and children had lowest wages of them all • • • • Many parents, needing all income, had to put ____________ to work No laws restricted child labor and factories hired children as young as _____! Children toiled in __________, crawling through narrow tunnels to haul heavy loads of ____. Some supervisors ________ child workers to keep them awake and alert (remember, according to your book, an example of a child work day is from ______________) ____________ was not an issue-accidents happened often. • • Workers sometimes lost __________ or suffered other injuries because of _____ machines. • • • Workers might perform the same _________, over and over, for up to ____ hours per day. Poor lighting, dirt, high noise levels, ________ and fumes caused other health risks. _____________ work often dull and repetitive. The __________, machine, and __________ schedule ruled the life on the job If workers failed to keep up, they were fined or __________ Grim Life in the Cities • • Industrial Revolution led to rapid _____________-growth of cities • • • • • 19th century cities were _____ prepared for the explosion! • Many people had no __________ and lived on the streets. Between 1801 to 1851, for example, the population in the English city of Birmingham grew from 71,000 to 233,000. Liverpool, England __________ from 82,000 to 376,000. Housing, ______________, and hospital facilities could not keep pace with growing numbers The _________ rate was high, police forces small, and little fire protection The ______ lived in crowded, ram shackled houses Sometimes whole families huddled together in ______ room or even shared a room with another family. • • Open sewers, polluted rivers, factory smoke, and filthy streets allowed disease to spread In Britain, about 26 out of every 100 children died before the age of 5! Changing Values In pre-industrial _________, most people lived in small villages and farmed the land worked by their families for years Relatives, friends, and the village church gave them a sense of belonging. The factory system with long hours and irregular work schedules __________ family life. ___________ and parents often worked in different parts of a factory and on different shifts. Parents found it hard to ____________ kids. ____________ and abandoned children roamed streets of every city in Britain. ____________ attendance dropped in urban areas. • • • To escape from their dreary lives, many men and women turned to alcohol. Treatment of older people changed Rural areas taught young people about nature and farming, while industrial cities lost some ________ and authority they had enjoyed, their experience simply did not apply to city life Top 10 Reasons why we like the Industrial Revolution: 10. Factory goods were plentiful and priced within the reach of most people (cheaper products) 9. Growing cities offered increased chance of achievement 8. Workers acquiring special skills or an education had a better chance of entering the middle class (a social class made up of skilled workers, professionals, businesspeople, and wealthy farmers 7. Created jobs for workers 6. Contributed to the _________ of the nation 5. Fostered __________ progress and invention 4. It greatly increased the production of __________ and raised the standard of living. *Allowed for healthier __________ and better housing 2. Expanded _____________ opportunities And finally, the most important reason: 1. The industrial revolution provided the ________ of improvement in people’s lives. Are the long-term effects of the Industrial Revolution still felt today?