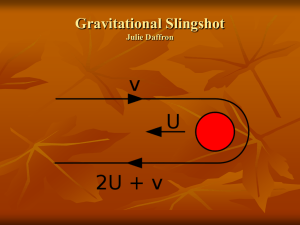
Dersin Adı
advertisement

I.T.U. FACULTY OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS DEPARTMENT OF SPACE ENGINEERING COURSE SYLLABUS Course Name SPACE ENVIRONMENT Department Lecturer and Office Hours Teaching Assistant and Office Hours Language Compulsory / Elective Classroom and Meeting Time Contents Objectives Topics-Course otline Textbook Other References Prerequisite(s) Laboratory Work Computer Usage Others Course Evaluation Method Prepared by: Code UZB 411E Space Engineering Zerefşan Kaymaz TBD Regular Semester Fall Credit 3 Lecture (hours/week) 3 Recitation Laboratory - English Compulsory TBD Introduction to Space Environment: fundamentals, the Earth in space, the neutral atmosphere, theplasma environment; Introduction to Sun: Solar radiation; Visible, Infrared, UV, EUV, and X-rays; Solar Wind, and Solar Activity; sun spots, solar flares, CMEs, SEPs, Geomagnetic and ionized environment; Ionosphere. Electromagnetic wave propagation, communication; Magnetosphere, Radiation Belts;Trapped radiation, Cosmic rays; Geomagntic storms and substorms, geomagnetic indices; Space weather concept: Techniques to observe space; Spacecraft orbits. LEO, HEO,Polar Geosyncronous; Spacecraft and ground systems; Spacecraft-Neutral atmosphere Interaction. Neutral gas flow around spacecraft, Atmospheric drag, Contamination, Erosion by atmosic oxygen, vehicle glow effect; Spacecraft plasma interactions. Effects of ionospheric and magnetospheric storms. Spacecraft charging.Current collection.Plasma flow around spacecraft.Plasma sources on spacecraft. Modelling studies of the spacecraft effects. To introduce space environment, the space events, and its variability, To study the effects of the space environment on the spacecraft and spacecraft systems and space instruments on board Week-1: Introduction to the Space Environment: fundamentals, the Earth in Space, Ambient Space Environment Week-2: Neutral and Plasma Environment Week-3: Introduction to Sun, Solar activity, Solar Wind, Solar radiation, Cosmic rays, SEPs Week-4: Geomagnetic environment, Solar-Terrestrial Interaction; Radiation Belts Week-5: Ionosphere, Atmospheric propagation and communication systems Week-6: Solar Effects on Earth’s Neutral Atmosphere and Plasma Environment; Geomagnetic storms, substorms Week-7: Midterm Week-8: Spacecraft orbits:Low Earth Orbit, Polar Orbits, Geosyncronous Orbits; Spacecraft and ground systems Week-9: Space Weather concept, Techniques Observing geospace, Technological applicationof geiospace sciences Week-10: Neutral Gas Flow around Spacecraft; Atmospheric Drag; Week-11:Contamination; Erosion by atomic oxygen; Vehicle Glow effect Week-12: Spacecraft-Plasma Interactions; Surface charging, Current collection; Potentials and spacecraft anomalies Week-13: Plasma sources on spacecraft; Plasma flow around the spacecraft; Radiation effects Week-14: Modelling studies of the spacecraft effects; shielding; solar array degradation, SEUs Spacecraft-Environment Interactions, 1996: D. Hastings and H. Garrett, Cambridge Univ. Pub. The Space Environment: Implications for Spacecraft Design, 2000: A. C. Tribble, Princeton Univ. Pub. 1.Science of Spacecraft Environment, 2000:T. Ondoh and K. Marubashi, Ohmsha Press. 2. Introduction to space environment, 1994: T. Tascione, Orbit Pub. 3.The Solar-Terrestrial Environment, 1992: J.K. Hargreaves, Cambridge Univ. Pub. 4.Space Weather, 2001, P. Song, H. Singer, and G.L. Siscoe, AGU Geophysical Monograph. 5.Space Weather, 1999: ESA, Workshop Proceedings. 6.Introduction to Space Physics, 1995: M.G. Kivelson and C. T. Russell, Cambridge Univ. Press. 7.Basic Space Plasma Physics, 1999: W. Baumjohann and R. A. Treumann, Imperial College Press. 8.Physics of the polar upper atmosphere, 1997: A. Drekke, John Wiley and SonsPub. 9.The physics of Atmospheres, 1986: J. T. Houghton, Cambiridge Univ. Pub. 10.Sun, Earth, and Sky, 1997: K.R. Lang, Springer Verlag Pub.S 11.Solar variability and its effects on climate, 2004: J. M. Pap and P. Fox, AGU Geophysical Monosgraph. 12.Sun-Earth Plasma Conenections, 1999: J.L. Burch, R.L. Carovillano, and S.K. Antiochos, AGU Monograph. 13.Radiation Belts and magnetosphere, 1968: W. N. Hess, Blaisdell Pub. Comp. 14.More books on individual topics are available. 15.There will be lecture notes, when available. Physics I, II; Fluid Mechanics None Basic computer knowledge and programming required for homeworks and projects -Number Ratio % 1 20 Midterm Quizes 4 10 Homeworks Projects 1 20 Term Projects Laboratory Others 1 50 Final Exam Prof. Dr. Zerefşan Kaymaz Date: August 15, 2005