Land use
advertisement
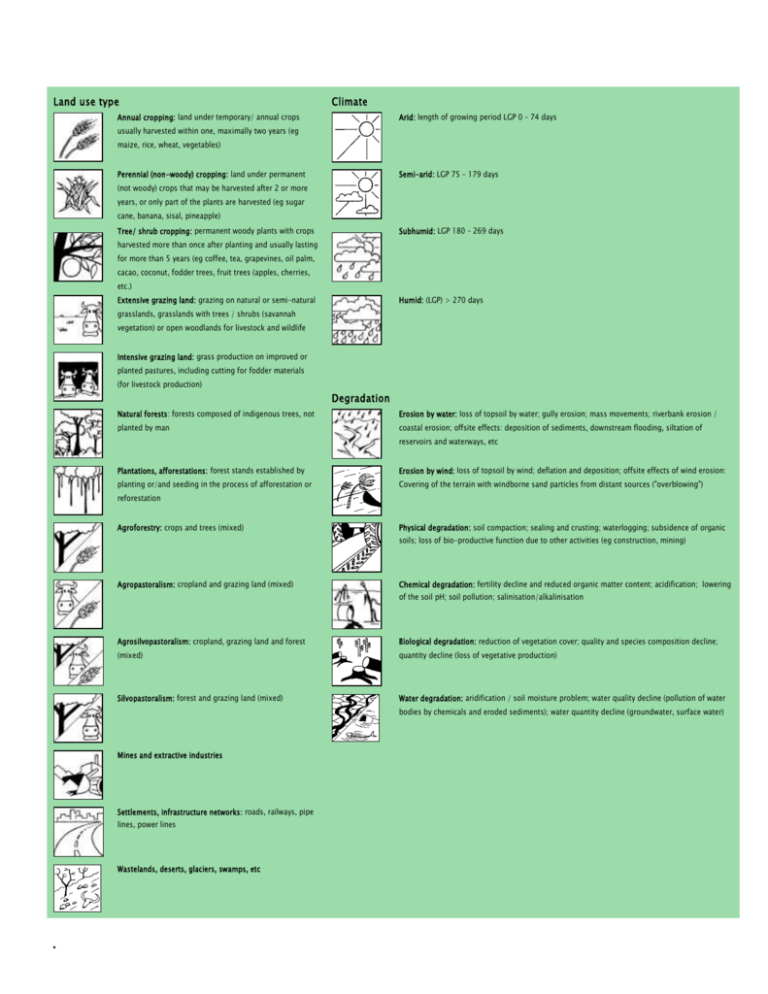
Land use type Climate Annual cropping: land under temporary/ annual crops Arid: length of growing period LGP 0 – 74 days usually harvested within one, maximally two years (eg maize, rice, wheat, vegetables) Perennial (non-woody) cropping: land under permanent Semi-arid: LGP 75 – 179 days (not woody) crops that may be harvested after 2 or more years, or only part of the plants are harvested (eg sugar cane, banana, sisal, pineapple) Tree/ shrub cropping: permanent woody plants with crops Subhumid: LGP 180 – 269 days harvested more than once after planting and usually lasting for more than 5 years (eg coffee, tea, grapevines, oil palm, cacao, coconut, fodder trees, fruit trees (apples, cherries, etc.) Extensive grazing land: grazing on natural or semi-natural Humid: (LGP) > 270 days grasslands, grasslands with trees / shrubs (savannah vegetation) or open woodlands for livestock and wildlife Intensive grazing land: grass production on improved or planted pastures, including cutting for fodder materials (for livestock production) Degradation Natural forests: forests composed of indigenous trees, not Erosion by water: loss of topsoil by water; gully erosion; mass movements; riverbank erosion / planted by man coastal erosion; offsite effects: deposition of sediments, downstream flooding, siltation of reservoirs and waterways, etc Plantations, afforestations: forest stands established by Erosion by wind: loss of topsoil by wind; deflation and deposition; offsite effects of wind erosion: planting or/and seeding in the process of afforestation or Covering of the terrain with windborne sand particles from distant sources ("overblowing") reforestation Agroforestry: crops and trees (mixed) Physical degradation: soil compaction; sealing and crusting; waterlogging; subsidence of organic soils; loss of bio-productive function due to other activities (eg construction, mining) Agropastoralism: cropland and grazing land (mixed) Chemical degradation: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content; acidification; lowering of the soil pH; soil pollution; salinisation/alkalinisation Agrosilvopastoralism: cropland, grazing land and forest Biological degradation: reduction of vegetation cover; quality and species composition decline; (mixed) quantity decline (loss of vegetative production) Silvopastoralism: forest and grazing land (mixed) Water degradation: aridification / soil moisture problem; water quality decline (pollution of water bodies by chemicals and eroded sediments); water quantity decline (groundwater, surface water) Mines and extractive industries Settlements, infrastructure networks: roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines Wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, etc . SLM measures Agronomic measures: measures that improve soil cover Stakeholders / target groups Land users, individual (eg green cover, mulch); measures that enhance organic matter / soil fertility (eg manuring); soil surface treatment (eg conservation tillage); subsurface treatment (eg deep ripping) Vegetative measures: plantation / reseeding of tree and Land users, group shrub species (eg live fences; tree rows), grasses and perennial herbaceous plants (eg grass strips) Structural measures: terraces (bench, forward / SLM specialists, agricultural advisor backward sloping); bunds, banks (level, graded); dams, pans; ditches (level, graded); walls, barriers, palisades Management measures: change of land use type (eg area Teachers / students / school children enclosure); change of management / intensity level: (eg from grazing to cut-and-carry); major change in timing of activities; control / change of species composition Planners Politicians, decision makers