Friends: - Bibb County Schools
advertisement

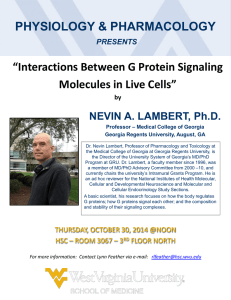
Page 1 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Educational Mineral & Fossil Sample Kits Guide Sheet Summer 2010 We wish to thank the following individuals for helping to make this project happen: Dr. David Schwimmer, Department of Chemistry & Geology Columbus State University Columbus, GA Dr. Burt Carter Department of Geology & Physics Georgia Southwestern State University Americus, Georgia Dr. Jo-ne Bourassa Coordinator of School Improvement, Science Bibb County Public Schools Macon, GA Ms. Tina Perkins Chair of Science Central High School Macon, GA Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society Our Purpose: To promote the earth sciences, the lapidary arts, and the collection, study and display of rocks, minerals and fossils; to promote the public awareness of these efforts in educational and recreational activities. We are a non-profit organization. Meetings are held at 7:30 pm on the first Monday of every month at the Museum of Arts & Sciences Macon, Georgia. Guests are Most Welcomed. No meetings in July & August. Due to insurance requirements, membership is required to attend club sponsored digs and collect similar, or better, samples. See our website for details Membership Adults (18+) 10.00 annually Juniors (less than 18) 2.50 annually Ms. Jalanda Goff 6th Grade Science Bonaire Middle School Bonaire, GA Ms. Ruby Ashley Education Curator Georgia Southern Museum Statesboro, GA Sample A: Fossil, Common Name: Goblin Shark Tooth Genus & species: Scapanorhynchus texanus. Stewart County, Georgia An excavation in the Blufftown Formation near Columbus produced a wealth of vertebrate fossils (including more than 1,000 goblin shark teeth) from the time of the dinosaurs. These fossils exceed 75 million years of age. The Cretaceous goblin shark was a shallow water coastal predator. Modern goblin sharks, while closely related, are deep water predators reaching 11 feet (3.3 meters) and can weigh 350 lbs. (159 kg). They have a long trowel shaped snout overhanging their mouth; the jaws shoot forward to the end of the snout, allowing the shark to bite out chunks. Donated by Dr. David Schwimmer at Columbus State University. Sample B: Fossil, Common Name: Side-necked turtle. Genus & Species: Bothremys barberi carapace (shell) fragment. Stewart County, Georgia This extinct, large, side-necked sea turtle had a carapace exceeding 2 inches thick and also lived during the time of the dinosaurs. Its modern descendents have evolved into much smaller freshwater turtles only found in the Southern Hemisphere including South America. Instead of pulling their long necks backwards into their shell, side-necked turtles fold them along either the left or right side for protection. Modern species are omnivores. The side necked family emerged 220 million years ago; this specimen lived more than 75 million years ago. The fossil came from the same excavation which produced abundant shark’s teeth, near Columbus, GA and represents one of the most common Cretaceous fossils in the Southeastern USA. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 2 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Donated by Dr. David Schwimmer at Columbus State University. Sample C: Sedimentary limestone from the Ocmulgee Formation Hawkinsville, Georgia The Ocmulgee Formation is moderately widespread in Georgia and has been well researched by scientists, it is known for both vertebrate fossils (such as fish, sharks & early whales) as well as a wealth of invertebrate fossils as seen in this sample. It represents one of many seas which covered South Georgia; this particular sea existed between 34 and 35 million years ago. The Coastline would have stretched across central Houston County. Collected for this project by club members; Thomas Thurman & Tina Perkins Sample D: Sedimentary Clay with fossils, Twiggs Clay (Small modern plant material may be present from screening process) Houston County, GA The Twiggs Clay can be found across Middle Georgia from the vicinity of Roberta to South Carolina. It represents another distinct sea which covered South Georgia. The enclosed bryozoan fossils are about 35 to 36 million years old. This was a quite sea and the coastline would have crossed South Macon. The Twiggs Clay was primarily formed by heavy sediments suspended in our rivers as they emptied at the shoreline. It is known for several large vertebrates. Clay collected, screened and washed by Thomas Thurman Sample Jars provided by Tina Perkins Sample E: Sedimentary mineral, Kaolinite (kaolin), also known as China Clay Kaolin is by far Georgia’s most economically important mineral. The state has large deposits from the Augusta area to the Columbus area ranging in age from more than 65million years to 33 million years. The deposits parallel the Fall Line, which runs from Columbus, through Macon, to Augusta. Kaolinite is derived from feldspar which eroded from Georgia’s Piedmont region and became suspended in our rivers. The feldspar was deposited as the rivers drained into the sea then decayed to become kaolinite. Kaolin has multiple uses; porcelain is made from kaolin, used in cosmetics, as a paper coating, the frosting of light bulbs, tooth paste and as a medicine for an upset stomach. Donated by KaMin Performance Minerals in Twiggs County Prepped for egg-cartons by Tina Perkins’ High School Science Class 2009-2010 Sample F: Mineral from iron oxide, Iridescent Hematite. *This iridescent variety of hematite is very rare globally and Georgia is one of few sources for many world famous, museum quality specimens. While harder than natural iron, hematite is more brittle and can be formed in hot spring or through volcanic/water interaction. In the case of Georgia’s hematite; hundreds of millions of years ago volcanoes stood over Lincoln County and interacted with ground water. Collected and donated by club officer Jay Batcha Graves Mountain, Lincoln County, Georgia during a Club dig. Sample G: Metamorphic rock, Kona Dolomite Marquette County, Michigan 2.1 to 2.2 billion years old Named after the Kona Hills south of Marquette County, Michigan where it is found. This dolomite is an ancient rock formed by fossil stromatalites between 2.1 to 2.2 billion years ago. These stromatolite formations are from some of the first life on earth. (No fossils will be visible.) Donated by club officer Jay Batcha. Sample H: Metamorphic mineral, Kyanite Southwest of Thomaston, Upson County, Georgia Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 3 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Blue bladed crystal widely distributed in Georgia’s metamorphic rocks. It can also occur as green, white, grey or black. Its presence in metamorphic rock is taken as an indicator of high pressure during the metamorphic process, low pressure metamorphic rocks carry different suite minerals. Donate by club officers Phil & Susan Hargrove Sample I: Igneous Rock; Obsidian (Volcanic glass from lava) **Beware of sharp edges!** Glass Butte, Central Oregon Obsidian is an example of a lava flow rock. It forms when dense; silica rich lava cools rapidly and lacks crystal structure. Silica is basic component in glass. Obsidian was the preferred American Indian material for stone projectile points; it can be shaped into more-than-razor-sharp edges. Typically black, reds, yellows, grays and green occur due to trace mineral content. **Beware of sharp edges!** Donated by club member Ray Crowfeather. Sample J: Igneous Rock; Ryholite, (Volcanic pumice from lava) New Mexico This form of rhyolite, lightweight with a porous structure, is from an explosive eruption and is called vascular pumice. Gas bubbles trapped inside the rock when it was expelled de-pressurized as the rock cooled (image bubbles popping), forming the sponge-like appearance. Some forms of pumice will float in water. Donated by club officer Jay Batcha. Sample K: Metamorphic, Granite Gneiss (gneiss is pronounced as “nice”) Vulcan Quarry, Bartow County, Cartersville, GA Part of the Corbin Gneiss Complex Originally formed during the Proterozoic Eon about 1.2 billion years ago. Granite; is formed by the slow cooling and crystallization of magma at some depth in the Earth’s crust, cooling is slow enough to allow various minerals to separate giving the common striped or blotchy appearance. Gneiss; refers to either sedimentary or igneous rocks (in this case igneous) which were exposed metamorphic processes. (In this case that process occurred during the continental impact event about 300 million years ago, this formed the folded Ridge & Valley region of North Georgia.) It is a reflection on a dynamic Earth that this granite formed from magma deep below the surface, then was folded and forced through the metamorphic process after a continental collision, and finally exposed at or near the surface through erosion. Donated by club officer Jay Batcha. Sample L: Calcite (Cave Onyx) Ladds Mountain, Bartow County, Cartersville, GA Cave Onyx is composed of calcite. It is the material which forms stalactites and stalagmites in caves. Water erodes the calcite from limestone which forms the cave and carries the water to a cave where it coats the cavity walls in colored layers, as seen in the sample. The color of the layer is dependent on the temperature of the cave as well as what minerals are suspended in the water. Donated by club officer Jay Batcha. Sample M: Fossil, Sea Urchin Species: Rhyncholampas gouldii Brooksville , Florida (also occurs in Georgia) Approximately 34 million years old, extinct species. Known in Jamaica as sea eggs, these specimens were collected by students of Georgia Southwestern during a research project. In life they were covered with short spines and burrowed Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 4 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org for food just beneath the sea floor. Urchins are members of echinoid class which includes sand dollars. Urchin and sand dollar shells are made of interlocking panels, and each panel is a distinct calcium (calcite) crystal. For this reason they are often preserved as limestone fossils, such as these sea eggs. Because the evolutionary history and fossil record of echinoids is well understood, they are very useful to paleontologists for dating sediments. Donated by Dr. Burt Carter, Department of Geology & Physics, Georgia Southwestern State University, Americus, Georgia. Sample N: Fossil, Petrified Wood (encrusted with quartz crystals) Brilliant, North-west Alabama At least 94 million years old. Known in Alabama as diamond rock. Wood is petrified when the plant material has been replaced by stone, or mineralized. Typically the replacing mineral is silica (quartz). Petrified wood is common in Alabama. It is formed when forests are flooded and material, whole or in fragments, becomes buried before it can decay. From there dissolved silica (quartz), suspended in water soaks into the wood and in time the wood becomes petrified. The quartz crystals slowly grew in cavities. Pure quartz is clear; the coloration seen here is due to trace minerals present in the water. Museum quality specimens occur. Diamond Rock logs 32 feet long have been reported. Petrified wood occurs in Georgia but it is rare. Collected and donated by club officers Phil & Susan Hargrove Sample O: Sedimentary rock, Dry Creek Jasper High grade chert, polished by tumbling Bartow County, Adairsville, GA Approximately 450 years old. Chert is a common sedimentary rock widespread in Georgia. It forms when limestone soaks up dissolved silica (quartz), over time this hardens the limestone. Chert can be very hard, much harder than the best concrete. Chert varies greatly in color, quality and composition depending on the quality of the original limestone and the amount of silica suspended in the water. Silica alone will form clear or translucent chert; if other minerals are present the chert will be variously colored. High quality chert lacking pits is sought after by those pursuing the lapidary, or rock polishing, arts. High quality colored chert is typically called jasper or chalcedony (shall-sea-dony) and can be very beautiful. Translucent or banded chert is called agate. Flint is typically solid grey high quality chert. Chert can also preserve very detailed, fine grained and enduring fossils. Chert was heavily used by American Indians, and most all early humans, as a tool making stone. The igneous obsidian, as included in this kit, was preferred for tool making, but it doesn’t widely occur. Most American Indian projectile points found in Georgia are made from chert in some form; the best samples are formed from jasper. Collected, polished and donated by club officer Jay Batcha. Sample P: Fossil, Coral Chert and/or agate from coral. Withlacoochee River, Lowndes County, Georgia A common fossil from southernmost Georgia to North Florida, large museum quality specimens are well known. Approximately 20 million years old. When this coral lived the coastline would have been across South Georgia, submerging North Florida with parts of South Florida standing as islands. Several major rivers drained into the area with heavy loads of silica (dissolved quartz). Hard coral is made of calcium, like limestone. (Chalk is a form of limestone) The coral absorbed the silica and in time became chert. Collected and donated by Susan & Phil Hargrove. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 5 of 17 Have Questions? Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 6 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Suggested Classroom Application For Sample Kits Kindergarten: Georgia Performance Standards Framework Unit One Organizer: SKE2, Rocks & Soil Identify differences between rocks and soil. Rocks: (Rocks are made up of one or more minerals, each formed by different processes) Samples C, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, O Soil: Soil is a mixture of weathered rock, air and humus (decomposed organic matter). Most local soils are clay based. Sample D: Twiggs Clay already possesses minerals & rock, it weathers to a light tan soil as the organic matter (fine roots can be seen in many samples) gradually decomposes. Sampled H: The red clay in the seams and cracks of the kyanite represent soil. Use attributes to classify and sort rocks and types of soil. Light coloration: Sample E Sparkly: Sample F Dark coloration: Sample J Rough: Samples C, J or K Shiny: Sample H Smooth:Samples B, H, I or O Demonstrate knowledge of terms, Rock, soil, water, air, large, heavy, dark, light, smooth, rough, smell, texture, grain, particle, color. For “heavy & light” feel difference between samples F (hematite) & J (rhyolite). Lesson 1; Introduce standards Here students are introduced to the basic concept of rock & soil. o Rock specimen, Sample K (Granite). This is commonly seen by Middle Georgia students and is widely used in commercial and residential applications. o Soil is not well represented in this kit, Sample D (Twiggs Clay) is closest but the presence of fossils would probably distract from the lesson. Lesson 2; Earth materials video Recommend staying within frameworks. Lesson 3; Nature walk Recommend staying within frameworks. In many cases students will collect granite samples from the school yard; these may be compared to the sample in the kit. There are subtle differences in granite from different parts of the state. Middle Georgia granite tends to be striped where the kit sample is from northwest Georgia. For complex reasons it is very different and tends to be blotchy in appearance. Lesson 4; Rock-A-Lot This activity is used to show how rocks are similar and different. Discuss the word attribute and teach what that means and relates to rocks. Use light, dark, shiny, sparkly, rough, smooth, big and small. Students can group rocks according to those attributes. Materials: Rocks from previous lessons, purchased rocks (Samples from kit should fill these needs. If teacher wishes to purchase (minimal expense) a bag of polished rocks from the club we can supply as needed. Lesson 5 & 6: Samples from kit can be used to support frameworks. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 7 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Grade 3 Unit One Organizer: S3E2, Framework Fossils This unit teaches that fossils lived long ago. 1) What are characteristics of different fossil types? Small pieces of large organisms Samples: A (shark’s tooth) & B (fragment of turtle shell) Small pieces or nearly whole pieces of small organisms Sample C: snails, clams and other small life Sample D: branches of small colonial animals Sample M: whole, or nearly whole, sea urchin Sample P; partial remains of coral colony 2) What information about the original organism did you gain from observing the fossil? These organisms were present at different points in Georgia’s history. Sample M, can be used to show that sand dollars and sea urchins are closely related. 3) Which organisms left these fossils? Samples A, B, C, D, M & P (see sample descriptions) 4) Why might you find a fossil of an aquatic organism in a desert? The Earth Changes Freshwater fossils in a desert show that at some point ample water was present. Salt water (marine) fossils in a desert show that oceans or seas were present in the past. This can be attributed to sea level change and/or continental drift. 5) What knowledge about fossils did you gain from your research? That climates change for a variety of reasons. That the presence of fossils allows scientists to interpret past environments. That by observing which fossils occur in what locations, and at what depth, scientists are able to not only date past environments, but understand how life and environments have changed. 6) How are different fossil types formed? Fossils are formed when organic remains become mineralized, in other words minerals become absorbed and in time replaces bone, shell or plant material. In most cases this occurred after the specimen was buried in sediments. Cave fossils are also known where organic remains may or may not have been buried, but were submerged in mineral rich, fresh, ground water for long periods and in repetitive cycles (especially during the repetitive ice ages), the minerals were absorbed and the very stable environment of the cave allowed mineralization. 7) Where are fossils most likely to be found? In the Middle Georgia area, especially just south of Macon and throughout Houston County, fossils are often found on the surface or in the walls of gullies, ditches, streams and river banks. (Be sure to get property owner permissions before looking for fossils.) Age and types of fossils can vary dramatically depending on where one looks in Middle Georgia’s complex geology. Fossils are well known in Georgia, especially north of Atlanta and south of Macon. Georgia’s oldest fossils, found in the Appalachian Plateau (see included physiographic map) are trilobites which lived approximately 500 million years ago. Our most recent fossils include both mammoths and mastodons which lived throughout Georgia about 12,000 years ago. Concept: Fossils as evidence of organisms that lived long ago. The presence of ocean fossils, in numbers, so far inland in Georgia (see physiographic map) is evidence that these organisms lived long ago. Scientists can date fossils accurately using various methods, including observation of the different layers, or stratigraphy, of sediments and comparisons with matching fossils of known age from different locations. The diversity of Georgia’s fossils, from a diversity of locations, clearly shows that Georgia has supported many different environments at different times in history. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 8 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Grade 3; Physical Attributes of Rock & Soil Focus Standard S3E1 Concept: Rocks and soils are made of minerals. There are no soil samples in this kit, but soil can be collected outside. Enduring understanding: (Definitions) The Earth is composed of mineral elements. Rocks are composed of one or more minerals. Minerals are a naturally occurring solid chemical substance for geologically. Rocks have physical characteristics (shape, color, texture). Scientists classify rocks by using observation and simple tests. Soil is composed of weathered rock, air, water, and humus. There are three basic types of soil, each with different characteristics. Scientists classify soils by observation and simple tests. Rocks are composed of one, or more, minerals. Rock Samples from kit; C, G, K & O (With Sample K being best.) Each of these samples represents a mixture of minerals assembled naturally to form a rock. Minerals Samples from kit; E, F, H, & L (With Sample E being best) Each of these represents naturally occurring solid (nearly pure) chemicals which naturally/geologically formed in distinct processes. Soil is composed of weathered rock, air, water and humus (Humus is the organic component of soil, made from decomposed plant and animal remains.) Sample D (Twiggs Clay) is sedimentary clay which weathers to a light tan soil and is often seen in this state in older exposures. In many of the collected samples (not all) fine roots, decaying seeds and modern snail shells can be seen. These are the beginnings of humus. Rocks are broken down to form soil. Sample H (Kyanite) a metamorphic mineral known for it’s resistance to weathering. It is only formed when existing rock is exposed to high pressure, deep underground, for extended periods of time. These samples of kyanite occur in loose red clay soil, as can be seen by the red clay which fills their seams and cracks. The metamorphic rock which held them when they formed eroded away into soil, leaving only the tougher kyanite. Explain that rocks and soils are made of minerals. Various minerals form in a variety of processes. One or more minerals forms a rock Different minerals weather at different rates. Sample E (kaolin) is a mineral formed when feldspar, under the right conditions, weathers. Silica is well represented in the kit. Sample I: Obsidian is nearly pure silica as lava, volcanic glass Samples A, B, N, O & P are all fossils formed when silica dissolved in water was absorbed my organic material and mineralized. Quartz sand, very common in Georgia, is nearly pure silica. Silica weathers very slowly. As shown by this kit, there are many types of minerals in Georgia. Georgia’s soils have a high mineral content and wide variety of weathered minerals. Additional example; the red color seen in many of Georgia’s soils and clays is the product of large amounts of oxidized (rusted/weathered) iron. The source of this iron was mountains and volcanoes, now weathered away, which once stood on the Piedmont (see physiographic map). Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 9 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Grade 5: Students will identify surface features of the Earth caused by destructive and constructive processes. Focus Standard S5E1, Earth Science A. Identify surface features caused by constructive processes. Deposition: *Fossil Samples A, B, N & P were formed when deposition buried organic material and began mineralization process. These deposited sediments became farmable land. *Sample C is a limestone created by deposition of sediments, including invertebrate & vertebrate remains. Limestones are frequently minded for building material (cement) as well as fertilizer (calcium). *Sample E is sedimentary clay deposited as river suspended sediments, originally feldspar, into coastal waters where it weathered into kaolinite (kaolin). Kaolin is, by far, Georgia’s most economically important mineral, Creating both industry and jobs at many levels. Earthquakes (There are no kit samples directly related to earthquakes) Sample K was formed when during a continental collision event 300 million years ago caused through continental drift. This event would have cause large scale earthquakes. This is a famous Georgia granite with both ornamental and construction uses. Volcanoes Sample F was produced by a combination of local volcanic activity and local water. The mineral remains hundreds of millions of years after the volcano has eroded away. The source for this material was Graves Mountain which has proven a valuable mining site for other minerals. Faults (Advised by Dr. Burt Carter, Georgia Southwestern State University) Georgia has numerous faults in the Piedmont, Blue Ridge, and Valley & Ridge provinces (see physiographic map) which formed between 253 and 542 million years ago, during times of continental collision when the current Appalachian Mountains and their predecessors were formed. These faults continue down into the deep Coastal Plain rocks buried beneath more recent sediments. (See page 11 of this paper, Hypsognathus entry, over South Carolina.) There are also surface faults on the Coastal Plain (see physiographic map) near Augusta. The exact age of these faults isn’t clear but they’re believed to be at least 33 million years old. It has been suggested that theses faults are associated with the hot springs of the Appalachian Mountains. It has also been suggested that the Charleston earthquake of 1886 (See Earthquake entry on page 10.) might have been caused by recent, renewed movement of these Augusta, Georgia area faults. Neither of these “suggestions”, or theories, has yet been shown by peer reviewed scientific research. B. Identify and find examples of surface features caused by destructive processes. Erosion (water – rivers and oceans, wind) Georgia’s exposed granite, in every case including Stone Mountain (which is not world’s largest granite outcrop), was formed several miles underground when lakes of lava slowly cooled. These were later exposed through erosion by water and wind. The granite itself is very resistant to weathering and erosion. Weathering Georgia’s red clay, so often seen along roadsides, is evidence of weathering in a destructive process of igneous and metamorphic rocks from the Piedmont (see physiographic map). In the Bibb and Houston Counties this clay is highly variable, in both color and hardness. The reddish coloration is typically from Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 10 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org oxidized (rusted) iron, oxidation is a weathering process, the deeper the reddishorange coloration the higher the content of weathered iron. Impact of organisms The red clay which shows erosion and weathering also shows the impact of organisms on Earth’s climate. The red coloration is due to the oxidation of iron. Iron oxidizes in the presence of oxygen. The main driving force for the presence of oxygen in our atmosphere is photosynthesis. So the oxidized iron in our red clays is one of Georgia’s best surface feature examples for the impact of organisms. Earthquake (Selections from USGS website: earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/states/georgia) The great Charleston, South Carolina earthquake of 1886 caused severe shaking in Georgia. On August 31 at 9:25 p.m., preceded by a low rumble, the shock waves reached Savannah. One woman died of fright as the shaking cracked walls, felled chimneys, and broke windows. Panic at a revival service left two injured. Two more were injured by leaping from upper story windows. Several more were injured by falling bricks. Ten buildings in Savannah were damaged beyond repair and at least 240 chimneys damaged. People spent the night outside. The Tybee Island Light Station’s 134 foot lighthouse was cracked near the middle where the walls were six feet thick, and the one-ton lens moved an inch and a half to the northeast. In Augusta the shaking was the most severe in Georgia. An estimated 1000 chimneys and many buildings were damaged. Business and social life was paralyzed for two days. Brunswick and Darien were alarmed. On November 1, 1875, at 9:55 in the evening, an intensity VI earthquake occurred near the South Carolina border. It was felt from Spartanburg and Columbia, South Carolina, to Atlanta and Macon, Georgia, from Gainesville to Augusta, and generally over an area of 2500 square miles. An earthquake of intensity V (or over) occurred on March 12, 1964, near Haddock, less than 20 miles northeast of Macon, shaking was felt in four counties over a 400-square-mile area. Volcano Graves Mountain, in Lincoln County Georgia, while generally constructive, has a distant volcanic past (more than 250 million years ago) which included eruptions producing large quantities of volcanic ash and free flowing lava. At the time these would have been highly destructive to local organisms and environments. The world has changed dramatically since then and there is no longer any danger of volcanic activity from Graves Mountain, or anywhere in Georgia. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 11 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Grade 6: Focus Standard S6E5. How do Fossils Show Evidence of Change in the Surface of the Earth? Georgia’s Oldest Fossils: Approximately 500 million years old. The finger-nail sized trilobite seen at the right was collected in Northwest Georgia’s Appalachian Plateau (see physiographic map). When it lived this area was the floor of a shallow sea and there were neither bones nor trees on all the Earth. The Appalachian Mountains didn’t exist yet and Georgia was in the Southern Hemisphere. South Carolina: Approximately 200 million years ago Coastal Plain sediments of South Georgia are a thick blanket of sediments covering much older sediments which often tell stories from different climates. Dr. Tim Chowns is a Professor of Geology for the University of West Georgia. He reports that the skull of a 200 million year old Triassic reptile, genus Hypsognathus, was recovered from a core sample near the Savannah River in South Carolina at a depth of 2,016 feet (nearly half a mile down), Hypsognathus was a primitive reptile about 13 inches long and very much like a modern lizard, though they are unrelated. Their bodies were low and broad with short tails; their heads were adorned with horns. Dr. Chowns reports that the area producing the fossil is a buried rift valley known as the Dunbarton Basin filled by red sandy, conglomerate mudstones. When Hypsognathus lived this was a desert basin with dry lake beds. Georgia was a desert 200 million years ago. Georgia: 75 Million Years Ago The outline of the human in the following images is only meant show a sense of how large these animals were. All of these animals went extinct many millions of years before humans appeared. Sixty-five million years ago all the dinosaurs went extinct. Seventy-five million years ago, ten million years before the dinosaurs disappeared, Georgia was still a very different place. The coastline stretched roughly along the Fall Line (see Physiographic Map) from Columbus, through Macon and on to Augusta, Georgia. To the west of Georgia, covering most of the Mid-Western United States was the Western Interior Seaway, as seen in the map to right. Georgia was at a crossroads between the Western Interior Seaway, the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean. Dinosaurs walked north of our Fall Line coastline. Interestingly, the Western Interior Seaway, as it split the landmasses of North America, also caused splits in the Dinosaur Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 12 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org populations and in many cases, such as the Tyrannosaurs, isolation led to the emergence of eastern and western species. Along this lost Georgia coastline, and in our rivers, there were huge crocodiles, 30 feet long and very capable of taking many dinosaurs. The sea covering South Georgia was an equally dangerous place full of large predators including many species of large sharks, and the bony fish seen below. The following research by shared by Dr. David Schwimmer, Professor of Paleontology at Columbus State University, Columbus Georgia Samples A & B in the egg carton kit represent two separate species, a large shark and a large sea turtle, which swam in a the sea covering South Georgia during the time of the dinosaurs more than 75 million years ago. Both of these fossils came from West Georgia, south of Columbus, east of the Chattahoochee River and on the banks of Hannahatchee Creek in Stewart County, Georgia. We will revisit this location a bit further on as we consider how fossils chow evidence of change in the surface of the Earth. Sample A: The tooth is from a species of extinct Goblin Shark which hunted the shallow water coastlines. Modern Goblin Sharks, a separate but closely related species, hunt deep water coastlines. The shallow water species went extinct with the dinosaurs, but its deep water cousin survived that extinction event. There were many sharks, rays and skates present in this sea; hump tooth sharks, thresher sharks, crow sharks, angel sharks, nurse sharks, ragged tooth sharks, large members of the great white shark family, several types of sawfish (including some decidedly odd species long extinct), several rays, cow-nosed rays, chimera, and guitar fish (a skate). Sample B; is from the large, side-necked sea turtle which was plentiful 75 million years ago. Now extinct, about 70 species of related side-necked freshwater, aquatic turtles endure in the Southern Hemisphere including the African dwarf mud turtle whose shell is about 5 inches long and the Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 13 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org giant South America river turtle whose shell reaches 35 inches long. These turtles would have shared the sea with the many sharks. Beyond sharks and turtles, bony fish are also present in the fossils record of this time and location; gar, bowfins, bonefish, and the small, odd looking saber-tooth herring (Enchodus petrosus) are all well known. There were also giants like the below illustrated Megalocoelacanthus dobiei (pronounced: mega-low-see-la-kanth-us dough-bee-ee). This is a new species discovered and named from a wealth of fossils found in Alabama and Georgia. Oddly, because of the large size of the remains many specimens housed in collections went unidentified or misidentified until a large mass of fossils from a single individual was found and confirmed as a new species. “Megalo” means giant. This fish is a famous “living fossil” though to be extinct until a live specimen was caught in 1938. They emerge into the fossil record about 390 million years ago. Modern species run about 5 feet long, so Megalocoelacanthus dobiei, at 11.5 feet, were large heavy bodied predators. The coelacanths are interesting in the fact that like the goblin sharks we discussed earlier; there were both deep water and coastal/shallow water species and only deep water species remain. Another very large predatory fish swimming in this Georgia was Xiphactinus vetus (pronounced: Zee-fact-teen-us vee-tus), a younger species and very close relative of the fish shown below. Xiphactinus vetus is another new species discovered and named by Dr. Schwimmer from fossils collected in Alabama and Georgia. It was identified as a distinct species by elongated, curved teeth and distinct vertebra which Xiphactinus audax lacked. Our local species, Xiphactinus vetus, was at least as large, or larger, than the specimen seen below. In life, Xiphactinus vetus would have probably been about 15 feet long. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 14 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Fossils give us information that 75 million years ago, the world was much warmer and sea levels were much higher. Scientists at Columbus State University, have identified fossils of at least two ocean going families of successful predatory marine reptiles, mosasaurs and plesiosaurs, from sediments in Georgia and Alabama. Mosasaurs and plesiosaurs were not dinosaurs. Dinosaurs are defined as land animals whose legs are vertically beneath them, not splayed to the sides like a lizard’s or an alligator’s. Most of these finds have been single bones which don’t allow for identification beyond saying it belong to a mosasaur or a plesiosaur, however sometimes scientists get lucky and find enough material to properly identify a specimen and confirm its presence, such was the case for the mosasaur Tylosaurus. Mosasaurs had large heads, short necks and long tails. They swam snake-like, except that they had four paddles instead of feet. They are related to lizards and snakes, closely related to monitor lizards. The mosasaur Tylosaurus was a 50 foot coastal predator, almost the length of two school buses. Plesiosaurs are an opposite approach to hunting in the sea. They had small heads, long necks and short tails; they swam by flapping their four large flippers and “flying” through the water. Several species have been identified in Western Alabama. Georgia has produced several plesiosaur fossils, but not enough material from any single individual to confirm the species. All these predators were feeding on schools of prey fish, many not so different than those found today. This was a healthy, diverse and thriving sea which left a strong fossil record in western Georgia and across a thin line between the Coastal Plain and the Piedmont along the Fall Line (see physiographic map). Back on land, 75 million years ago, we find dinosaurs in Georgia. Appalachiosaurus montgomeriensis, a member of the tyrannosaur family has been confirmed in both Georgia and Alabama. An amazing complete juvenile was recovered in Alabama. The white bones shown in the “to scale” reconstructed image represents the actual fossils found. Isolated bone fossils from other individuals have been found in Georgia. We saw how the Western Interior Sea split what would become the United States into western and eastern landmass. Members of the Tyrannosaur family are rare in the eastern United States as conditions which favored the preservation of land animal fossils in the eastern United States were decided rarer than in the west. But as Appalachiosaurus shows us, fossil were preserved from time to time. Tyrannosaurus rex is a western species. Appalachiosaurus was its equally formidable eastern descendent which hunted here in Georgia. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 15 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org Hadrosaurs, seen below, also walked Georgia and no doubt in fear of Appalachiosaurus. Leg and foot bones from Hadrosaurs are frequently found but not enough material from any single individual have yet been discovered to allow species identification. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 16 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org We’ve seen how Georgia’s fossil record shows the evidence of change in the surface of the Earth. We’ve seen how Northwest Georgia was part of a shallow sea in the Southern Hemisphere, more than 500 million years ago, and hosted trilobites before there were either bones or trees. Other strange animals were also present. We’ve seen that 200 million years ago South Carolina, right across the state line, was a desert, with dried lakes, inhabited by desert reptiles. Desert conditions were also seen in Georgia. We’ve seen that 75 million years ago dinosaurs walked in the northern half of the state while monstrous fish and marine reptiles hunted the sea which covered the southern half of the state. Ten million years later nearly all of these animals went extinct with only a few of the fish remaining in Georgia waters today. There isn’t room here to show the dizzying array of changes the fossil record reveals in the tens of millions of years after the dinosaurs, sea levels rose and fell many dozens of times. The powerful Suwannee Current became established across South Georgia while sea levels were high, linking the Gulf of Mexico to the Atlantic, it carved a canyon 150 miles long, which was backfilled by later large scale erosion so that very few traces remains today. Whales emerged into the global fossil record, the proto-whale Georgiacetus vogtlensis swam our sea for a few million years and went extinct, one of the last links between the proto-whales and modern toothed and baleen whales. (See the Georgia Southern Museum online.) But Georgia’s changing environments aren’t finished yet. Lastly we’ll look at the fossils of ice ages in Georgia. Many of the dinosaur era sharks, bony fish and reptile bones we discussed came from the banks of Hannahatchee Creek in Stewart County. In 1986 amateurs found something unexpected in the creek bed itself. A beautiful mastodon tooth and a partial leg bone. Both specimens remain in private collections. The tooth was collected by Jimmy Stafford of Lumpkin, Georgia and the leg bone was collected by Len and Josephine Lee of Omaha, Georgia. Both were loaned to David Schwimmer for study. A cast of the tooth was made and then both fossils were returned to their owners. The tooth cast can be seen at Tellus Museum in Cartersville, Georgia. This paper was published by the Georgia Journal of Science. These fossils came from Mammut americanum, the American Mastodon, and size comparisons suggest that they both could have come from the same adult individual. This animal lived in Georgia around 12,000 year ago. Fossils from this species, and this same time frame, are known from North Georgia, Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com Page 17 of 17 Middle Georgia Gem & Mineral Society www.midgagms.org West Georgia and Coastal Georgia. The American Mastodon is only distantly related to mammoths and elephants. Mammoths (as in the movie Ice Age) and elephants are closely related as both are grazers, eating grass. Mastodons were browsers, eating brush and leaves. Their teeth are distinctly different from elephants or mammoths. The slightly larger Mammoths were also present in Georgia at this time, mammoth fossils are very well known from Georgia’s coast where large herds likely lived. It is believed that mastodons lived in herds. They emerge into the fossil about 3.7 million years ago and the American Mastodon is the most recent species, it went extinct about 10,000 years ago. Mammals from the ice ages are well represented in Georgia and the evidence strongly suggests that both forests and large grass covered prairies were present in Georgia during the ices ages. Paleontologists from several of Georgia’s universities have shown that fossils are present for mastodons, mammoths, caribou, horses, llamas, giant bison, giant beavers, tapirs, glyptodonts (like giant armadillos), black bears, cave bears, cougars, jaguars, ocelots, gray wolves, capybara, giant ground sloths (3 species, with one 20 feet tall on its hind legs), and several giant land turtles. Animals whose fossils haven’t been seen but are expected to be found would include several species of big sabertooth cats including the famous Smilodon, the American lion and dire wolves. I called the mastodon tooth recovered from Hannahatchee Creek “beautiful.” Below are the quoted descriptions which Dr. Schwimmer reported. “The molar features a complete crown and nearly complete roots… relatively little chemical-physical alteration, other than the striking blue-black mineral coloration… the tooth roots retain the typical offwhite color of fresh ivory.” These fossils show that Georgia has indeed changed many times and that change is ongoing. Have Questions? Contact Education Chairperson Thomas Thurman Email: tpangangan@aol.com