L1-Circles are Everywhere
advertisement

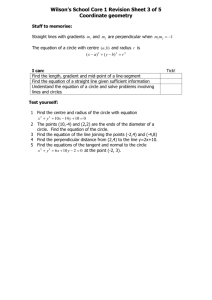
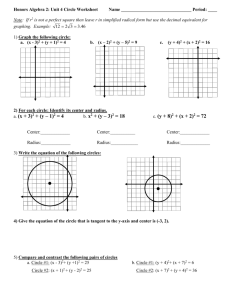
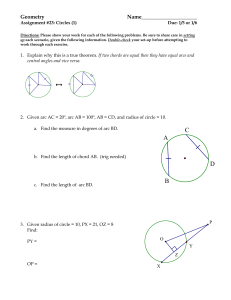
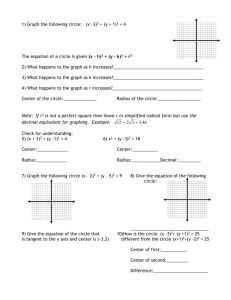
Name___________________________________Date________________ Circles are Everywhere Vocabulary 1. A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a given point. The given point is called the center of the circle. 2. A radius of a circle is a line segment whose endpoints are the center of the circle and a point on the circle. The distance from the center of a circle to a point on the circle is also called the radius. The plural of radius is radii. 3. A chord of a circle is a line segment whose endpoints are both points on the circle. 4. A diameter of a circle is a chord that passes through the center of the circle. D A Diameter O Radius Chord E 5. A secant is a line that intersects a circle at two points. A secant of a circle includes a chord of the circle. 6. A tangent of a circle is a line that intersects a circle at a single point. The point of intersection is called the point of tangency. Pair-Share: Using the circle below, complete the following: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Label the center of the circle using a marker as point P Create a radius (make sure to label all new points!) Create a diameter (label all new points!) Create a chord (label all new points!) Create a secant (label all new points!) Create a tangent line (label all new points!) Tangent B C Secant Thinking Questions: 1) Are the two circles congruent? Why or why not? 2) How do we know if two circles are congruent? 3) What geometric relationship exists between the two circles? Two circles are congruent circles if and only if they have congruent radii. Short form: 2 circles radii ≅ Short form: 2 radii of circles ≅ circles Two shapes are similar if there are a set of transformations that will move one figure to cover completely the other figure. (ex 1) Can we move a circle D with center (-1, 2) and radius of 3 to cover circle P with center (3, 4) and radius of 5? What have you just learned? Will this always work for any two circles? Why or why not? Show the two given circles are similar by stating the necessary transformations from C to D. (ex 2) C: center (2, 3) radius 5; D: center (–1, 4) radius 10. (ex 3) C: center (0, –3) radius 2; D: center (–2, 5) radius 6. Pair-Share: 1) Identify the tangent line: _____ 2) If O is the center, then PO is a ___________ 3) Measure <QPO is ________ 4) Write a rule: A line tangent to a circle 5) Is the opposite of your rule also true? THEOREM: If a line is tangent to a circle, then it is perpendicular to the radius drawn to the point of tangency. l A Short form: line tangent to a circle line to radius drawn to pt of tangency In the diagram to the right, if line l is tangent to circle P at A, then line l PA . THEOREM: In a plane, if a line is perpendicular to a radius of a circle at its endpoint on the circle, then the line is tangent to the circle. Short form: line is to radius of a circle at its endpt on circle line is tangent to circle In the diagram to the right, if line l is to PA at A, then line l is tangent to circle P. P (ex 4) Amiko is riding her bike on a wet street. As the bike wheel spins, water drops are sprayed off tangent to the wheel. Amiko’s bike wheels have a radius of 12 inches. Find the distance the water drops have been sprayed when they are 13 inches from the center of the wheel. l (ex 5) Line l is tangent to circle P at A. If CB = 8 and AB = 20, find the radius. (r + 8)2 = r2 + 202 A r 20 P r C 8 (ex 6) A green on a golf course is in the shape of a circle. A golf ball is 8 feet from the edge of the green and 28 feet from a point of tangency on the green, as shown below. Assume the green is flat. What is the radius of the green? How far is the golf ball from the cup at the center? A Investigate: P C 1) What kind of point is point C? B 2) How could we prove that tangent line AC is congruent to tangent line BC? Watch this video to discover: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R1PBIyuFvAQ B THEOREM: If two segments are tangent to a circle from the same exterior point, then they are congruent. from same ext pt segs are Short form: 2 segs are tangent to A If CA and CB are tangent to circle P, then CA CB . P C B GH and GI are tangent to J . Find GH. (ex 7) (ex 8) More Practice 14: Find the value of x in each of the following. 1. 3. 2. 4. A 24 10 C D x BD = x B 5. If the diameter of a circle measures 15 ft, what is the length of the radius? 6. If the radius of a circle measures 3.08 ft, what is the length of the diameter? Show the two given circles are similar by stating the necessary transformations from C to D. 15. C: center (–2, 8) radius 4; D: center (0, 4) radius 9 16. C: center (2, 8) radius 5; D: center (–2, 4) radius 1.