Coordinate geometry
advertisement

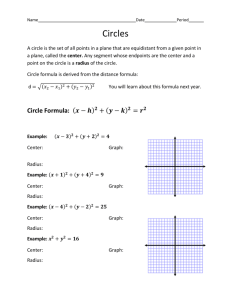
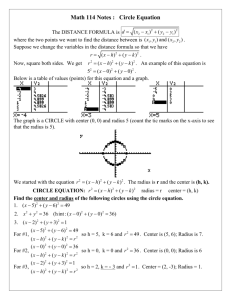
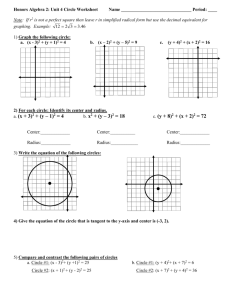
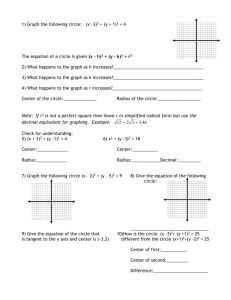
Wilson’s School Core 1 Revision Sheet 3 of 5 Coordinate geometry Stuff to memorise: Straight lines with gradients m1 and m2 are perpendicular when m1m2 1 The equation of a circle with centre (a, b) and radius r is ( x a) 2 ( y b) 2 r 2 I can: Find the length, gradient and mid-point of a line-segment Find the equation of a straight line given sufficient information Understand the equation of a circle and solve problems involving lines and circles Test yourself: 1 Find the centre and radius of the circle with equation x 2 y 2 10 x 14 y 10 0 2 The points (10,-4) and (2,2) are the ends of the diameter of a circle. Find the equation of the circle. 3 Find the equation of the line joining the points (-2,4) and (-4,8) 4 Find the perpendicular distance from (2,4) to the line y=2x+10. 5 Find the equations of the tangent and normal to the circle x 2 y 2 6 x 10 y 2 0 at the point (-2, 3). Tick! Answers: 1 Complete the square to give ( x 5) 2 25 ( y 7) 2 49 10 0 ( x 5) 2 ( y 7) 2 64 Hence centre (-5,7) radius 8 2 2 10 2 4 , Centre is the midpoint (6,1) 2 2 Radius is length of line from centre to one of the points r 2 62 2 12 25 5 Hence equation of circle is x 6 y 1 25 84 4 3 2 Gradient of line is 4 2 2 y 4 2 ( x 2 ) Using y y1 m( x x1 ) gives y 2x 0 4 2 2 1 2 y 4 1 2 ( x 2) Using y y1 m( x x1 ) gives equation of the perp line y 12 x 5 These two lines intersect when Gradient of line is 2 hence gradient of perpendicular line is 12 x 5 2 x 10 x 10 4 x 20 x 2, y 6 Hence the distance required is the distance from (2,4) to (-2,6) 2 22 4 62 x 32 y 52 36 d 5 20 2 5 Centre (-3,-5) radius 6 Gradient from centre to point [ ie of radius] = Equation of normal, using y y1 m( x x1 ) y 3 8( x 2) 0 8 x y 19 Gradient of tangent = 1 8 Equation of tangent, using y y1 m( x x1 ) 1 y 3 ( x 2) 8 8 y 24 x 2 x 8 y 22 0 3 5 8 2 3