Chapter 10: Circles Assignment Packet
advertisement

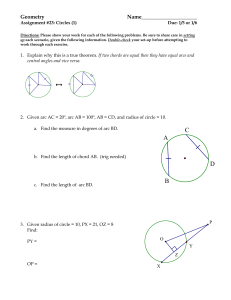
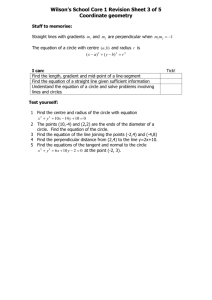
Chapter 10: Circles Assignment Packet 10.1-10.4 Section Assignments 10.1 10.2 10.3 Pg 443: Pg 447: Pg 454: Pg 455: Pg 463: Pg 463: 10.4 10.1 The Circle 5, 6, 8, 11, 12, 14, 15, 17, 24 2, 6, 8, 11, 12, 13 1 – 4, 9a, 10a, 11 6, 8, 9d, 10b, 19 1-3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 16 12, 14, 22, 25, 27 Read pages 439-442 (including Sample problems) Defn: Circle – Defn: Radius – Defn: Concentric Circles – Defn: Congruent Circles – Defn: Interior/Exterior/On – Defn: Chord – Defn: Diameter – Special Formulas: Area Perimeter Radius-Chord Relationships Complete the theorems. Theorem: If a radius is perpendicular to a chord, then _______________________________________ Theorem: If a radius of a circle bisects a chord that is not a diameter, then_____________________________. Theorem: The perpendicular bisector of a chord passes through_______________________________________. Examples 1. Given O AO = 5 DB = 2 Find OC, OD, CD 2. Given O RT = 12 radius = 10 How far is the chord from the center? Use the diagram below to answer questions 1-14 3. Given O OT = 15 radius = 17 Find AB 10.2 Congruent Chords Read pages 446-447 (including Sample problems) Theorem: If 2 chords are equidistant from the center of the circle, then____________________________ Theorem: If 2 chords are congruent, then _____________________________________________________________. Examples: Given: O, AB CD OP = 12x – 5, OQ = 4x + 19 Find OP Given: ABC is isosceles, with base AC P, PQ AB, PR CB Prove: PQR is isosceles 10.3 Arcs of a Circle Defn: Arc– Defn: Minor Arc – Defn: Major Arc– Defn: Semi-Circle – Defn: Central Angle – Defn: Congruent Arcs – Read pages 450-454 (including Sample problems) congruent central angles Examples 1. 2. Given: B; D is the midpoint Prove: BD bisects <ABC congruent intercepted arcs congruent chords 10.4 Secants and Tangents Defn: Secant– Defn: Tangent– Defn: Point of Tangency– Defn: Tangent segment– Defn: Secant Segment– Defn: External part– Defn: Tangent circles– Read pages 450-454 (including Sample problems) externally tangent– internally tangent– Defn: Common tangent– Defn: Tangent circles– external tangent– internal tangent– Theorem: Two-Tangent Theorem________________________________________________________________________ Walk-around problems Given: Each side of quad ABCD is tangent to the circle. AB = 10, BC = 15, AD = 18 Find CD Common Tangent Procedure 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Draw an appropriate diagram Draw the line of centers Draw the radii to the points of contact Through the center of the smaller circle, draw a line parallel to the common tangent Extend any radius if necessary to obtain right triangles and rectangle. Use the Pythagorean Theorem and properties of a rectangle. A. Circles O and P are tangent to each other and have a common external tangent AB. If the radius of O is 8 and the radius of P is 18, find the length of the common tangent. B. Circles O and P have a common internal tangent. The radius of O is 1 and the radius of P is 2. If the distance between their centers is 5, find the length of the common tangent. C. Circles O and P have a common external tangent. Their centers are 39 cm apart. If the radius of the smaller circle is 25 and the length of the common tangent is 36, find the radius of the larger circle. D. Circles O and P have a common internal tangent. The radius of O is 4 and the radius of P is 3. If the distance between their centers is 7 , find the length of the common tangent. Chapter 10: Circles Assignment Packet 10.1-10.4 Section Assignment Answers 10.1 5. Distance from AB to P = 8mm 9. statements 1. Given 2. DA CB 3. ABCD is 6. CD = 16 reasons 1. Given 2. All radii 3. 2 sides and 12. OS = 15 15. 8. C = 24.5cm A = 47.8 cm 11. CD = 8m 14. Radius of other circle = 20 statements 1. Given 2. PQ PT 3. <PQT <PTQ 4. <PQT <PRS 5. <PTS <PSR 6. <PRS <PSR 7. PR PS 8. QR TS reasons 1. Given 2. All radii 3. If sides then angles 4. Corr <’s 5. Corr <’s 6. Transitive 7. If angles then sides 8. Subtraction 17. a. 13 b. 5 c. 24 10.2 23. PS = 2 8. statements 1. Given 2. RS ST 3. SP SP 4. <QSR is rt < 5. <QST is rt < 6. <QSR <QST 7. PSR PST 8. RP TP 9. MQ QN 24. BO = 16.9 2. AB = 8 6. a. 8 cm b. circle reasons 11. a. 8 b. 5 1. Given 2. Radius chord 12. AB = 12 3. Reflexive 4. forms rt < 13. a. 15∏ b. 18∏ 5. forms rt < 6. All rt <’s 7. SAS 8. CPCTC 9. chords are =dist from center 10.3 1. a. 6 b. 2 c. 5 d. 4 e. 3 f. 7 g. 1 2. a. b. c. 180 d. m e. No the arcs must be in the same circle or congruent circles 3. a 90 b. 130 c. 230 d. 180 e. 220 4. 9a. 1/45 10a. 216 11. 132 6. statements 1. Given 2. AB AC 3. reasons 1. Given 2. If angles then sides 3. chords -> arcs 8. Statements 1. Given 2. reasons 1. Given 2. chords -> arcs 3. 3. Reflexive 4. 4. Addition 5. BD AC 5. arcs -> chords Statements 1. Given 2. <ABD <CDB 3. BA DC 4. BD BD 5. ABD CDB 6. AD BC 7. ABCD reasons 1. Given 2. arcs -> central angles 3. All radii 4. Reflexive 5. SAS 6. CPCTC 7. Both pairs of sides 16. 9d. 7/8 10.4 1. AC = 17cm 3. 2. XY = 12 statements 1. Given 2. PQ PR 3. Draw RO, OQ 4. RO OQ 5. PO PO 6. PRO PQO 7. <QPO <RPO 8. PO bis <RPQ 5. a. Q(16, 0) S(38, 0) b. 3 reasons 1. Given 2. Two-tangent theorem 3. 2 points make a line 4. All radii 5. Reflexive 6. SSS 7. CPCTC 8. Defn bisector 10b. 200 6. OC = 2.5 9. Statements 1. Given 2. PW PZ 3. PX PY 4. WX YZ 10. AD = 23 reasons 1. Given 2. Two-tangent theorem 3. Two-tangent theorem 4. Subtraction 16. Radius of A= 3 Radius of B = 5 Radius of C = 8 Pacing Chart for 10.1-10.4 Date: Date: Date: Date: 10.1-10.4 packet distributed 10.2 Examples Q/A 10.2 10.3 Examples Q/A 10.1 Skill Set 10.1-10.2 Q/A 10.3 10.3 Examples 10.1 Examples Date: Date: Date: 10.4 Examples Q/A 10.4 Homework 10.1-10.4 Q/A 10.3 Skill Set 10.3-10.4 10.1-10.4 packet due Quiz 10.1-10.4 EXTRA CREDIT