Radioactivity: The release of nuclear radiation in the form of particles
advertisement

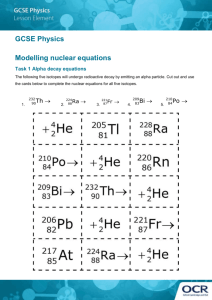
Radioactivity: The release of nuclear radiation in the form of particles and rays from a radioactive element Scientists to remember for their contributions: Henri Becquerel (1896): French scientist, Provided evidence of x-rays and Uranium “nuclear radiation” Marie Curie (Polish): She and her husband (Pierre) discovered radioactive elements and named them Polonium (after Poland) and Radium (shining element). Coined the term “radioactivity”. Ernest Rutherford: Produced the first artificial transmutation (an element changing into another), A particle accelerator uses magnets and electric fields to speed up particles What happens during radioactivity? •Particles and rays are emitted when a radioactive element or isotope breaks down. •The reason they break down has to do with stability. •All atoms want to be stable and sometimes radioactive ones aren’t resulting in radioactive decay. Nuclear Stability •Binding energy is needed for the stability of a nucleus. The binding energy keeps the nucleus together, it’s like glue •High: stable •Low: unstable •Many elements have radioactive isotopes. Ex. Carbon 12: nonradioactive (coal, diamond, graphite) Carbon 14: radioactive (used for carbon dating) * a nucleus that is unstable can become stable by undergoing a nuclear reaction or change * Radioactive Decay •The spontaneous breakdown of an unstable atomic nucleus. The unstable nucleus breaks apart. •When it breaks apart it emits particles or rays to become lighter and become more stable DECAY SERIES •The series of steps by which a radioactive nucleus decays into a non-radioactive nucleus. The element goes from radioactive to non-radioactive. Alpha Decay •Occurs when a nucleus releases an alpha particle •Alpha particles result from the decay of relatively heavy radioisotopes. They consist of two neutrons and two protons, bound together (a Helium nucleus). •Example: Americium is commonly found in household smoke detectors. Alpha Particles (made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons) •Comes from the nucleus of a He (Helium) atom, It is the weakest type of particle •Has a positive charge (+), Can burn flesh but is stopped by a sheet of paper Beta Decay •Loses a beta particle (an electron) and the # of protons increases by 1, In beta decay, a neutron converts (changes) to a proton emitting a beta particle (electron) in the process. The beta particle is identical to an ordinary electron. •Example: Carbon-14 (C-14) is a radioisotope of carbon, which undergoes beta decay and may be familiar for its use to establish the age of ancient artifacts ("carbon dating"). •Remember isotopes are when you have more neutrons than protons Transmutation: Where one element changes into another as a result of changes in the nucleus (beta decay). Beta Particles (the same as an electron) •An electron is formed in the nucleus of an atom when a neutron breaks apart, It is 10x stronger than an alpha particle, It can pass through 3 mm of solid aluminum Gamma Decay •Release of a gamma ray •The nucleus is not changed only lowered to a different energy level •Gamma rays are emitted (released) if a nucleus still has more energy after decay. The energy is electromagnetic in nature and has a unique energy. •Gamma rays are not physical particles, but their interactions with matter are described by assigning them particle-like properties. Gamma Rays (Actually a burst of high frequency waves) •An electromagnetic wave of high frequency and short wave length, Strongest type, very harmful, Can pass through several cm of solid lead Radioactive Half-Life •The halflife is the amount of time it takes for half of the atoms in a sample to decay. •The halflife for a given isotope is always the same ; it doesn't depend on how many atoms you have or on how long they've been sitting around. The halflife is always the same, but the half (the sample) gets smaller and smaller. Nuclear Fission: Splitting of an atomic nucleus into 2 smaller nuclei of approximately equal mass. A nucleus breaks into 2 pieces. “I BREAK” “I break a nucleus in 2” Nuclear Fusion •Joining of 2 atomic nuclei of smaller mass to form a single nucleus of a larger mass. •Temperature must be well over a million degrees Celsius •Fusion produces less radioactive waste –Ex: the sun & atomic bombs “U MAKE” “you make a nucleus” Radioisotopes and tracers Used for detecting chemical leaks, diagnosing disease, Killing cancers cells Effects: Can actually cause the very disease that it fights, Can damage DNA Devices that detect radioactivity: •Cloud Chambers: detects alpha and beta particle radiation, leaves a trail of ions in the water or ethanol vapor (gas) in the chamber •Bubble Chamber: detects alpha and beta particle radiation, holds a superheated liquid in which particles leave a path of bubbles if they are present •Electroscopes: Has leaves that repel or attract each other depending on the charge in the air •Geiger Counter: measures radioactivity by producing an electric current when radiation is present, detects alpha, beta and gamma radiation Radiation Sickness Symptoms: 1. Nausea 2. Fatigue 3. Loss of hair 4. Can cause death