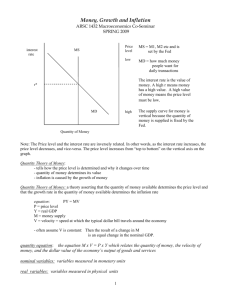
1) Which theory is used to explain what determines the price level?
advertisement

1) When the money supply exceeds the demand for money, theory predicts a. the real interest rate will drop b. the nominal interest rate will drop c. the discount rate will increase d. the price level will rise e. the federal funds rate will rise 2) As income rises, money demand a. rises, because there are more goods to buy b. falls, because with higher income, you don’t need as much money c. stays the same, because money and income aren’t the same thing. d. rises, because higher income makes velocity fall e. rises, because prices will rise which makes people demand more money 3) A brokerage firm creates a new free account where you can sell financial investments and have the proceeds deposited in your checking account the next day. This will a. Increase money multiplier because people will prefer checking accounts b. Decrease the money multiplier because people will not want to save their money c. Increase money demand because people will want to buy more goods d. Decrease money demand because its less costly to do banking e. Not affect the money market, only the market for loanable funds. 4) What would best describe what causes inflation? a. greed b. more money chasing fewer goods c. excess money demand d. higher prices e. the spiral of higher wages leading to higher prices 5) The most important factor that determines the rate of inflation is a. The greediness of businesses to make profit b. The strength of the dollar in international exchange markets c. The size of the government deficit d. The increase in the money supply e. How high the minimum wage rate is set. 6) The Fed is a. a private corporation that owns other banks b. a private corporation that controls but does not own other banks c. under direct control of the president d. under direct control of Congress e. part of the US government, but fairly independent 7) People would increase velocity because a. banking has become less convenient b. they want to spend more money c. money has become expensive to hold d. inflation is declining e. real income growth is higher 8) The cost of holding money is the a. the price of goods and services which the money could buy b. inverse of the price level which prevails at the current time c. expected real rate of interest a person could earn by holding another asset d. nominal interest rate a person could earn by holding another asset e. current inflation rate 9) Assume that real GDP grows at 3%, and velocity increases by 1%. What is the inflation rate if the money supply grows by 4%? a. -2% b. 0% c. 2% d. 6% e. 8% 10) Which of the following best illustrates the medium exchange function of money? a. You keep some money hidden in your shoe. b. The government sets tax rates in terms of currency c. You keep track of the value of your assets in terms of currency. d. You pay for your Starbucks double-latte using currency. e. None of the above. 11) Which of the following functions of money is also a common function of most other financial assets? a. Earns a positive nominal interest rate b. A store of value. c. A unit of account. d. Medium of exchange. e. None of the above. 12) Economists use the word "money" to refer to a. Income generated by the production of goods and services. b. Those assets regularly used to buy goods and services. c. The value of a person's assets. d. The value of stocks and bonds. e. A sure thing 13) Which of the following is not included in M1 a. checkable deposits b. currency c. demand deposits d. savings deposits e. travelers checks 14) Credit cards are a. Included in M2, but not M1 b. Included in M1 and M2 c. Considered checkable deposits d. not money e. All of the above 15) In the market for money, hoarding is a. the method people use to deal with an excess supply b. how people will try to acquire more money c. the process that will make prices rise d. the same as savings e. all the above 16) Which of the following does the Federal Reserve not do a. conduct monetary policy b. act as a lender of last resort c. make loans to individuals d. regulate the banking system e. control the money supply 17) When the Fed Conducts Open Market Purchases a. It buys treasury securities, which increases the money supply. b. It buys treasury securities, which decreases the money supply. c. It borrows money from member banks, which increases the money supply. d. It lends money to member banks, which decreases the money supply. e. Private banks buy treasury securities from the Fed, which increases the money supply. 18) The required reserve ratio is 5%, and a bank receives a new deposit of $1000. This bank a. Will increase its required reserves by $50. b. Will initially see its total reserves increased by $1000. c. Will be able to make a new loan of $950 d. Will create money when it lends the excess reserves out. e. All of the above. 19) If the required reserve ratio increased from 10% to 20%, the money multiplier would a. Rise from 10 to 20. b. Rise from 5 to 10. c. Fall from 10 to 5. d. Fall from 20 to 10. e. Not change. 20) When the price level falls, the number of dollars needed to buy goods a. Increases, so the value of money rises. b. Increases, so the value of money falls. c. Decreases, so the value of money rises. d. Decreases, so the value of money falls. e. Decreases, but the value of money doesn't change. 21) In the 14th century, the Western African Emperor Kankan Musa traveled to Cairo where he gave away a lot of gold, which was used as a medium of exchange. We would predict that this a. Raised both the price level and the value of gold. b. Raised the price level, but decrease the value of gold. c. Lower the price level, but increase the value of gold. d. Lower both the price little and the value of gold. e. Had no effect on prices or the value of gold in Cairo. 22) The principle of monetary neutrality implies that an increase in money supply will a. Increase real income, and the price level. b. Increase real income, but not the price level. c. Increase the price level, but not real income. d. Increase neither the price level nor real income. e. Increase real income, but reduce the price level. 23) According to the equation of exchange, if P = 12, Y = 6, and M = 8, then V = a. 16 b. 9 c. 6 d. 4 e. 1 24) The Velocity of Money is a. The rate at which the Fed put money into the economy. b. The same thing as the long-term growth rate of the money supply. c. The money supply divided by nominal income. d. The average number of times per year a dollar is spent. e. The rate at which prices rise. 25) Which of the following statements about U.S. inflation is not correct? a. Low inflation was viewed as a triumph of President Carter's economic policy. b. There were long periods in the nineteenth century during which prices fell. c. The U.S. public has viewed inflation of even 7 percent as a major economic problem. d. The U.S. inflation rate has varied over time, but international data shows even more variation. e. All the above are true 26) Which of the following is correct? a. hyperinflation is a period of extraordinarily high inflation. b. deflation is negative inflation, not just a decrease in the inflation rate. c. during the 1990s US inflation averaged about 2% per year. d. the highest inflation rates for the US were experienced in the 1970’s. e. All of the above are correct. 27) The inflation tax a. is an alternative to income taxes and government borrowing. b. is easy for a government to impose c. taxes most those who hold the most money. d. is the revenue created when the government prints money. e. All of the above are correct. Answers: 1) d. when supply exceeds demand there is a money surplus. The market will raise demand by making the price level rise. 13) d. M1 does not include savings accounts. Only currency (and coin) and checkable deposits (including travelers checks). 14) d. Credit cards are not a store value, so they are not money. When you use a credit card, you are not providing anything of value. You are promising to provide something of value later, thus credit cards are a “deferred” payment. 15) b. Hoarding is what people do to try to acquire more money because money supply is less than money demand (people have less money than they want). It means people are neither spending nor saving the money. And since people are not spending, the prices will fall. 16) c. The Fed only makes loans to member banks, not to individuals. 17) a. OMO purchases is the Fed going into the open market to buy securities which causes the money supply to increase. 18) e. If a $1,000 is deposited into a bank, then its reserves rise by $1,000 initially (before the bank has made any loans). If there’s a 5% reserve requirement, the bank must keep $50 in reserve (5% of $1,000). This means the bank can lend out $950, and as they do, this will multiple the money. 2) a. Higher income means more goods to buy so more money demand. 19) c. With 10% reserve requirement, the money multiplier would be 10 (= 100% / 10%). With a 20% requirement, the money multiplier would be 5 (= 100% / 20%). 3) d. This is a decrease in the cost of banking. So people will want to hold less money and try to put more in financial investments (portfolio choice). This increases velocity. 20) c. With lower prices, you need fewer dollars to buy goods, so money has more value. 4) b. Inflation occurs when Money Supply expands over Money Demand causing a potential surplus. The market adjusts prices higher (inflation) to compensate. Higher prices is inflation, not what causes it. 5) d. The only factor that would cause inflation in this list is an increase in the money supply, and it's the biggest factor. 6) e. The Fed is part of the US government. But because the governors are appointed for long terms and they generate their own funding, they are largely independent of politics. 7) c. If the nominal interest rate rose, money becomes more expensive to hold. People will increase velocity to try and hold less money. 8) d. What you give up by having money is the nominal interest paid on other assets. By holding money, you lose both the real interest rate and inflation. 9) c. The formula is money growth plus velocity growth minus real income growth. So we have 4% + 1% - 3% = 2%. 10) d. Medium of exchange means that you purchase things with money, like coffee. 11) b. Financial assets are a store of wealth, as is money. By having a financial asset, including money, you are holding on to something that has value (though that value may be changing). Money is different from other financial assets, though, because it’s also a medium of exchange. 12) b. Basic definition of money is an asset (or store of value) that purchases things (or a medium of exchange) 21) b. An increase in the money supply will create a money surplus. This will cause splurging which will make prices go up and the value of money go down. 22) c. Money neutrality means that an increase in the money supply will only affect nominal variables, like prices, but not affect real variables, like real income. So real income won’t change. But prices will rise. 23) b. 12 * 6 = 8 * V. So V = 72 / 8 = 9. 24) d. Velocity is the number of times in a year that money will circulate through the economy and purchases new final goods or services 25) a. The highest inflation rates of US history were experienced while Carter was president. Inflation was brought down under the Reagan administration. 26) e. All statements are true. 27) e. All are true