Biology Exam: Eye, Transpiration, Photosynthesis, Nerves
advertisement

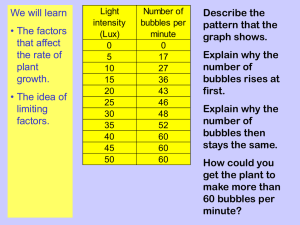
The King's School Q1.Diagram 1 shows cells from the light-sensitive layer in the eye. Diagram 1 (a) On Diagram 1, add labels to name part A and part B of the light-sensitive cell. (2) (b) There is a junction between the connecting neurone and the neurone carrying the impulse to the brain. (i) What name is given to the junction? ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) In what form is information passed across the junction? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) Page 1 The King's School (c) Diagram 2 shows a bee flying towards a man’s eye. In the blink reflex , light from the bee reaches the light-sensitive cell in the eye. The muscles in the eyelid shut the man’s eye before the bee hits the eye. Describe the pathway taken by the nerve impulse in the blink reflex. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (4) (Total 8 marks) Q2. Plants lose water vapour from their leaves. Most of this water vapour is lost through the stomata. (a) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. distillation. Plants lose water vapour by filtration. transpiration. (1) Page 2 The King's School (b) A class of students investigated the number of stomata per mm2 on the upper surface and on the lower surface of the leaves of three species of plant, P, Q and R. The students placed samples of the surface cells onto a grid on a microscope. Student X counted the stomata on the lower surface of a leaf from one of the plant species. The diagram shows part of the grid that student X saw under the microscope. (i) Complete the calculation to estimate the number of stomata per mm2 on the lower surface of this leaf. Number of stomata in mm2 = ......................................................... Number of stomata in 1 mm2 = ............................................................ (2) The table shows the mean results for the class. Mean number of stomata per mm2 of leaf Plant species (ii) Upper surface of leaf Lower surface of leaf P 40 304 Q 0 11 R 85 195 Student X had counted the stomata on the lower surface of a leaf from one of the plant species. Use your answer to part (b)(i), and information in the table, to help you to answer this question. From which plant species, P, Q or R, was student X’s leaf most likely to have been taken? (1) Page 3 The King's School (iii) Species Q is normally found growing in hot, dry conditions. Explain one way in which species Q is adapted for living in hot, dry conditions. Use information from the table. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q3.This question is about photosynthesis. (a) Plants make glucose during photosynthesis. Some of the glucose is changed into insoluble starch. What happens to this starch? Tick ( ) one box. The starch is converted into oxygen. The starch is stored for use later. The starch is used to make the leaf green. (1) Page 4 The King's School (b) A student investigated the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis in pondweed. The diagram shows the way the experiment was set up. (i) The student needed to control some variables to make the investigation fair. State two variables the student needed to control in this investigation. 1............................................................................................................. 2............................................................................................................. (2) (ii) The bubbles of gas are only produced while photosynthesis is taking place. What two measurements would the student make to calculate the rate of photosynthesis? 1............................................................................................................. 2............................................................................................................. (2) (c) The graph shows the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis in the pondweed. Page 5 The King's School Temperature in °C (i) Name the factor that limits the rate of photosynthesis between the points labelled A and B on the graph. ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Suggest which factor, carbon dioxide, oxygen or water, might limit the rate of photosynthesis between the points labelled C and D on the graph. ............................................................................................................... (1) (Total 7 marks) Q4.The nervous system allows humans to react to their surroundings. (a) Sense organs have receptors. Receptors detect changes in the environment. Which word describes a change in the environment? Draw a ring around one answer. an effector a neurone a stimulus (1) (b) The photograph shows a baby. Labels A, B, C, D and E show some of the baby’s sense organs. A B C D E Photo by D. Sharon Pruitt [CC-BY-2.0], via Wikimedia Commons Page 6 The King's School Answer each question by writing one letter, A, B, C, D or E, in each box. (i) Which sense organ has receptors sensitive to light? (1) (ii) Which two sense organs have receptors sensitive to chemicals? and (2) (iii) Which sense organ has receptors sensitive to changes in the baby’s position? (1) (c) Information from sense organ A is passed along nerve cells. The information is coordinated to produce a response. Which organ in the body coordinates the information? ........................................................................................................................ (1) (Total 6 marks) Page 7 The King's School Q5. Changing the conditions in which plants grow affects how fast they grow. The diagram shows a propagator in which scientists can control temperature, light intensity and carbon dioxide concentration. The graph shows the effects of changing the temperature, light intensity and carbon dioxide concentration on the growth of lettuce plants. (a) Describe and explain the effect of increasing light intensity on the mean mass of lettuce plants at 4% carbon dioxide and 15 °C. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) Page 8 The King's School (b) Growers wish to make maximum profits from their lettuces. What do they need to consider before making decisions about the growing conditions for their lettuces? .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) The nutrient solution contains nitrate ions and magnesium ions. Complete the table to show the functions of these ions in plants and their deficiency symptoms. Ion Function in plants Deficiency symptoms ......................................................... ........................................................ Nitrate ......................................................... ........................................................ ......................................................... ......................................................... ......................................................... .......................................................... Magne ......................................................... sium ......................................................... ......................................................... ......................................................... (4) (Total 9 marks) Page 9 The King's School Q6. The graph shows the effect of temperature on photosynthesis. (a) Between which temperatures is the rate of photosynthesis fastest? ............................... and .......................... °C (1) (b) Suggest why the rate of photosynthesis stays the same between these two temperatures. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) A greenhouse owner wants to grow lettuces as quickly and cheaply as possible in winter. At what temperature should he keep his greenhouse in order to grow the lettuces as quickly and cheaply as possible? .......................... °C Explain your answer. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 6 marks) Page 10 The King's School Q7. (a) What is the name of the organ which controls the nervous system? .................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) The diagram shows a reflex arc. Label the three neurones. (3) (c) Snatching your hand from a hot object is an example of a reflex action. Give one other example of a reflex action. .................................................................................................................................... (1) (d) Describe the stages that happen in a reflex action. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 8 marks) Page 11 The King's School Q8. Some students investigated the effect of nitrates on the growth of seedlings. The diagram shows the apparatus the students used. The students set up three test tubes. • Tube A contained pure water • Tube B contained all the mineral salts that a seedling needs for healthy growth • Tube C contained all the mineral salts that a seedling needs for healthy growth, but no nitrate. (a) Why did the students set up tubes A and B? ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (1) (b) To make it a fair test, what should each of the tubes, A, B and C, contain? ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (1) The table shows the students’ results. Tube Solution in test tube Mass of seedling after 14 days in g A Pure water 0.10 B All the mineral salts a seedling needs for healthy growth 0.45 C All the mineral salts a seedling needs for healthy growth but no nitrate 0.30 Page 12 The King's School (c) Give two conclusions that you can make from the students’ results. 1 ..................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................ 2 ..................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................ (2) (Total 4 marks) Q9.The diagram shows a section through a plant leaf. (a) Use words from the box to name two tissues in the leaf that transport substances around the plant. epidermis mesophyll phloem xylem .................................................................. and ............................................................ (1) (b) Gases diffuse between the leaf and the surrounding air. (i) What is diffusion? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... Page 13 The King's School ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Name one gas that will diffuse from point A to point B on the diagram on a sunny day. ............................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) Q10. A student grew a plant in an upright pot. She then put the pot in a horizontal position and left the plant in the dark for two days. Diagram 3 shows the potted plant after two days in the dark. Plant growing upright Plant put horizontal in the dark Plant after 2 days in the dark Explain fully why the plant responded in this way. ................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................. ................................................................................................................................. (Total 4 marks) Page 14 The King's School Q11.The diaphragm and ribcage move air into the lungs and out of the lungs. The graph shows changes in the volume of the lungs in one breathing cycle. Time in seconds (a) (i) Describe the changes in the volume of the lungs in one breathing cycle. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Explain how the diaphragm and ribcage cause the changes in lung volume shown in the graph. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (3) Page 15 The King's School (b) Sometimes patients are unable to breathe for themselves. Mechanical ventilators are used to make these patients breathe. Photograph 1 shows a patient in an iron lung ventilator. Photograph 1 CDC [Public domain], via Wikimedia Commons Air is pumped out of the iron lung, creating a very low pressure. This low pressure causes the thorax to expand, causing air to flow into the lungs. When air is pumped back into the iron lung the pressure inside the tank increases, causing air to move out of the lungs. Photograph 2 shows a modern ventilator. Photograph 2 By Calleamanecer (Own work) [CC-BY-SA-3.0], via Wikimedia Commons Modern ventilators increase the pressure in the patient’s airways using a tube put into the trachea. The increased pressure in the patient’s airways causes air to flow into the patient’s lungs. Then, the ventilator causes the pressure in the patient’s airways to drop to zero, and the patient breathes out. Page 16 The King's School (i) The ventilators shown in Photographs 1 and 2 make the patient inhale in a very different way. Describe this difference. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) The iron lung ventilator was used mainly in the 1900s. Most patients are now treated with the type of ventilator shown in Photograph 2. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of using the modern ventilator rather than the iron lung ventilator. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 10 marks) Page 17 The King's School Q12. A student‘s breathing was monitored before and after vigorous exercise. The student breathed in and out through a special apparatus. The graphs show the changes in the volume of air inside the apparatus. Each time the student breathed in, the line on the graph dropped. Each time the student breathed out, the line went up. Page 18 The King's School \(a) How many times did the student breathe in per minute: before exercise; ........................................................................................................... after exercise? ............................................................................................................. (1) (b) On each graph, the line A – B shows how much oxygen was used. The rate of oxygen use before exercise was 0.5 dm3 per minute. Calculate the rate of oxygen use after exercise. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Rate of oxygen use after exercise = ................................................. dm3 per minute (2) (c) The breathing rate and the amount of oxygen used were still higher after exercise, even though the student sat down to rest. Why were they still higher? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 7 marks) Page 19 The King's School Q13. Emphysema is a lung disease. (a) The drawings show sections through the lung of a healthy person and through the lung of a person with emphysema. The drawings are drawn to the same scale. Use information from the drawings to answer the questions. What effect does emphysema have on: (i) the thickness of the surface used for gas exchange ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (ii) the total area available for gas exchange? ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Two men did the same amount of exercise. One man was in good health. The other man had emphysema. The results are shown in the table. Man with good health Man with emphysema Oxygen entering blood in dm3 per minute 2.1 1.1 Air flow into lungs in dm3 per minute 90.7 46.0 The man in good health was able to take more oxygen into his blood than the man with emphysema. Page 20 The King's School Calculate how much more oxygen was taken into the blood per minute by the man in good health. Show your working. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... Answer = ....................................................... dm3 per minute (2) (Total 4 marks) Q14. Some students set up the following apparatus. The balances show the same mass at the start of the investigation. After 24 hours the mass of flask B was the same but the mass of flask A had changed. (i) Describe and explain the change to the mass of flask A. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (ii) Why did the students need to set up flask B? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (Total 4 marks) Page 21 The King's School Q15. (a) Complete the equation for photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide + ............................... light energy ............................... + oxygen (2) (b) A farmer grew tomato plants in a greenhouse. The graph shows the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis in the tomato plants growing in the greenhouse. (i) What was the highest rate of photosynthesis? .................................................................. arbitrary units (1) (ii) The farmer wants to increase the rate of photosynthesis in his tomato plants. Apart from light intensity, name one factor that the farmer could change to increase the rate of photosynthesis in his tomato plants. ........................................................................................................................ (1) (Total 5 marks) Page 22 The King's School Q16. Students investigated the effect of changing the carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis in pieces of leaf. Diagram 1 shows the type of leaf used by the students. The students: • cut pieces of leaf from the green region • put the pieces into tubes • added different concentrations of carbon dioxide to each tube • shone lights on the tubes with either high or low light intensity • recorded the concentration of oxygen in the tubes after 5 hours. Diagram 2 shows how each experiment was set up. The graph shows the results of the investigation. Page 23 The King's School (a) (i) Describe the effect of increasing carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis at low light intensity. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain the effect that you have described. In your answer you should refer to limiting factors. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (b) What would have been the effect on oxygen concentration over the five-hour period if a white region of the leaf had been used, instead of a green region? Effect ............................................................................................................. Explain your answer. Explanation .................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) (c) Some people keep indoor plants which have variegated leaves (leaves with green and white regions). If plants with variegated leaves are kept in dim light conditions the white areas of the leaves start to turn green. This is an advantage to the plant. Suggest why. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) (Total 7 marks) Page 24 The King's School Q17. The diagram shows a small part of a lung. (a) The arrow on the diagram shows the movement of oxygen from the air in the alveolus to cell X. Complete the sentences by drawing a ring around the correct answer. platelet (i) Cell X is a red cell white cell (1) diffusion (ii) Oxygen moves from the air in the alveolus into cell X by filtration respiration (1) Page 25 The King's School glycogen (iii) The substance in cell X that combines with oxygen is called haemoglobin lactic acid (1) a cell membrane (iv) Cell X does not have cytoplasm a nucleus (1) (b) On the diagram, draw an arrow to show the movement of carbon dioxide during gas exchange. (1) (Total 5 marks) Q18. Charles Darwin investigated tropisms in plants. Some students did an investigation similar to Darwin’s investigation. The students: • grew seeds until short shoots had grown • used black plastic to cover parts of some of the shoots • put the shoots in light coming from one direction • put boxes over the shoots to keep out other light. Page 26 The King's School The diagrams show how the investigation was set up. Two days later the students took off the black plastic covers and looked at the shoots. The diagrams show the results. (a) Give two variables that the students should control in this investigation. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) (b) Shoot A bent towards the light as it grew. Explain how. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (4) Page 27 The King's School (c) What conclusions can be drawn from the results about: (i) the detection of the light stimulus ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) where in the shoot the response to the light takes place. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (Total 8 marks) Q19.Some students used the apparatus shown in the diagram to measure the rate of water uptake by a plant cutting. The students set up the apparatus in three different conditions: • no wind at 15°C • no wind at 25°C • wind at 25°C For each experiment, the students recorded the movement of the air bubble along the scale. Page 28 The King's School (a) (i) Name the two variables the students chose to change in these experiments. 1 ............................................................................................................... 2 ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) It was important to use the same plant cutting each time to make these experiments fair. Explain why. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (b) The graph shows the students’ results. Time in minutes Which line on the graph, A, B or C, shows the results for each of the three different experiments? Write each of the letters, A, B and C, in the correct boxes in the table. Conditions Letter No wind at 15°C No wind at 25°C Wind at 25°C (2) Page 29 The King's School (c) Water is lost from the leaves of the plant cutting. Name this process. Draw a ring around one answer. distillation respiration transpiration (1) (Total 6 marks) Q20. A student breathed out into an empty breathing bag five times. After breathing out five times the volume of air in the bag was measured. The volume was 3000 cm3. (a) Complete the following sentences. The air the student breathed in would contain more ........................................ than the air the student breathed out. The air the student breathed out would contain more ...................................... than the air the student breathed in. (2) Page 30 The King's School (b) The student then did some exercise for two minutes. The volume breathed out in five breaths was again measured. This time there was 9000 cm3 of air in the bag. What does this tell you about the effect of exercise on breathing? ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (1) (c) (i) Name the chemical process that releases energy when it takes place in the cells of the body. ................................................ (1) (ii) Name the substances produced by this process. .......................................................... and .......................................................... (2) (iii) Explain as fully as you can why this process has to take place more rapidly during exercise. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) Page 31 The King's School M1.(a) A cytoplasm in this order only 1 B (cell) membrane do not accept (cell) wall 1 (b) (i) synapse 1 (ii) (as) chemical accept neurotransmitter or named ignore references to how the chemical is passed do not accept electrical 1 (c) (from light-sensitive cell to connecting neurone) to sensory neurone ignore references to synapses accept ‘nerve cell’ for neuron(e) throughout penalise ‘nerve’ for neurone once only 1 (sensory neurone) to brain / CNS allow (sensory neurone) to relay neurone / spinal cord 1 (brain / CNS) to motor neurone allow (relay neurone / spinal cord) to motor neurone 1 (motor neurone) to (eyelid) muscle ignore effector 1 [8] M2. (a) transpiration 1 (b) (i) 200 correct answer with or without working if answer incorrect: allow 1 mark for 8 × 25 or allow 1 mark for answer from candidate’s count × 25 2 Page 32 The King's School (ii) R allow P or Q if candidate’s answer to (b)(i) nearer to value for one of those do not allow R if the answer to (b)(i) would give an answer of P or Q allow R if (b)(i) is blank 1 (iii) few stomat allow no stomata on upper surface / all stomata on lower surface 1 little / less transpiration or little / less water (vapour) loss / enable water to be retained allow no water loss from upper surface 1 [6] M3.(a) The starch is stored for use later no mark if more than one box is ticked 1 (b) (i) any two from: do not accept temperature apply list principle ignore reference to time • carbon dioxide (concentration) • light intensity • light colour / wavelength allow 1 mark for light if neither intensity or colour are awarded • pH • size / amount of pondweed / plant • same / species / type pondweed • amount of water in the tube ignore amount of water alone 2 Page 33 The King's School (ii) number / amount of bubbles or amount of gas / oxygen allow volume of bubbles (together) ignore ‘the bubbles’ unqualified 1 (relevant reference to) time / named time interval allow how long it bubbles for do not accept time bubbles start / stop ignore speed / rate of bubbling ignore instruments do not accept other factors eg temperature accept how many bubbles per minute for 2 marks 1 (c) (i) temperature allow heat / cold / °C 1 (ii) carbon dioxide / CO2 allow CO2 do not accept CO2 1 [7] M4. (a) a stimulus 1 (b) (i) A 1 (ii) C either order D (iii) 1 E 1 (c) brain allow spinal cord / CNS / central nervous system do not allow spine 1 [6] Page 34 The King's School M5. (a) any three from: • ((mean) mass) increases up to 7 / 8 units (of light) then levels off • light limiting factor up to 7 / 8 units • for photosynthesis must be in correct context • other factor / temperature limiting above 7 / 8 units 3 (b) any two from: • cost of providing conditions / heat / light / CO 2 • effect of treatment on profit allow too much of factor is wasteful • relevant use of data from graph eg limiting factors • named other factors eg fertiliser / pest control / weeds / density of planting allow taste / appearance 2 (c) nitrate function produce amino acids / proteins / enzymes ignore DNA do not allow chlorophyll 1 nitrate deficiency stunted growth allow description ignore plant dies 1 magnesium function produce chlorophyll ignore chloroplasts 1 magnesium deficiency yellow leaves / plant ignore plant dies 1 [9] Page 35 The King's School M6. (a) 21.5 – 22 and 27 – 27.5 for 1 mark 1 (b) ideas of limiting factor / shortage of e.g. light / carbon dioxide / water / chlorophyll each for 1 mark (allow 1 for ‘maximum / optimum rate of enzyme activity if no reference to limiting factors) (ignore denaturation) 2 (c) 21.5 – 22° C (allow first figure from answer to (i) so that no ‘double-penalty but only if this first answer is 20 or greater) maximum rate of photosynthesis / highest / fastest but related to flat part of curve most economical heating / cheapest related to heating must relate to the temperature the candidate has given each for 1 mark 3 [6] M7. (a) brain 1 (b) receptor or sensory or afferent connector or relay 3 effector or motor or efferent (c) any one from blink (of eye) accept a violent movement of a limb from pain or sharp object knee jerk do not credit snatch from cold object or any temperature reference e.g. boiling water accept sneezing, coughing, choking, vomitting, pupil closing or reflex 1 (d) danger or a signal detected (by nerve) Page 36 The King's School or impulse sent 1 goes to or through spine accept impulse by-passes the brain do not award mark if brain mentioned do not credit message to spine 1 a very rapid response occurs or then to effector or muscle or motor accept no thinking time is needed 1 [8] M8. (a) as control(s) ignore fair test 1 (b) the same volume of culture solution 1 (c) plants with all mineral salts grew best 1 plants with mineral salts but no nitrate grow better than without any mineral salts 1 [4] M9.(a) xylem and phloem either order allow words ringed in box allow mis-spelling if unambiguous 1 (b) (i) movement / spreading out of particles / molecules / ions / atoms ignore names of substances / ‘gases’ 1 from high to low concentration accept down concentration gradient ignore ‘along’ / ‘across’ gradient ignore ‘with’ gradient 1 Page 37 The King's School (ii) oxygen / water (vapour) allow O2 / O2 ignore O2/ O allow H2O / H2O ignore H2O 1 [4] M10. gravity accept gravitropism / geotropism 1 caused redistribution of auxin / hormone to lower side of stem 1 these hormones stimulate growth of cells on the lower side of the stem only 1 so the stem grows upwards 1 [4] M11.(a) (i) rise then fall 1 to peak at 0.48 dm3 / after 1.2s 1 (fall) back to 0 / (falling) back after 2.5s allow 2.6s allow after a further 1.3s / 1.4s 1 (ii) rise / air in caused by upward/outward movement of ribcage 1 Page 38 The King's School decrease / air out caused by return of ribcage to original position/downward 1 and (rise / air in) by downward movement / flattening of diaphragmor(decrease / air out) by upward movement / doming of diaphragm ignore contraction and relaxation of muscles ignore reference to pressures, ribcage expanding 1 (b) (i) in iron lung atmospheric / outside pressure forces air into lungs allow air sucked / drawn into lungs 1 in modern respirator air forced (mechanically) into lungs allow for one mark pressures acts externally in iron lung and internally in modern ventilator 1 (ii) advantage any one from: • more freedom of movement for patient • more portable • does not affect blood flow in lower body ignore cost 1 disadvantage any one from: • (tube in trachea) uncomfortable • more difficult to eat / talk allow it can damage / overinflate the lungs / over breathe 1 [10] Page 39 The King's School M12. (a) (before exercise) – 9 to 11 and (after exercise) – 12 or 13 both correct 1 (b) 0.75 to 0.90 ignore working or lack of working eg. 2.35 – 1.55 or for 1 mark or other suitable figures 2 (c) any four from: still need to remove extra carbon dioxide still need to remove heat / to cool (some) anaerobic respiration (in exercise) lactic acid made (in exercise) oxygen needed to break down lactic acid or suitable reference to oxygen debt lactic acid broken down to CO2 and water or lactic acid changed into glucose 4 [7] M13. (a) (i) increased / thick(er) allow more / wide(r) / broad 1 (ii) decreased 1 (b) 1 IGNORE working or lack of working correct figures from table 2.1 and 1.1 but no answer / wrong answer = 1 mark Page 40 The King's School 2 [4] M14. (i) the mass got less accept it got lighter award 1 mark for water was lost from the plant 1 water was taken into the plant or roots absorbed water do not accept soaked into plant 1 and lost through transpiration or the leaves or evaporated from the leaves or stomata 1 (ii) to check the effect of the plant or to act as a control or to show that it was not due to evaporation from water do not accept to keep it fair or to check that it was fair do not accept fair test 1 [4] M15. (a) (LHS) water / H2O allow H2O do not accept H2O 1 (RHS) glucose / sugar / C6H12O6 allow starch / carbohydrate allow C6H12O6 do not accept C6H12O6 1 (b) (i) 210 1 Page 41 The King's School (ii) carbon dioxide / CO2 / CO2 or temperature / heat / warmth do not accept CO2 ignore mineral ions ignore water 1 [5] M16. (a) (i) increase (and then level off) and max / up to at 0.15 (%) (carbon dioxide) ignore references to oxygen concentration only ignore mention of 23 1 (ii) CO2 is limiting at low CO2 / at first ignore specific numbers 1 light is limiting at high CO2 / at end 1 (b) mark both parts together effect: (oxygen) falls 1 explanation: (oxygen) used for respiration if no other marks awarded allow (effect) no change and (explanation) no photosynthesis for 1 mark 1 (c) more chlorophyll / chloroplasts 1 allows more photosynthesis / description for both marks must refer to more at least once 1 [7] Page 42 The King's School M17. (a) (i) red cell 1 (ii) diffusion 1 (iii) haemoglobin 1 (iv) a nucleus 1 (b) (on diagram) arrow from any part of blood to air 1 [5] M18. (a) any two control variables for 1 mark each: • age / size of shoots • species or type of plant / seeds • light intensity accept amount of light / colour of light • (other) named condition eg temperature / water 2 (b) ignore reference to phototropism ref to auxin / hormone 1 unequal (lateral) distribution 1 more hormone on dark side 1 causes growth on dark side 1 (c) (i) (detection) in tip / top / end 1 (ii) (response) behind tip allow at tip / end / top half 1 [8] Page 43 The King's School M19.(a) (i) wind answers in either order 1 temperature ignore weather 1 (ii) different plants have different sizes ignore reference to validity / different numbers of leaves / different sizes of leaves / different plants take up different amounts of water / different number of stomata / different surface area allow different plants need different amounts of water 1 (b) in table, in sequence: C B A all 3 correct = 2 marks 2 correct = 1 mark 0 or 1 correct = 0 marks max 2 (c) transpiration 1 [6] (a) oxygen, carbon dioxide or water (vapour) for 1 mark each 2 (b) idea of more air per breath/deeper breaths for 1 mark 1 (c) (i) respiration for 1 mark Page 44 The King's School 1 (ii) carbon dioxide, water for 1 mark each 2 (iii) more energy required, for increased muscular activity for 1 mark each 2 [8] Page 45