geometry spring
advertisement
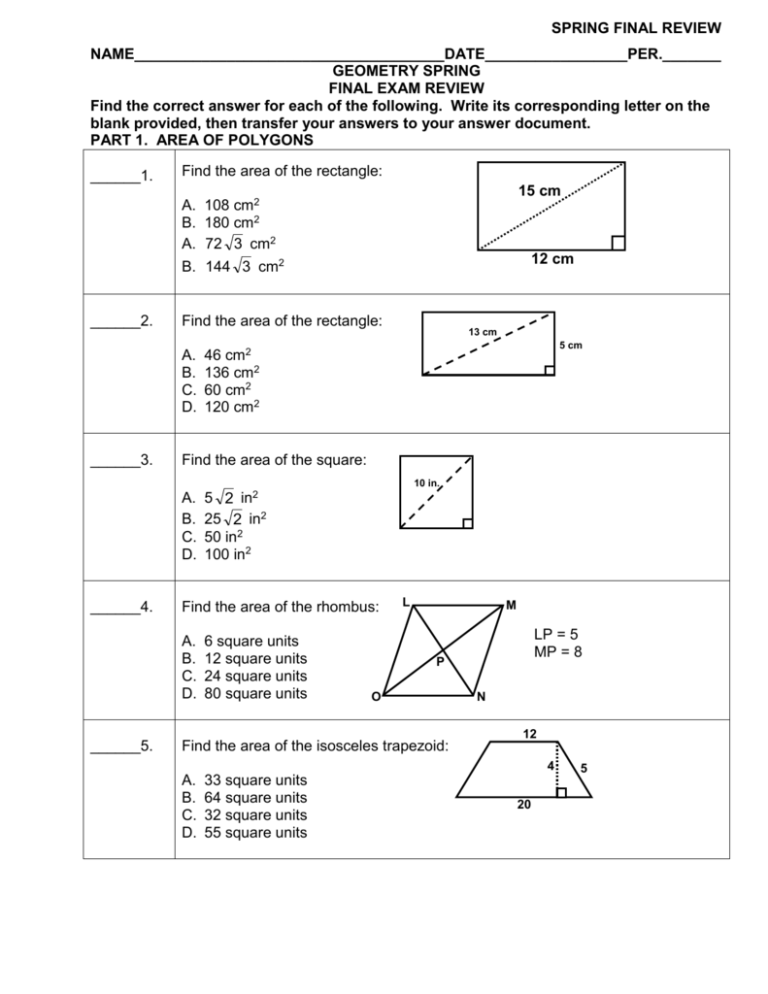
SPRING FINAL REVIEW NAME_____________________________________DATE_________________PER._______ GEOMETRY SPRING FINAL EXAM REVIEW Find the correct answer for each of the following. Write its corresponding letter on the blank provided, then transfer your answers to your answer document. PART 1. AREA OF POLYGONS ______1. Find the area of the rectangle: A. B. A. B. ______2. 12 cm Find the area of the rectangle: A. B. C. D. ______3. 15 cm 108 cm2 180 cm2 72 3 cm2 144 3 cm2 13 cm 5 cm 46 cm2 136 cm2 60 cm2 120 cm2 Find the area of the square: 10 in. A. B. C. D. ______4. Find the area of the rhombus: A. B. C. D. ______5. 5 2 in2 25 2 in2 50 in2 100 in2 6 square units 12 square units 24 square units 80 square units L M LP = 5 MP = 8 P O Find the area of the isosceles trapezoid: N 12 4 A. B. C. D. 33 square units 64 square units 32 square units 55 square units 20 5 SPRING FINALREVIEW; Pg. 2 ______6. The area of a triangle is 243 in2. If both its length and width are reduced to onethird their original length, what would its new area be? A. 81 in2 B. 27 in2 1 2 C. in 3 1 2 D. in 9 ______7. A trapezoid with a height of 8 ft has bases of lengths 14 ft and 12 ft. Find the area of the trapezoid. 12 A. B. C. D. ______8. 8 14 Find the area of the regular polygon with the indicated radius: A. B. C. D. ______9. 104 ft2 52 ft2 208 ft2 1344 ft2 100 in2 25 in2 50 in2 25 2 in2 5 2 in The diagonals of a rhombus are 7 cm and 12 cm long. Find the area of the rhombus. A. B. C. D. 21 cm2 42 cm2 84 cm2 168 cm2 SPRING 2006 FINAL FORM A; Pg. 3 PART 2. AREA & VOLUME OF PRISMS ______10. The isometric drawing shows a three-dimensional figure composed of cubes. Front Which of the following orthogonal views shows the top view of the figure? A. ______11. D. Not Here Rectangular Prism Triangular Prism Rectangular Pyramid Triangular Pyramid The base of a right prism is a square 6 cm on a side. The height of the prism is 10 cm. The volume is _?_ cm3. A. B. C. D. E. ______13. C. Which solid corresponds to the net shown? A. B. C. D. ______12. B. 28 192 768 312 600 8 8 12 Find the volume of a cube whose edge measures 12 inches. A. B. C. D. E. 156 in3 2197 in3 144 in3 39 in3 338 in3 13 13 13 SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 4 The base of a right prism is a right triangle whose legs are 6 feet and 9 feet long. The height of the prism is 15 feet. The lateral area is _?_ ft2. ______14. A. B. C. D. E. 828 648 168 480 576 12 18 9 ______15. A cube has a volume of 54 square centimeters. Find its volume if one of its dimensions were reduced to one-third its original length, a second dimension was reduced to one-ninth its original length, and a third dimension remained unchanged. A. B. C. D. 486 cm2 18 cm2 6 cm2 2 cm2 PART 3. AREA & VOLUME OF PYRAMIDS ______16. Identify the solid formed if this net were folded along the dotted lines to form a 3dimensional figure. A. B. C. D. ______17. Pentagonal Pyramid Pentagonal Prism Hexagonal Pyramid Hexagonal Prism Find the Total Area of the regular triangular pyramid: 24 m (h) A. 672 3 m2 B. 525 3 m2 C. 147 3 m2 D. 42 3 m2 E. 25 m2 ______18. 14 3 m Find the Volume of the square pyramid: A. 8 in3 32 3 B. in 3 C. 16 in3 D. 32 in3 2 2 in 4 in 4 in SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 5 ______19. If the volume of a prism is 360 cubic centimeters. Find its new volume if two dimensions were tripled. A. B. C. D. ______20. 1080 cubic centimeters 2160 cubic centimeters 3240 cubic centimeters 129600 cubic centimeters A pyramid that has four vertices and four faces is a triangular pyramid. TRUE or FALSE PART 4. CIRCLE BASICS ______21. In a given circle, the radius is 41cm. The measure of this circle’s diameter is: A. B. C. D. ______22. 82 cm 41 cm 82 cm 20.5 cm In a given circle, the diameter is 6 m. The circumference of the circle is: A. B. C. D. 3 m 36 m 9 m 6 m Y 23. Name a diameter,Chord, ecant, Tangent and Point of Tangency P X R L ______24. In a given circle, the diameter is 12 ft. The area of the circle is: A. B. C. D. 12 sq ft 6 sq ft 36 sq ft 144 sq ft T S M SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 6 ______25. The radius of a circle is 32 cm. Find the EXACT circumference. A. B. C. D. ______26. 64 cm 16 cm 32 cm 32 cm What is the EXACT area of circle P? A. B. C. D. 56.25 square units 225 square units 15 square units 7.5 square units 9 P 12 ______27. The area of a circle is 32 square units. Find its radius in simplest terms. A. 32 units B. 4 units C. 4 2 units D. 16 units ______28. Find the EXACT area of the circle. A. B. C. D. ______29. 10 in 16 Find the area of the shaded region. A. B. C. D. ______30. 25 square inches 12.5 square inches 50 square inches 100 square inches 256 square units 256 - 64 square units 64 - 256 square units 256 - 16 square units AC is a tangent to Circle D at B. DB is a radius. Find the measure of CBD. A A. B. C. D. 30 60 90 Cannot be determined B D C SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 7 ______31. LN is tangent to circle M. The mLMN = 60 and LN = 8 3 . Find the length of MN. L A. B. C. D. ______32. 8 8 3 16 16 3 N M SR and ST are tangent to circle U. RS = 12x + 2 and TS = 62. Find the value of R ‘x’. S A. B. C. D. ______33. U 60 58 10 5 T 3 Find the perimeter of the quadrilateral. 8 10 A. B. C. D. 25 28 44 42 6 PART 5. CYLINDERS, CONES, & SPHERES ______34. A cylinder has a diameter of 10 and a height of 14 The volume of the cylinder is: A. B. C. D. E. ______35. 350 cubic units 432 cubic units 140 cubic units 288 cubic units None of the above. 10 m 14 m A cylinder has a lateral area of 48 square yards and a height of 6 yards. What is the diameter of the cylinder? A. B. C. D. E. 40 yd 12 yd 8 yd 4 yd 2 yd SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 8 ______36. Find the lateral area of a right cone that has a slant height of 13 and the base has a radius of 5. A. B. C. D. E. ______37. 54 cubic units 96 cubic units 81 cubic units 48 cubic units 60 cubic units 9 4 8 units 6 units 12 units 24 units The diameter of a sphere is 16 cm. Find its total area. A. B. C. D. E. ______40. 5 The lateral area of a right cone is 60. Its slant height is 5. Find the length of the diameter of its base. A. B. C. D. ______39. 13 A cone has a radius of 4 and an altitude of 9. What is its volume? A. B. C. D. E. ______38. 325 square units 65 square units 130 square units 18 square units 60 square units 1024 256 324 162 18 16 m A certain red rubber ball is 12 inches in diameter. Find the volume of the ball. A. B. C. D. E. 36 in3 288 in3 144 in3 27 in3 72 in3 SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 9 ______41. The total area of a sphere is 196. Find its diameter. A. B. C. D. ______42. 14 units 7 units 3.5 units 98 units The volume of a cylinder is 216 cm3. If its dimensions are reduced to one-sixth their original length, by what factor will its volume be affected? A. 6 B. 1 1 C. 6 1 D. 216 PART 6. CENTRAL ANGLES, ARCS, & SECTORS ______43. M In the diagram, the measure of NDM = ? 75 A. B. C. D. ______44. N O D B Given that BA is a diameter, find m CA . A. B. C. D. ______45. 105 265 285 75 73 107 28 58 P (4x – 5) C A (2x+ 17) Find m AB. B A A. B. C. D. 19 26 48 14 (3x) K (2x + 5) (5x + 15) ______46. C Find m AE. E A. B. C. D. 48 132 123 95 D Use for 45 & 46. (AD & EB are diameters) ______47. B A If AC = 13 and CD = 5, then find AB. D A. 24 B. 12 C. 2 194 D. 194 ______48. Find the value of ‘x’. C 20 110 A. 48 B. 46 C. 4 2 D. 6 3 34 12x – 2 46 110 78 120 D ______49. Find AC. A. B. C. D. 7 14 49 Cannot be determined 7 E A O F B C Use the figure below for problems 50. – 55. All answers are rounded to the nearest tenth where necessary. Q ______50. Find the circumference of circle O. A. B. C. D. ______51. O 7 14 49 154 Find the length of MR. A. B. C. D. 3.7 4.4 31.4 6.1 M 30 60 R Find the area of circle O. A. B. C. D. ______52. 14 49 7 14 S OM = 7 SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 11 ______53. Find the area of QOM. A. B. C. D. 98 24.5 35.4 17.7 Q ______54. Find the area of sector QOM. A. B. C. D. ______55. 38.5 153.9 19.6 11 O R Find the area of the shaded region. A. B. C. D. M 30 60 19.6 14 7.1 5.4 S OM = 7 PART 7. CIRCLES & ANGLES Use the figure below for problems 56. – 62. ______56. Find m BC. A. B. C. D. ______57. Find m EF. A. B. C. D. ______58. 40 50 60 30 53 43 23 63 Find m1. A. B. C. D. 120 204 50 102 B A 1 3 G F 5 2 H 4 J C K 6 E D Use for problems 56- 62. F and B are points of tangency. m AB = 60, m CD = 70, m AF = 43, and m ED = 84. AD is a diameter. SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 12 ______59. Find m2. A. B. C. D. ______60. 51.5 90 76.5 43 Find m3. B A A. B. C. D. ______61. 1 90 60 72 12 3 G F 5 2 H Find m4. 4 J C K 6 E A. B. C. D. ______62. Use for problems 56- 62. F and B are points of tangency. m AB = 60, m CD = 70, m AF = 43, and m ED = 84. AD is a diameter. 106 53 50 78 Find the mA. A. B. C. D. ______64. D Find m5. A. B. C. D. ______63. 50 78 77 25 16 33 57 90 (3x + 6) B (6x + 3) C A Find the m1. 1 A. B. C. D. 104 14 284 Cannot be determined 76 SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 13 ______65. Find the value of ‘x’. 11 3 A. B. C. D. ______66. 17 5 11 4 x 3 Find the value of ‘x’. x 2 A. B. C. D. ______67. 2 14 15 28 4 4 12 Find the value of ‘x’. 8 A. B. C. D. 8 10 12 17 x PART 8. VOCABULARY ______68. Which of the following terms describes a segment that joins the center of a polygon and a vertex? A. B. C. D. ______69. Apothem Radius Regular Polygon Side Which of the following terms best describes a segment with both endpoints on the circle? A. B. C. D. chord secant tangent point of tangency SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 14 ______70. Which of the following terms best describes a line or ray that intersects a circle at exactly one point? A. B. C. D. chord diameter secant tangent Which of the following terms best describes a quadrilateral with 4 right angles and ______71. 4 congruent sides E. F. G. H. square diameter regular polygon triangle Which of the following terms best describes a segment connecting the center of a ______72. polygon to the midpoint of a side I. J. K. L. chord diameter apothem tangent line Which of the following terms best describes a dimensional figure with 1 base ______73. M. N. O. P. square pyramid apothem triangle Which of the following terms best describes a dimensional figure with 2 bases ______74. Q. R. S. T. square triangle prism pyramid Which of the following terms best describes lines whose slopes are negative ______75. reciprocals of each other U. chord V. diameter W. secant line X. perpendicular SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 15 Which of the following terms best describes a segment from the center of a circle ______76. to the edge Y. Z. AA. BB. radius diameter apothem secant Which of the following terms best describes a line that touches a circle at only one ______77. point CC. DD. EE. FF. radius diameter secant line tangent line ______78. Which of the following terms best describes a line that touches a circle at 2 points GG. HH. II. JJ. chord diameter secant line tangent line ______79. Which of the following terms best describes a segment inside a circle that touches the edge at 2 points KK. chord LL. vertex MM. secant NN. tangent ______80. Which of the following terms best describes lines with equal slopes OO. PP. QQ. RR. perpendicular secant parallel tangent ______81. Which of the following terms best describes a chord that passes through the center of a circle SS. TT. UU. VV. radius diameter secant apothem SPRING FINAL REVIEW; Pg. 16 ______82. Which of the following terms best describes a polygon with 3 sides WW. XX. YY. ZZ. square pyramid rectangle triangle ______83. Which of the following terms best describes a polygon with 4 sides AAA. BBB. CCC. DDD. vertex triangle quadrilateral perpendicular ______84. Which of the following terms best describes a polygon with all congruent sides and angles EEE. FFF. GGG. HHH. regular polygon triangle prism pyramid ______85. Which of the following terms best describes a corner, where 2 rays meet to form an angle III. JJJ. KKK. LLL. parallel vertex apothem tangent