Graph Matching
advertisement

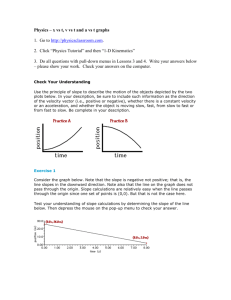
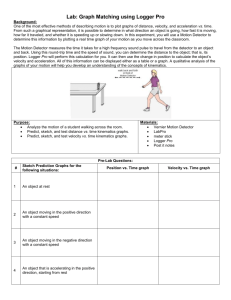
Graph Matching I. On the graph paper provided, sketch the distance vs. time graph for each of the following situations. (Use a coordinate system with the origin at far left and positive distances increasing to the right.) a. b. c. d. An object at rest An object moving in the positive direction with a constant speed An object moving in the negative direction with a constant speed An object that is accelerating in the positive direction, starting from rest II. Now sketch the velocity vs. time graph for each of the situations described above (a-d) in part I. III. Using short strips of masking tape, mark on the floor, an origin and the 1 m, 2 m, and 3 m distances from the Motion Detector. walk back and forth in front of Motion Detector A. Make a graph of your motion when you walk away from the detector with constant velocity. To do this, stand about 1 m from the Motion Detector and have your lab partner push . Walk slowly away from the Motion Detector when you hear it begin to click. After the graph shows on the screen, sketch this graph on the sheet provided (or print). B. Now sketch, on the same graph as (A) what the distance vs. time graph would look like if you were to walk faster. Make sure to label which graph is A and which is B. Check your prediction with the Motion Detector. C. Try to match the shape of each of the distance vs. time graphs that you sketched in part I above by walking in front of the Motion Detector. IV. Now use the Motion Detector and try to match some of the following motion graphs. Your graphs will probably look a little different as you attempt to match the smooth motion of the graphs. Before beginning, describe how you would attempt to generate the graph with motion. Write this description for each graph in the space provided on the back of the graph sheet provided. V. Now using the Motion Detector, try to match the velocity vs. time graphs that were drawn in part II. Before beginning, describe how you would attempt to generate the graph with motion for each of the graphs. Write this description for each graph in the space provided on the back of the graph sheet provided. VI. Now create your own graphs to match by drawing on the graph paper for this section some graphs to attempt to match. Have each student attempt to match the graphs you have created for each other. Analysis 1. What does the slope of a distance vs. time graph represent? 2. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a distance vs. time graph is negative? 3. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a distance vs. time graph is positive? 4. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a distance vs. time graph is zero? 5. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a distance vs. time graph is constant (straight)? 6. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a distance vs. time graph is changing (curved)? 7. What does the slope of a velocity vs. time graph represent? 8. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a velocity vs. time graph is zero? 9. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a velocity vs. time graph is not zero? 10. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a velocity vs. time graph is positive? 11. What type of motion is occurring when the slope of a velocity vs. time graph is negative? Teacher Notes: Part I: Hand out graph paper and have students make graphs (this is conceptually based so no calculations needed) Part II: Sketch part one Part III: A. Play with sensors B. Predict if velocity will increase-determine expected outcome C. Perform test with sensor and determine actual outcome and compare to expected. Part IV: Play with sensors and try to match graphs for position vs. time Part VI: 1. velocity 2. negative velocity=motion moving toward the sensor 3. positive velocity = motion moving away from sensor 4. the object is not moving relative to the motion sensor 5. velocity is constant which equals an upward slope or positive if negative it would have a downward slope 6. non zero acceleration is occurring or just acceleration 7. acceleration 8. constant velocity and zero acceleration 9. accelerated motion; could be positive or negative relative to the motion sensor 10. positive slope for positive acceleration meaning motion is away from the sensor 11. negative slope = acceleration is toward the sensor ** pos. vs. time is the same thing as dis. vs. time where the slope = velocity** **velocity vs. time is acceleration**