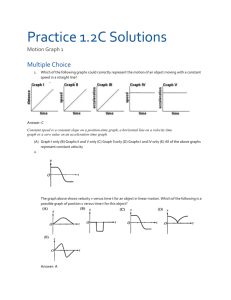
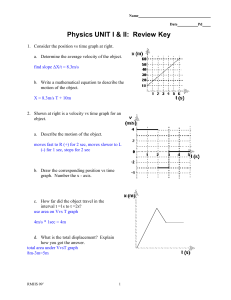
Chapter 11 section 1 Measuring Motion
advertisement
Measuring Motion Chapter 11 What is Motion? • Motion is changing position along a certain path. • In the first part of physical science, we have 2 goals: • To understand how things move (kinematics) • To understand why things move (dynamics) How do things move? • Vocabulary • • • • • • • • Frame of reference Distance Displacement Speed Velocity Slope Acceleration Gravity • As we go through the section, create flashcards for these words. Frame of Reference • A reference point is a starting point… a place that everyone calls zero. • When everyone knows where 0 is, then it is much easier to describe the location or position of objects. • Example: In races, the starting line is 0, or your reference point. Everything is measured from the starting line. Distance vs. Displacement • Distance is the total path an object travels. • Measures how far an object moves along a path. End • Displacement is the line from the beginning to the end. • Measures how far between the starting point and ending point. Start Distance vs. Displacement • You start at your house (0). You go to the store. Then you go to your friend’s house. • What is the distance that you travel? • 8 houses • What is your displacement from the beginning to the end? • 2 houses 0 friend store Speed vs. Velocity • Speed describes how fast an object is moving. • Velocity is an object’s speed in a particular direction. • Ex. Does your car’s speedometer read speed or velocity? • Speed • What could make this a velocity? • If your car also has a compass in it. Variables • Time is shown as a little t. • “t” is measured in seconds, usually. • Sometimes minutes or hours • Distance is shown as a little d or a little x. • “d” or “x” both mean the same thing. • Usually measured in meters • Sometimes kilometers, miles, feet, or inches • Velocity & speed are shown as little v. • “v” is usually measured in m/s • Sometimes mph, km/hr, ft/s Finding speed and velocity • To calculate speed, you need to know 2 things • Distance that an object traveled (in meters) • Time it took to travel that distance (in seconds) Speed = distance time Or Units for speed and velocity: m/s or km/hr or miles/hour Calculating • Examples: • Find the speed of a runner who runs 120m, south in 2 minutes. d = 120m t = 2 min = 120s v = 120m 120s = 1m/s • For velocity, we need to specify direction. • 1m/s, SOUTH • Find the distance a horse travels, who is galloping at 15m/s for 90 seconds. V = 15 m/s 15m/s = d 90s d = 15m/s x 90s d = 1350m t = 90s Problems for you p. 369: practice problems: #1-3 Graphing Motion • To investigate the relationship between distance and time, you can use • Mathematical equations Distance (m) or • Graphs of distance vs. time Time (s) Here is an example of a distance vs. time graph. • What can it tell us? • Where the object was at any time. • How long it took the object to travel a certain distance. • The speed of the object. = SLOPE What is slope? Definition: How steep a line is • In math, to find slope, you have to • Pick 2 points B • A = (5s, 15m) • B = (15s, 45m) • Calculate rise • Change in y = rise • 45m -15m = 30m • Calculate run • Change in x = run • 15s – 5s = 10s • Slope = rise run • 30m 10s = 3m/s A What does the slope mean? • The slope of a distance vs. time graph gives us the velocity. • For the object graphed below, the velocity is 3m/s in the positive direction. Direction from a graph • Line A is in the positive direction, because x is steadily increasing as time increases. • Line C is in the negative direction, because x is steadily decreasing as time increases. • What direction is the object in line B going? • Positive direction A C B What else does this graph tell us? • It tells us • • • • Starting position of each object Ending position of each object Speed and direction of each object Which object is going faster or fastest A C B What else does this graph tell us? • What is B’s speed? 1.33m/s • Who is going faster, A or B? A • How could we tell that without doing the math? because the line of B is not as steep as A’s line A C B • What does a flat horizontal line mean? • Time • Distance • Staying the same • Speed • None. The object is not moving Distance (m) • Increasing Time (s)