Final Exam Phys 111 Fall 2002 Version A Section
advertisement
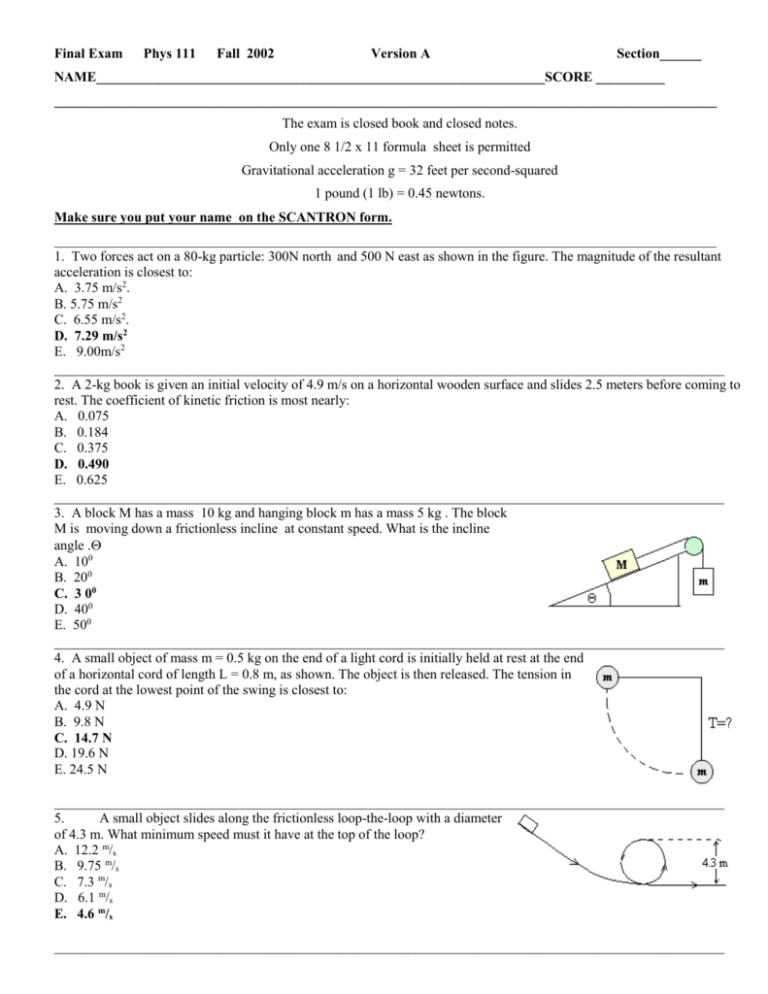
Final Exam Phys 111 Fall 2002 Version A Section______ NAME_________________________________________________________________SCORE __________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ The exam is closed book and closed notes. Only one 8 1/2 x 11 formula sheet is permitted Gravitational acceleration g = 32 feet per second-squared 1 pound (1 lb) = 0.45 newtons. Make sure you put your name on the SCANTRON form. ________________________________________________________________________________________________ 1. Two forces act on a 80-kg particle: 300N north and 500 N east as shown in the figure. The magnitude of the resultant acceleration is closest to: A. 3.75 m/s2. B. 5.75 m/s2 C. 6.55 m/s2. D. 7.29 m/s2 E. 9.00m/s2 _________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. A 2-kg book is given an initial velocity of 4.9 m/s on a horizontal wooden surface and slides 2.5 meters before coming to rest. The coefficient of kinetic friction is most nearly: A. 0.075 B. 0.184 C. 0.375 D. 0.490 E. 0.625 _________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. A block M has a mass 10 kg and hanging block m has a mass 5 kg . The block M is moving down a frictionless incline at constant speed. What is the incline angle . A. 100 B. 200 C. 3 00 D. 400 E. 500 _________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. A small object of mass m = 0.5 kg on the end of a light cord is initially held at rest at the end of a horizontal cord of length L = 0.8 m, as shown. The object is then released. The tension in the cord at the lowest point of the swing is closest to: A. 4.9 N B. 9.8 N C. 14.7 N D. 19.6 N E. 24.5 N _________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. A small object slides along the frictionless loop-the-loop with a diameter of 4.3 m. What minimum speed must it have at the top of the loop? A. 12.2 m/s B. 9.75 m/s C. 7.3 m/s D. 6.1 m/s E. 4.6 m/s _________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. A horizontal force, F, exerted on a body, which weighs 8 N and moves on a horizontal surface at constant speed. The coefficient of friction between the body and the surface is 0.25. The work done by F (in Joules) when the body has moved 12 m is: A. 0 B. 2 C. 10 D. 24 E. 96 __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. A cart of mass m, traveling on a horizontal air track with speed v, collides with a stationary cart of mass 2m. The carts stick together. The impulse exerted by one cart on the other has magnitude: A. 0 B. 2mv/3 C. mv D. 3mv/2 E. 2mv __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. A small object, released from a height of 15 m, slides along the frictionless loop-the-loop with a diameter of 4.3 m. What is its speed at the top of the loop? A. 14.5 m/s B. 9.75 m/s C. 7.3 m/s D. 6.1 m/s E. 4.6 m/s __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. A wheel starts from rest and has an angular acceleration of 4.0 rad/s2 . The time it takes to make 10 revolutions is: A. 0.50 s B. 0.71 s C. 1.4 s D. 1.8 s E. 5.6 s __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Three identical objects of mass M are fastened to a massless rod of length L as shown. The rotational inertia about one end of the rod of this array is: A. B. C. D. E. ML2/2 ML2 3ML2/2 5ML2/4 3ML2 ____________________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. A disk with a rotational inertia of 5.0 kg ×m2 and a radius of 0.25 m rotates on a fixed axis perpendicular to the disk and through its center. A force of 2.0 N is applied tangentially to the rim. As the disk turns through half a revolution the work done by the force is: A. 1.6 J B. 2.5 J C. 6.3 J D. 10 J E. 40 J __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2 12. A 6-kg particle moves to the right at 4 m/s as shown. Its angular momentum in kg ×m2 /s2 about the point O is: A. zero B. 288 C. 144 D. 24 E. 249 __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. A playground merry-go-round has a radius of 3.0 m and a rotational inertia of 600 kg × m2 . It is initially spinning at 0.80 rad/s when a 20-kg child crawls from the center to the rim. When the child reaches the rim the angular velocity of the merry-go-round is: A. 0.61 rad/s B. 0.73 rad/s C. 0.80 rad/s D. 0.89 rad/s E. 1.1 rad/s __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 14. A picture P of weight W is hung by two strings as shown. The total upward pull of the strings on the picture is: A. B. C. D. E. 2 W cos T sin T cos 2T sin 2T cos __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 15. The 150-lb ball shown is suspended on a string AB and rests against the frictionless vertical wall . The string makes an angle of 30° with the wall. The tension in the string is: A. B. C. D. E. 173 lb 520 lb 300 lb 600 lb none of these __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 16. A 100-lb uniform vertical boom is attached to the ceiling by a hinge, as shown. A 200lb weight W and a horizontal guy wire are attached to the lower end of the boom as indicated. The tension T in the horizontal guy wire is: A. 86 lb B. 100 lb C. 172 lb D. 200 lb E. 300 lb __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 3 17. Let M denote the mass of Earth and let R denote its radius. The ratio g/G at Earth's surface is: A. R2/M B. M/R2 C. MR2 D. M/R E. R/M __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 18. The mass of an object: A. is slightly different at different locations on the Earth B. is a vector C. is independent of g D. is the same for all objects of the same size and shape E. can be measured directly and accurately on a spring scale __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 19. A planet is in circular orbit around the Sun. Its distance from the Sun is four times the average distance of Earth from the Sun. The period of this planet, in Earth years, is: A. 4 B. 8 C. 16 D. 64 E. 2.52 __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 20. A particle moves back and forth along the x axis from x = -xm to x = +xm, in simple harmonic motion with period T. At time t = 0 it is at x = -xm. When t = 0.75T: A. it is at x = 0 and is traveling toward x = +xm B. it is at x = 0 and is traveling toward x = -xm C. it is at x = +xm and is at rest D. it is between x = 0 and x = +xm and is traveling toward x = -xm E. it is between x = 0 and x = -xm and is traveling toward x = -xm __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 21. An object attached to one end of a spring makes 20 vibrations in 10 seconds. Its frequency is: A. 2 Hz B. 10 s C. 0.05 Hz D. 2 s E. 0.50 s __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 22. A 0.25-kg block oscillates on the end of the spring with a spring constant of 200 N/m. If the system has a total energy of 6.0 J, then the amplitude of the oscillation is: A. 0.06 m B. 0.17 m C. 0.24 m D. 4.9 m E. 6.9 m __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 23. If the length of a simple pendulum is doubled, its period will: A. halve B. double C. increase by a factor of 2 D. remain the same 2 E. decrease by a factor of __________________________________________________________________________________________________ 4