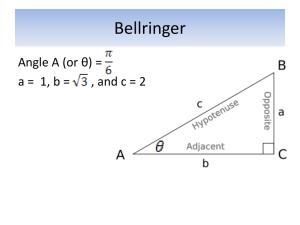
Geometry Definitions (so far)

Geometry Definitions:
Point : An idea of position represented by a dot. It has no dimension (length/width/height). It is named with a capital letter.
Line : A line is a straight arrangement of points extending infinitely in both directions. It is represented by an arrow
↔
.
It has only one dimension; length. It is named by stating two points on the line.
Plane : A flat surface extending infinitely in all directions. It has two dimensions; length and width.
Collinear Points : Points that lie on the same line.
Coplanar Points : Points that lie on the same plane.
Space : The set of all points in 3-D form. Note: it takes a minimum of 4 points to create 3-D form.
Line Segment : Part of a line. It consists of two points and all points in between them. It is represented with a line
—
above two points on the line.
End Points : Two points that determine a line segment.
Ray : Part of a line from one endpoint extending infinitely in one direction. It is represented with an arrow → above an endpoint and another point on the line.
Angle : Two rays that share a common endpoint.
Vertex : The common endpoint of the two rays which form an angle.
Sides : Any of the two rays that form an angle.
Congruent : The exact same size and shape.
Similar : The exact same shape.
Inductive: Reasoning from the specific to the general.
Deductive: Reasoning from the general to the specific.
Right Angle: An angle that equals 90 degrees.
Acute Angle: An angle that is less than 90 degrees.
Obtuse Angle: An angle greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
Straight Angle: An angle that equals 180 degrees (a straight line).
Midpoint of a Segment: A point which divides a line segment into two equal parts.
Angle Bisector: A line or line segment that divides an angle into two equal parts.
Parallel Lines: Lines in the same plane that never intersect.
Perpendicular Lines: Intersecting lines that form a right angle.
Complementary Angles: Angles that add-up to 90 degrees.
Supplementary Angles: Angles that add-up to 180 degrees.
Vertical Angles: Angles that are opposite each other.
Linear Pair of Angles: Angles next to each other (adjacent) that
add-up to 180 degrees.
Adjacent Angles: Angles that are next to each other. They share a
vertex and a ray.
Skew Lines: Lines that are not in the same plane and do not intersect.
Polygon: A closed figure in a plane with 3 or more connected straight lines.
Convex Polygon: A polygon whose vertices, when connected, remain within the figure.
Concave Polygon: A polygon whose vertices, when connected, reside outside the figure.
Perimeter: The sum of the lengths of the sides of a figure.
Equilateral Polygon: A polygon with all sides of equal length.
Equiangular Polygon: A polygon with all angles equal.
Regular Polygon: A polygon with all sides and angles equal.
Right Triangle: A triangle with one right angle (90 degree angle).
Acute Triangle: A triangle with all acute angles (all angles less than 90 degrees.)
Obtuse Triangle: A triangle with all obtuse angles (all angles greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.)
Equiangular Triangle: A triangle with all angles equal (60 degrees).
Isosceles Triangle: A triangle with 2 equal sides.
Scalene Triangle: A triangle with no equal sides.
Equilateral Triangular: A triangle with all equal sides.
Median of a Triangle: A line segment that starts from a vertex and bisects the base angle into 2 congruent parts.
Altitude of a Triangle: A line segment that starts from a vertex and intersects the base angle at a right angle (90 degree intersection).
This is the height of a triangle.
Quadrilateral : A polygon with four sides.
Trapezoid : A quadrilateral with one pair of opposite sides parallel.
Kite : A quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides that are congruent.
Parallelogram : A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides.
Rhombus : A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and congruent and no right angles (a tilted square).
Rectangle : A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and congruent and all right angles
Square: a quadrilateral with four congruent sides and four congruent 90 degree angles.
Transformations: Operations that alter the form of a figure.
Reflections: A transformation in which a geometric figure is reflected across a line , creating a mirror image. That line is called the axis of reflection.
Translations: A transformation in which a graph or geometric figure is picked up and moved to another location without any change in size or orientation.
Rotations: A transformation in which a plane figure turns around a fixed centerpoint. In other words, one point on the plane, the center of rotation, is fixed and everything else on the plane rotates about that point by a given angle.
Symmetry: “the same measure” Describes a geometric figure consisting of two parts that are congruent to each other.