ch21
advertisement
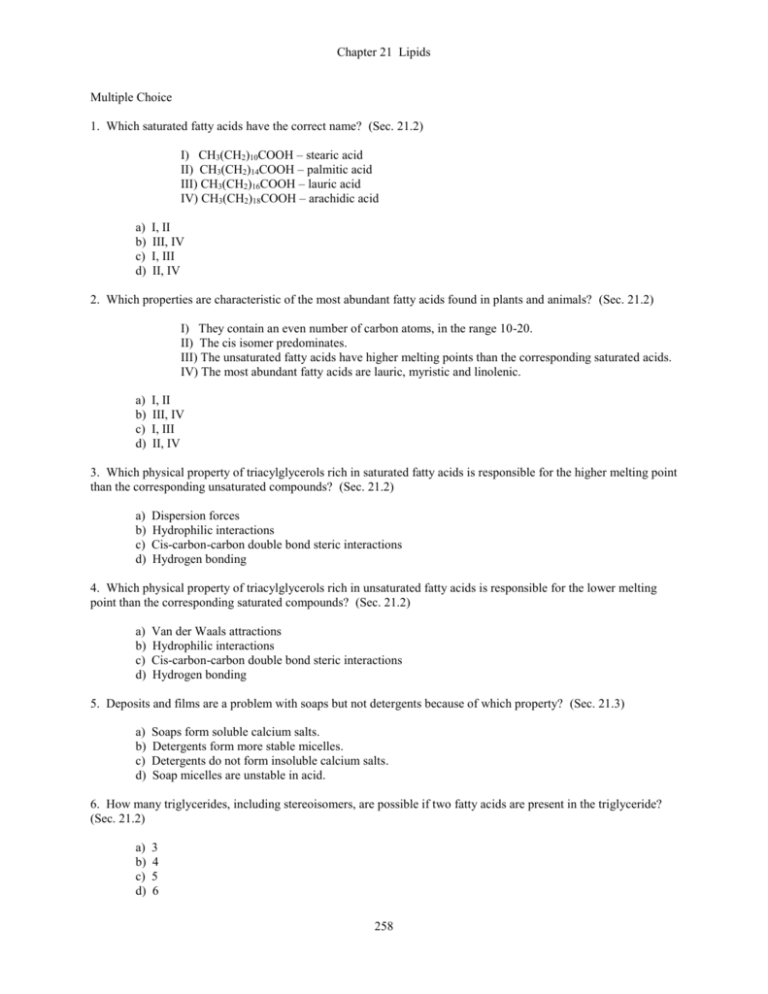
Chapter 21 Lipids Multiple Choice 1. Which saturated fatty acids have the correct name? (Sec. 21.2) I) CH3(CH2)10COOH – stearic acid II) CH3(CH2)14COOH – palmitic acid III) CH3(CH2)16COOH – lauric acid IV) CH3(CH2)18COOH – arachidic acid a) b) c) d) I, II III, IV I, III II, IV 2. Which properties are characteristic of the most abundant fatty acids found in plants and animals? (Sec. 21.2) I) They contain an even number of carbon atoms, in the range 10-20. II) The cis isomer predominates. III) The unsaturated fatty acids have higher melting points than the corresponding saturated acids. IV) The most abundant fatty acids are lauric, myristic and linolenic. a) b) c) d) I, II III, IV I, III II, IV 3. Which physical property of triacylglycerols rich in saturated fatty acids is responsible for the higher melting point than the corresponding unsaturated compounds? (Sec. 21.2) a) b) c) d) Dispersion forces Hydrophilic interactions Cis-carbon-carbon double bond steric interactions Hydrogen bonding 4. Which physical property of triacylglycerols rich in unsaturated fatty acids is responsible for the lower melting point than the corresponding saturated compounds? (Sec. 21.2) a) b) c) d) Van der Waals attractions Hydrophilic interactions Cis-carbon-carbon double bond steric interactions Hydrogen bonding 5. Deposits and films are a problem with soaps but not detergents because of which property? (Sec. 21.3) a) b) c) d) Soaps form soluble calcium salts. Detergents form more stable micelles. Detergents do not form insoluble calcium salts. Soap micelles are unstable in acid. 6. How many triglycerides, including stereoisomers, are possible if two fatty acids are present in the triglyceride? (Sec. 21.2) a) b) c) d) 3 4 5 6 258 Chapter 21 Lipids 7. Which natural products have structures derived from cholesterol? (Sec. 21.5, 21.7) I) vitamin A II) vitamin D III) cholic acid IV) cortisone V) squalene a) b) c) d) I, II, III II, III, IV III, IV, V I, III, V 8. Which is not a characteristic group in phospholipids? (Sec. 21.4) a) b) c) d) phosphate esters fatty acid esters glycerides polyamides 9. Which property of phospholipids accounts for their ability to form micelles? (Sec. 21.4) a) b) c) d) nonpolarity unsaturation hydrophilicity and lipophilicity lipophilicity 10. Which property of phospholipids accounts for their ability to form fluid membranes? (Sec. 21.4) a) b) c) d) nonpolarity unsaturation hydrophilicity and lipophilicity lipophilicity 259 Chapter 21 Lipids 11. Which is the structure of a phosphatidyl choline? (Sec. 21.4) O H2C O O O a) H2NCH2CH2 O (CH2 )16CH3 O (CH2 )14CH3 HC O H2C O O P O CH2 O HC O + COO c) NH3 CH CH2 O P O CH2 O (CH2 )16CH3 (CH2 )14CH3 O O H2C O O + b) (CH3 )3NCH2CH2 O O HC O (CH2 )16CH3 (CH2 )14CH3 O P O CH2 O H2C O O OH O HO HO d) O HO OH HC O (CH2 )16CH3 (CH2 )14CH3 P O CH2 O 12. The fluid-mosaic model of the lipid bilayer states; (Sec. 21.4) a) lipids coexist side by side as discreet units and proteins float in the bilayer, able to move along the plane of the membrane. b) the lipids form new covalent bonds between chains and lock the proteins into position, much like a mosaic tile. c) the lipids form a fluid-like membrane that metabolic components (the mosaic) can freely cross. d) the lipid bilayer forms a rigid structure with channels that allow fluid to pass. 13. Which are the most common fatty acids found in phospholipids? (Sec. 21.4) a) b) c) d) palmioleic, stearic, lauric lauric, myristic, palmitic palmitic, stearic, oleic stearic arachidic, oleic 260 Chapter 21 Lipids 14. Which is the number of stereocenters in methandrostenolone? (Sec. 21.5) OH CH3 CH3 CH3 H H O a) b) c) d) 4 6 8 10 15. Which reagents could be used to harden an oil to a fat? (Sec. 21.3) a) b) c) d) NaBH4 / H2O Ni / H2 Ag(NH3)2+ / H2O Cu2+ / buffer 16. Which common structural feature of vitamin E and vitamin K 1 best accounts for the greater solubility of these molecules in organic solvent than water? (Sec. 21.7) O CH3 O CH3 vitamin K1 HO H3C O CH3 CH3 vitamin E a) b) c) d) aromatic rings oxygen atoms 4 isoprene units a quinone / hydroquinone units 261 Chapter 21 Lipids 17. Which is a prostaglandin? (Sec. 21.6) CH3 CH3 CH3 HO CH2OH a) COOH b) CH3 CH3 HO HO H O CCH2OH CH3 OH HO CH3 c) H H H d) O HO 18. Which structure is vitamin A? (Sec. 21.7) CH3 CH3 CH3 HO CH2OH a) COOH b) CH3 CH3 HO HO O CCH2OH CH3 OH HO CH3 c) H H H d) O HO 262 H Chapter 21 Lipids 19. Which structure is a cortisone? (Sec. 21.5) CH3 CH3 CH3 HO CH2OH a) COOH b) CH3 CH3 HO HO H O CCH2OH CH3 OH HO CH3 c) H H H d) O HO 20. Fats, oils, phospholipids, prostaglandins and steroids have which properties in common? (Sec. 21.1) I) oxygen functionality II) nonpolar groups III) rings IV) unsaturation a) b) c) d) I, II III, IV I, III II, IV 263 Chapter 21 Lipids 21. Which is the best description of the first step (A) of the biosynthesis of prostaglandin? (Sec. 21.6) COOH A O COOH O OOH a) b) c) d) hydration reduction oxidation Claisen condensation 22. Which is the best description of the second step (B) of the biosynthesis of prostaglandins? (Sec. 21.6) O COOH O OOH B O COOH O OH a) b) c) d) hydration reduction oxidation Claisen condensation 264 Chapter 21 Lipids 23. Which statements about steroids are false? (Sec. 21.5) I) The fusion of all rings is cis. II) Sex hormones, adrenocorticoid hormones, bile acids and vitamin D are derived from cholesterol. III) The biosynthesis of cholesterol produces several isomers. IV) Steroids are tetracyclic ring systems a) b) c) d) I, III II, IV I, II III, IV 24. Which statements about vitamins are true? (Sec. 21.7) I) Vitamins A, D, E and K are fat soluble. II) Vitamins A, D, E and K are derived from cholesterol. III) Vitamins A, D, E and K each contain 4 isoprene units. IV) Vitamins A, D, E and K have distinct physiological activities. a) b) c) d) II, III III, IV I, III I, IV 25. The key step in the preparation of soap, saponification, is best described by which mechanism? (Sec. 21.3) a) b) c) d) base catalyzed acyl addition electrophilic addition acid catalyzed acyl substitution base catalyzed acyl substitution Fill in the Blank 1. The melting point order of the following fatty acids is (lowest to highest), lauric (12:0) _______ palmitic (16:0) _______ palmitoleic (16:1) _______ oleic (18:1) ______ (Sec. 21.2) 2. The lower melting point of unsaturated fatty acids compared to saturated fatty acids is due to ______________________________ differences. (Sec. 21.2) 265 Chapter 21 Lipids 3. Complete the reaction below by providing the missing products. (Sec. 21.3) O H2C O O 3NaOH, H2O (CH2 )7 C C H H HC O H2C (CH2 )14CH3 O H2C OH HC OH (CH2 )7CH3 H2C (CH2 )16CH3 + OH O 4. Complete the structure of the alkylbenzene sulfonate detergent below. (Sec. 21.3) CH3 (CH2 )12CH2 5. Complete the structure of the phospholipid below. (Sec. 21.4) O H2C O O O HC O (CH2)16CH3 (CH2)14CH3 P O CH2 O 6. The forces which drive bilayer formation by phospholipids are __________________ and ________________. (Sec. 21.4) 7. Androsterone has ________ stereocenters and ____________ possible stereoisomers. (Sec. 21.5) CH3 O CH3 H H H HO 8. Vitamin A precursor -carotene belongs to the _____________ class of compounds and contains ________ isoprene units. (Sec. 21.7) 9. Prostaglandin is a member of the _________________ class of compounds, which are synthesized from ____________________. (Sec. 21.6) 10. Vitamins A, D, E, and K are included in the lipid class because they are _______ soluble. (Sec. 21.7) 266 Chapter 21 Lipids True-False 1. Stearic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid. (Sec. 21.2) 2. Human fat has more unsaturated fatty acids than plant fats. (Sec. 21.2) 3. Soaps and detergents form micelles when added to water. (Sec. 21.3) 4. Soap micelles form in water by aggregating the negatively charged carboxylate groups toward the inside and the lipophilic carbon chains toward the outside of the micelle. (Sec. 21.3) 5. The forces that drive micelle and lipid bilayer formation are the same. (Sec. 21.4) 6. There are several stereoisomers of cholesterol found in living systems. (Sec. 21.5) 7. Aldosterone is an androgen. (Sec. 21.5) 8. Vitamin D precursors have the cholesterol ring system. (Sec. 21.7) 9. Vitamin E is required for blood clotting. (Sec. 21.7) 10. Prostaglandins are involved with the inflammatory response. (Sec. 21.6) 267 Chapter 21 Lipids Answers Multiple Choice 1. d 2. a 3. a 4. c 5. c 6. d 7. b 8. d 9. c 10. c 11. b 12. a 13. c 14. b 15. b 16. c 17. b 18. a 19. c 20. a 21. c 22. b 23. a 24. d 25. d Fill in the Blank 1. 3, 4, 1, 2 2. Conformational 3. O -O (CH2 )14CH3 O -O (CH2 )7 C C H H -O (CH2 )16CH3 (CH2 )7CH3 O 4. CH3 (CH2 )12CH2 _ SO3 268 Chapter 21 Lipids 5. O (CH2)16CH3 H2C O O O H2NCH2CH2O (CH2)14CH3 HC O P O CH2 O O or H2C O O O (CH3)3NCH2CH2O (CH2)16CH3 (CH2)14CH3 HC O P O CH2 O O or H2C O O _ O OOC C C O + NH3 H H2 (CH2)16CH3 (CH2)14CH3 HC O P O CH2 O O or H2C O O OH HO HO OH O OH O (CH2)14CH3 HC O P O CH2 O 6. hydrophobic and electrostatic 7. 7, 128 8. terpene, 8 9. eicosanoid, arachidonic acid 10. fat or low polarity organic True-False 1. 2. 3. 4. (CH2)16CH3 F F T F 269 Chapter 21 Lipids 5. T 6. F 7. F 8. T 9. F 10. T 270