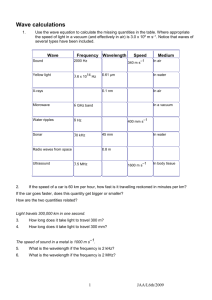
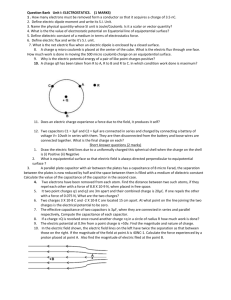
Year 9 waves - Erina High School
advertisement

Devonshire 2006 Year 9 waves School Certificate answers 1. X-rays are a high energy form of electromagnetic radiation. To use them for X-ray photography a sheet of photographic film is placed under the body part. X-rays are fired at the body part from above. The X-rays easily penetrate and pass straight through the less dense skin, muscle and fat of the body part, bones (being denser) allow less X-rays to pass and metal implants (being very dense) allow no X-rays to pass through them. Any X-rays that pass through and contact the photographic film develop the film so it appears dark coloured. Film not exposed to the X-rays remains white coloured. A is the answer. 2. C. An example of absorption occurs when sunlight strikes an object that we see as black. No light is reflected of the object, all the light is absorbed by the object and converted into heat energy (black objects heat up most in sunlight). Interference in light is a little more difficult to explain however, in water waves often interfere with each other. A wave bouncing off the shore and heading back out to sea will run into a wave coming towards the shore. The two waves will interfere with each other. As the two crest meet they combine to produce a double sized wave. As they continue in their different directions, the crest of one meets the trough of the other. At this point the waves combine to cancel each other out, the wave goes flat. Scattering of light can be observed with our eyes. Visible light reaching the Earth is made up of the colours of the rainbow, when it strikes an uneven surface the various colours are reflected in different random directions. Our eyes detect this scattering of light as ‘white’ light, the object appears white. In the atmosphere gas particles happen to scatter blue light more than the other colours, so we see the sky as blue. Red skies appear in the early evening or early morning when the sun is low in the sky. The light has to pass through the atmosphere at a low angle closer to dust and pollution. The dust or pollution scatters red light most. 3. All electromagnetic radiation travels at the speed of light (300 000km/s) in a vacuum (the emptiness of space is close enough to a vacuum). EM radiation includes gamma rays, X rays, UV rays, visible light, infrared, microwaves, TV, radio waves. Light will slowdown by a very tiny amount if it has to move through a substance; the more dense the substance, the slower the speed of light. This fact is what results in light changing its direction when moving from air to water or from air to glass, known as refraction. A is the correct answer. 4. In diagram 1 on the wavelength scale, 103 means 1000m (big wavelength), whereas 10-13 means 0.0000000000001m (small wavelength). A is the correct answer. Devonshire 2006 5. To answer this you need to be reasonably good at maths ratio type questions. On wave Q the wavelength from W to X is given as 60m, on the screen it measures 18mm. On wave R the wavelength from Y to Z is unknown (?), on the screen it measures 12mm So, ? = 60 12 18 ? = 60 X 12 18 = 40 The answer is C 6. Wave Q has a wavelength of 60m and this can be rewritten as 6 X 101m. Look at Diagram 1 and wavelengths of 101m are radio waves, B 7. The shorter the wavelength of EM radiation, the more the energy it carries. All EM waves travel at the constant speed of light and therefore are not accelerating. Frequency refers to how many waves pass a point per second so in this case R would have the greater frequency. Q definitely has a longer wavelength than R so D is the answer. 8. There is a faster time for sound travelling in shallow water because it has less distance to travel! So A and B are incorrect. From the data, the sound travels further in salt water than fresh water over the same time period so D is the correct answer. 9. In fresh water the sound wave travels 6.8m in 0.01s. So in 0.04s it will travel 6.8 X 4 = 27.2m. B is the best answer. 10. The speed of light in air is 300 000 000 m/s. The speed of sound in air is 340 m/s B is the answer. 11. William appears to be about twice as far from the storm as the other 3 people so the time should be twice as long to here the thunder, D 12. The storm is moving towards Quentin which is half way between north and west, north-west, B 13. Frequency is how many waves pass a point each second. Increased frequency should show more waves. The amplitude (height of the wave) should not change. A 14. Energy 15. Wavelength 16. Infrared 17. Frequency