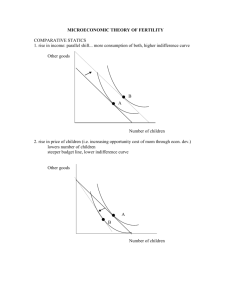
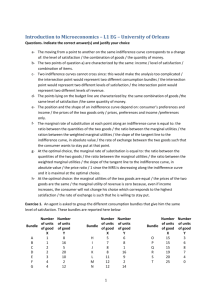
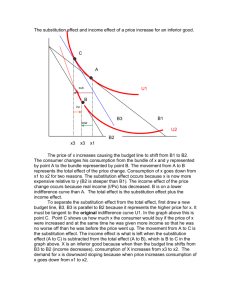
2003
advertisement

Exercise 1 : Suppose a production function is given by f ( K , L) K 1/ 2 L1/ 2 ,the price of capital is $10 and the price of labor is $16. 1. Does the technology exhibits increasing, decreasing or constant return to scale? Answer: Constant return to scale. 2. What is the marginal product of capital? of labor? What is the Marginal rate of technical substitution? MPL K 1 1/ 2 1/ 2 1 L K , MPK K 1/ 2 L1/ 2 , MRTS 2 2 MPK L 3. The capital is fixed at the level K 4 . Is it long run or short run Answer: MPL analysis? (a) What is the quantity of labor that minimizes the cost of producing any given input? Answer: q 41/ 2 L1/ 2 2 L1/ 2 q L q2 4 (b) What is the minimum cost of producing q units of output (long-run)? Answer: cos t 10 4 16 q2 40 4q 2 4 4. What will be the long run optimal bundle to produce a given output? And compare the long-run cost with the short-run cost? Answer: MRTS w K 10 , then substitute this equation into the r L 16 production function, and you can solve out optimal input for labor and capital. Put optimal labor and capital into the cost function, then we get the long-run cost function. Exercise 2 : Mary consumes only apples and chocolate. Fortunately she likes both goods. The consumption bundle where Mary consumes x1 units of apples per week and x2 units of chocolate per week is written as ( x1 , x2 ) . The preferences of Mary are represented with the following utility function U ( x1 , x2 ) x12 x2 . 1. On a graph plot several points that lie on the indifference curve that passes through the point (1, 4), and sketch this curve. What is the level of utility that corresponds to this indifference curve? What is the equation of the indifference curve? Do the same with the indifference curve that passes through the point (2, 6). What is the level of utility? What is the equation of the indifference curve? 2. Use pencil to shade in the set of commodity bundles that Mary prefers to the bundle (1, 4). Use red ink to shade in the set of all commodity bundles (x1, x2) such that Mary prefers (2, 6) to these bundles. 3. Determine the marginal rate of substitution, MRS(x1, x2). Give the economic definition of the marginal rate of substitution. (a) What is the slope of Mary’s indifference curve at the point (1, 4)? (b) What is the slope of her indifference curve at the point (2, 6)? (c) What is the slope of his indifference curve at the point (2, 1)? and at the point (1, 24)? (d) Do the indifference curves you have drawn for Mary exhibit diminishing marginal rate of substitution? Explain. 4. Suppose that the price of each good is 2 and the income of Mary is 20. Draw her budget line. 5. What is the optimal bundle? At this optimal bundle, what is the level of utility of Mary? 6. What happens to the optimal bundle if price of x1 increases? Decompose the price effect into substitution effect and income effect graphically. ANSWER: 1. The level of utility that corresponds to this indifference curve that passes through the point (1, 4) is U(1, 4) = 1 ×4 = 4. The equation of the indifference curve is x2 4 / x12 . The level of utility that corresponds to this indifference curve that passes through the point (2, 6) is U(2, 6) = 2 2 × 6 = 24. The equation of the indifference curve is x2 24 / x12 . 2. GRAPH. The set of commodity bundles that Mary prefers to the bundle (1, 4) is on the right of the IC of equation x2 4 / x12 . The set of all commodity bundles (x1, x2) such that Mary prefers (2, 6) to these bundles is on the left of the IC of equation x2 24 / x12 . 3. MRS x2 forx1 MU x1 MU x2 2 x1 x2 2x 2 2 x1 x1 (a) The slope of Mary’s indifference curve at the point (1, 4) is MRS(1, 4) =-8. (b) The slope of her indifference curve at the point (2, 6) is MRS(2, 6) = -6. (c) The slope of his indifference curve at the point (2, 1) is MRS(2, 1) =-1 and at the point (1, 24) is MRS(1, 24) =-48. (d) The indifference curves you have drawn for Mary exhibit diminishing marginal rate of substitution as along the same IC of equation x2 4 / x12 , the MRS is decreasing: at the point (1, 4) it is -8 and at (2, 1) it is -1. Same along the IC x2 24 / x12 : the MRS is decreasing: at (1, 24) it is -48 and at the point (2, 6) it is -6. 4. p1 p2 2 and m = 20. The budget line is 2 x1 2 x2 20 or equivalently x2 10 x1 . 5. At the optimal bundle, the MRS x2 forx1 p1 2x 2 . So 2 , p2 x1 2 i.e., x1 2 x2 .Plug that into budget constraint, we can solve out x1 20 10 , x2 3 3 . Thus the level of utility of Mary is U ( x1 , x2 ) 148.15 .