Results
advertisement

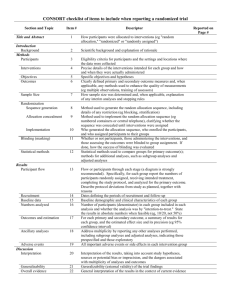
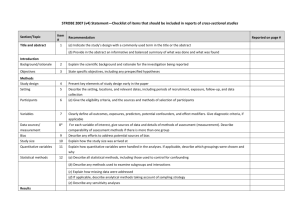
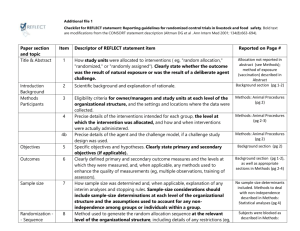
Results Summarizes data collected and the statistical treatment used report data in sufficient detail to justify conclusions mention all relevant results, including those that run counter to the hypothesis no raw data unless used one or a few subjects don’t discuss implications of results tables and figures are included here Statistical presentation when reporting inferential statistics (e.g., t tests, F tests and chi-square), include information such as: the obtained magnitude or value of the test statistic degrees of freedom probability of obtaining a value as extreme (or more) than the one obtained direction of effect include descriptive statistics (e.g., per-cell sample size, means, correlations, standard deviations) so nature of effect can be understood recommends use of confidence intervals, generally one (e.g., a 95% or 99%) throughout course of paper Informationally adequate statistics 1. For parametric tests of location (generally) use cell means, cell sample sizes, and a measure of variability. 2. For randomized-block layouts, repeated measures designs, and multivariate analyses of variance, vectors of cell means and cell sample sizes, along with the pooled within-cell variance-covariance matrix 3. For correlational analyses, sample size and variance-covariance (or correlation) matrix, with other information specific to procedure 4. For nonparametric analyses, various summaries of raw data Statistical power (likelihood of correctly of rejecting the tested hypotheses, given a particular alpha level, effect size, and sample size.) Provide evidence that your study has sufficient power to detect effects of substantive interest Statistical significance, in general recommends reporting the exact probability (p value). Effect size and strength of relationship, should include some index of effect size or strength of relationship which can be estimated with a number of common effect size estimates. General rule is to provide reader with enough information to access the magnitude of the observed effect or relationship Mike