Unit 3 Curriculum map template-Physical Science (Repaired) 2013

Lafayette Parish School System
2013-2014 Curriculum Map
Physical Science: Unit 3:
Waves
Time Frame:-3 weeks-January 7 – January 24, 2014
Unit Description and Student Understandings :
This unit thoroughly examines the properties of waves, including visible light and the electromagnetic spectrum and sound. Two activities in this unit provide earth science-based applications of physical science principles. These activities could also be completed along with activities of Unit 9, which is dedicated to earth science applications. Incorporating inquiry processes, students will examine and identify properties of waves as they relate to light and sound. The electromagnetic spectrum will be analyzed, and connections will be made among the phenomena of light, electricity, and magnetism. Students will be able to identify and explain the Doppler Effect .
Guiding Questions:
1.
Can student classify matter based on observable and measurable properties?
2.
Can student differentiate the types of mixtures?
3.
Can student describe how stated factors affect rate of dissolving?
4.
Can student utilize the kinetic molecular theory to describe the properties and structure of the different states of matter?
5.
Can students identify how thermal energy is transferred?
6.
Can student describe the behavior of matter during phase changes?
7.
Can student classify changes as chemical or physical?
8.
Key Concepts:
Waves travel through matters as energy is transferred from particle to particle.
Wave properties depend on the vibrations of the wave source and the material in which the wave travels
Waves interact with matter and with each other
Sounds waves are longitudinal waves that travel only through matter
The loudness of a sound depends on its intensity, and the pitch of a sound depends on its frequency
A musical instrument produces combinations of frequencies that determine how the instrument sounds
Sound waves are used to locate objects, to form images, and to treat medical problems
Vibrating electric charges produce electromagnetic waves
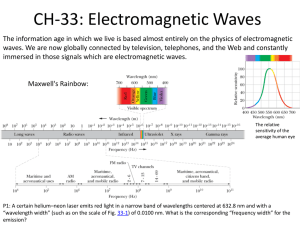
The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into several sections, each with certain range of frequencies and specific properties
Materials can absorb, transmit, or reflect light waves
Light waves of different wavelengths or combinations of wavelengths cause the human eye to detect different colors
Heating a filament and passing a current through a gas are common ways of producing light
Light can be used to form three-dimensional images and to transmit information in optical fibers
Mirrors from images by reflecting light rays
1
Physical Science 2013-2014
Lafayette Parish School System
2013-2014 Curriculum Map
Physical Science: Unit 3:
Waves
Time Frame:-3 weeks-January 7 – January 24, 2014
Vocabulary List:
Wave, longitudinal wave, medium, mechanical wave, transverse wave, crest, trough, compression, rarefaction, wavelength, frequency, period, amplitude, refraction, diffraction, interference, standing wave, node, resonance, eardrum, cochlea, intensity, loudness, decibel, pitch, Doppler effect, music, sound quality, overtone, resonator, acoustics, echolocation, sonar, ultrasound, electromagnetic wave, photon, radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves X-rays, gamma rays. Carrier wave, modulation, analog signal, digital signal, transceiver, Global
Positioning System (GPS), opaque, translucent, transparent, index of refraction, mirage, filter, pigment, incandescent light, fluorescent light, coherent light, incoherent light, linearly polarized light, holography, total internal reflection, optical scanner,plane mirror, virtual image, concave mirror, optical axis, focal point, focal length, real image, convex mirror
GLEs
CCSS Literacy
Standards
NGSS Practices
Instructional Strategies
(Activity directions are found in the Unit folder in Environmental
Science documents on LPSS Blackboard)
Differentiation
(Enrichment/Remediation Strategies)
SI-5 (E)
Utilize mathematics, organizational tools, and graphing skills to solve problems
(SI-H-A3)
Glencoe Textbook Correlations—Unit 3
Chapter 9- Introduction to Waves—pp. 272---303
Chapter 10- Sound---pp. 304---335
Chapter 11—Electromagnetic Waves—pp. 336—365
Chapter 12-Light—pp. 366—397
Chapter 13—Mirrors and Lenses—pp. 398--427
Focus: How we perceive waves in our lives
Students will learn about the types of waves, wave anatomy, and the properties of waves.
Video(s)
Teacher Demonstration
vocabulary self-awareness chart ( view literacy strategy descriptions ) science learning logs ( view literacy strategy descriptions ). http://www.bro.lsu.edu/radio/Classroom/cla ssroom.html
.
Instructions on how to make and use spectroscopes can be found at http://asdwww.larc.nasa.gov/edu_act/simple_spec.h
tml http://scitoys.com/scitoys/scitoys/light/cd_spectros cope/spectroscope.html
http://eosweb.larc.nasa.gov/EDDOCS/Wav
2
Physical Science 2013-2014
SI-7 (E)
Choose appropriate models to explain scientific knowledge or experimental results (e.g., objects, mathematical relationships, plans, schemes, examples, role-playing,
Physical Science 2013-2014
Lafayette Parish School System
2013-2014 Curriculum Map
Physical Science: Unit 3:
Waves
Time Frame:-3 weeks-January 7 – January 24, 2014
Lab Activities
Activity 1: Waves—Energy in Motion
Activity 2: Understanding Transverse and Compression Waves
BLM—Wave Venn Diagram
Activity 4: Electromagnetic Spectrum
Measuring Visible Light BLM
Activity 5: Properties of Light
Activity 7: Sound Waves and the Doppler Effect
Sound KWL BLM elengths_for_Colors.html
learning logs ( view literacy strategy descriptions ) sound waves and the Doppler Effect can be found at http://www.walterfendt.de/ph11e/dopplereff.htm
http://www.glenbrook.k12.il.us/gbssci/phy s/Class/waves/u10l3d.html
. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Spectral_class http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Red_shift , http://imagine.gsfc.nasa.gov/YBA/M31velocity/spectral-info.html
Vocabulary self-awareness chart
Science learning logs
Wave Venn Diagram
Spectroscopes
Sound KWL
Focus: Types of wave propagation using a slinky.
Students will learn about types of waves, wave propagation, effect of wavelength on frequency, and effect of frequency on our senses.
Lab activities
Teacher Demonstrations
Science Learning Logs
Activity 1—Waves in Motion
3
computer simulations) (SI-H-
A4)
SI-9 (E)
Write and defend a conclusion based on logical analysis of experimental data
(SI-H-A6) (SI-H-A2)
SI-6 (I)
Use technology when appropriate to enhance laboratory investigations and presentations of findings (SI-H-A3)
Lafayette Parish School System
2013-2014 Curriculum Map
Physical Science: Unit 3:
Waves
Time Frame:-3 weeks-January 7 – January 24, 2014
Activity 2—Understanding Transverse and Compression Waves
Activity 4—Electromagnetic Spectrum
Activity 6—Stellar Spectra
Activity 7—Sound Waves and the Doppler Effect
Focus: The EM Spectrum
Activity 2: Understanding Transverse and Compression Waves
Activity 3: Opposing Viewpoints
Radiation Opinnionaire BLM
Focus:
Use Doppler ball to demonstrate phenomenon
Doppler Radar images
Students will learn about sound waves and the Doppler Effect.
Video(s)
KWL chart
Science learning logs
Activity 7: Sound Waves and the Doppler Effect
Doppler Effect Applet
Spectral Images of Red and Blue Shifted Objects
Sound KWL BLM
Physical Science 2013-2014
4
Lafayette Parish School System
2013-2014 Curriculum Map
Physical Science: Unit 3:
Waves
Time Frame:-3 weeks-January 7 – January 24, 2014
Physical Science 2013-2014
5