Jan 2015 Midterm Study Guide

CP CHEMISTRY STUDY GUIDE
MIDTERM EXAMINATION JANUARY 2015
CONTENT TOPICS: STATES of MATTER, PHYSICAL/CHEMICAL PROPERTIES & CHANGE
CORRESPONDING TEXTBOOK CHAPTER/SECTIONS: C1 Section 2, 3
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Distinguish between the physical properties and chemical properties of matter.
Classify changes of matter as physical or chemical.
Explain the gas, liquid, and solid states in terms of particles.
Distinguish between a mixture and a pure substance.
Use a periodic table to name elements, given their symbols.
Use a periodic table to write the symbols of elements, given their names.
Describe the arrangement of the periodic table.
CONTENT TOPICS: MEASUREMENT, SCI NOTATION, DENSITY & CALCULATIONS
CORRESPONDING TEXTBOOK CHAPTER/SECTIONS: C2 Section 2, 3
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Distinguish between a quantity, a unit, and a measurement standard.
Name and use SI units for length, mass, time, volume, and density.
Distinguish between mass and weight.
Perform density calculations.
Transform a statement of equality into a conversion factor.
Convert between units.
Convert measurements into scientific notation.
CONTENT TOPICS: ARRANGEMENT OF THE ELECTRONS
CORRESPONDING TEXTBOOK CHAPTER/SECTIONS: C4, C5
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Explain the mathematical relationship among the speed, wavelength, and frequency of electromagnetic radiation.
Discuss the dual wave-particle nature of light and Louis de Broglie’s role in the development of the quantum model of the atom.
Describe the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom.
List the four quantum numbers, and describe their significance.
Relate the number of sublevels corresponding to each of an atom’s main energy levels, the number of orbitals per sublevel, and the number of orbitals per main energy level.
State the Aufbau principle, the Pauli Exclusion Principle, and Hund’s rule.
Describe the electron configurations for the atoms of any element using orbital notation, electronconfiguration notation, and when appropriate, noble-gas notation.
Define valence electrons, and state how many are present in atoms of each main-group element.
Define isotopes. Determine the number of protons, neutrons and electrons present in a given isotope of an element. Use isotope nomenclature to describe an isotope.
CONTENT TOPICS: CHEMICAL EQUATIONS, REACTION TYPES, ACTIVITY SERIES
CORRESPONDING TEXTBOOK CHAPTER/SECTIONS: C8 Section 1-3
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
List observations that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place.
List requirements for a correctly written chemical equation.
Write a word equation and a formula equation for a given chemical reaction.
Balance a formula equation by inspection.
Define and give general equations for synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, and double-
displacement reactions.
Classify a reaction as synthesis, decomposition, single-displacement, double-displacement, or combustion.
Predict the products of simple reactions given the reactants.
Explain the significance of an activity series.
Predict whether a given reaction will occur and what the products will be, using an activity series.
CONTENT TOPICS: MOLECULAR & NET IONIC EQUATIONS, SOLUBILITY
CORRESPONDING TEXTBOOK CHAPTER/SECTIONS: C13 Section 1
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Predict whether a precipitate will form when solutions of soluble ionic compounds are combined using the solubility rules, and write the molecular and net ionic equations for precipitation reactions.
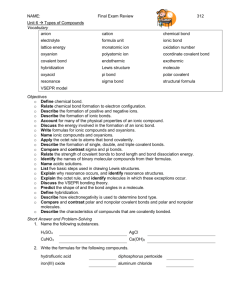
CONTENT TOPICS: CHEMICAL FORMULAS AND COMPOUNDS, MOLE, STOICHIOMETRY
CORRESPONDING TEXTBOOK CHAPTER/SECTION: C7 Section 1-4, C9 Sections 1-3
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Explain the significance of a chemical formula.
Determine the formula of an ionic compound formed between two given ions.
Name an ionic compound given its formula.
Name a binary molecular compound from its formula, using prefixes.
Write the formula of a binary molecular compound given its name.
Name binary molecular compounds using oxidation numbers and the Stock system.
Calculate the formula mass or molar mass of any given compound.
Convert between mass in grams and amount in moles of a chemical compound, using molar mass.
Calculate the number of molecules, formula units, or ions in a given molar amount of a chemical compound.
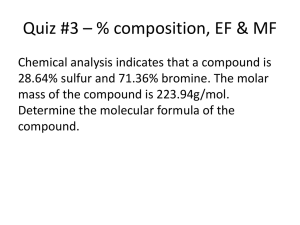
Calculate the percentage composition of a given chemical compound.
Define empirical formula, and explain how the term applies to ionic and molecular compounds.
Explain the relationship between the empirical formula and the molecular formula of a given compound.
Describe the importance of the mole ratio in stoichiometric calculations.
Write a mole ratio relating two substances in a chemical equation.
Calculate the amount in moles of a reactant or product from the amount in moles of a different reactant or product.
Calculate the mass of a reactant or product from the amount in moles of a different reactant or product.
Calculate the amount in moles of a reactant or product from the mass of a different reactant or product.
Calculate the mass of a reactant or product from the mass of a different reactant or product.
CONTENT TOPICS: LABORATORY
WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
Determine density by displacement (density labs).
Technique for ‘massing out’ a substance.
How to reading a graduated cylinder.
Simple tests to identify a gas (physical/chemical changes lab).
Separation techniques: gravity filtration (physical/chemical changes, mole labs).
Reading data tables.
How to determine the % water in a hydrate.
Laboratory safety.