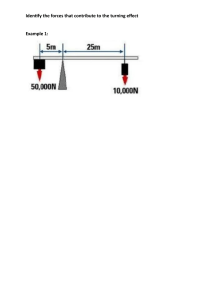
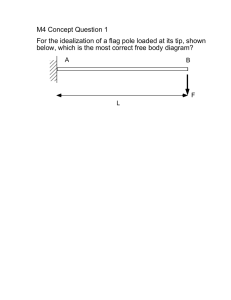
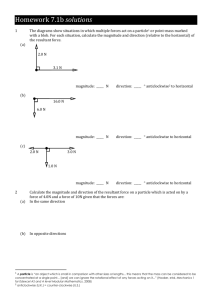
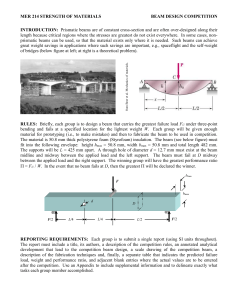
Word - Foundation Coalition
advertisement
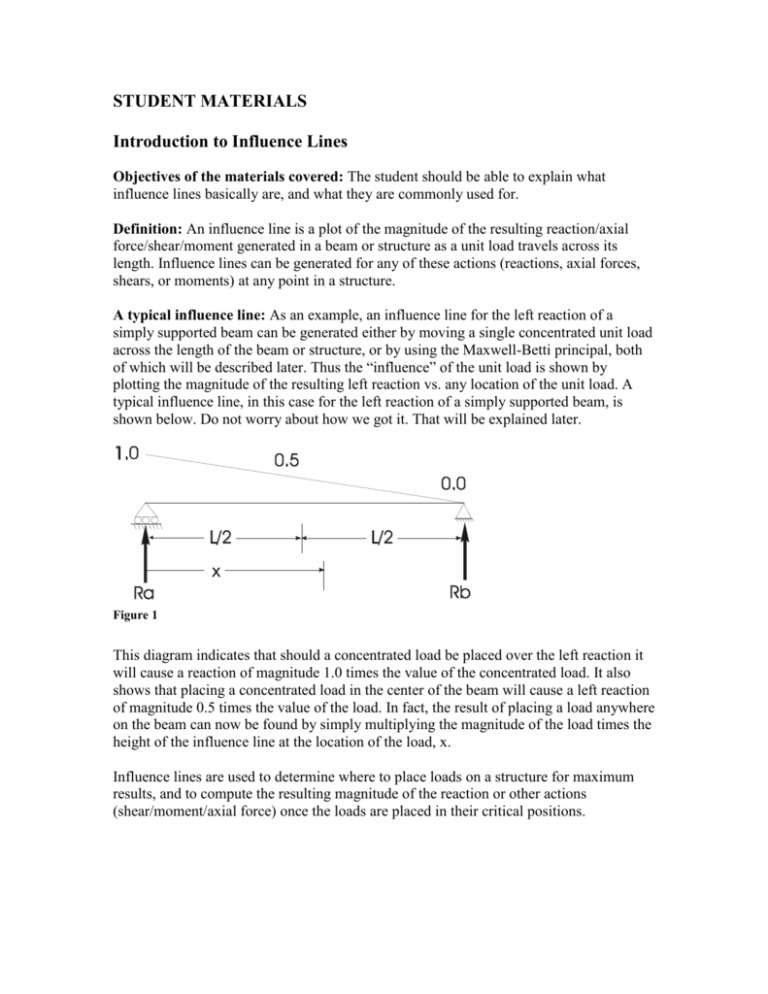
STUDENT MATERIALS Introduction to Influence Lines Objectives of the materials covered: The student should be able to explain what influence lines basically are, and what they are commonly used for. Definition: An influence line is a plot of the magnitude of the resulting reaction/axial force/shear/moment generated in a beam or structure as a unit load travels across its length. Influence lines can be generated for any of these actions (reactions, axial forces, shears, or moments) at any point in a structure. A typical influence line: As an example, an influence line for the left reaction of a simply supported beam can be generated either by moving a single concentrated unit load across the length of the beam or structure, or by using the Maxwell-Betti principal, both of which will be described later. Thus the “influence” of the unit load is shown by plotting the magnitude of the resulting left reaction vs. any location of the unit load. A typical influence line, in this case for the left reaction of a simply supported beam, is shown below. Do not worry about how we got it. That will be explained later. x Figure 1 This diagram indicates that should a concentrated load be placed over the left reaction it will cause a reaction of magnitude 1.0 times the value of the concentrated load. It also shows that placing a concentrated load in the center of the beam will cause a left reaction of magnitude 0.5 times the value of the load. In fact, the result of placing a load anywhere on the beam can now be found by simply multiplying the magnitude of the load times the height of the influence line at the location of the load, x. Influence lines are used to determine where to place loads on a structure for maximum results, and to compute the resulting magnitude of the reaction or other actions (shear/moment/axial force) once the loads are placed in their critical positions.