Lesson Plan
advertisement

Student’s Name
March 14, 2004
Lesson 7-1 Integers
Grade 7 – Average Ability
Goal / Behavioral Objective: Given an exercise set, the students will be able to read an
integer, write an integer, find the opposite of an integer, and find the absolute value of an
integer at an 85% success rate.
Pre-knowledge: Knowledge of whole numbers.
Equipment/Special Needs: Practice Worksheet 7-1 and Study Guide Worksheet 7-1.
Techniques Used: S: Student T: Teacher
___ Use of Manipulative
_S Work in Pairs
_T_ High level of Questioning Techniques
_S_ Cooperative Learning
_S__ Work at Desk
_T_ Work at Board
___ Work at Overhead
_ST__ Oral Work
_ST_ Written Work
____ Use of Calculators
____ Use of Computers
____ Student Presentations
____ other _____________
_____________________
STATEMENTS OF NCTM STANDARDS EMPLOYED
Enable all students to:
Problem Solving
Build new mathematical knowledge through problem solving.
Solve problems that arise in mathematics and other contexts.
Monitor and reflect on the process of mathematical problem solving.
Reasoning and Proof
Make and investigate mathematical conjectures.
Develop and evaluate mathematical arguments and proof.
Communication
Organize and consolidate their mathematical thinking through communication.
Communicate their mathematical thinking coherently and clearly to peers, teachers,
and others.
Analyze and evaluate the mathematical thinking and strategies of others.
Use the language of mathematics to express mathematical ideas precisely.
Connections
Recognize and use connections among mathematical ideas.
Understand how mathematical ideas interconnect and build on one another to produce
a coherent whole.
Recognize and apply mathematics in contexts outside mathematics.
Representation
Create and use representations to organize, record, and communicate mathematical
ideas.
Select, apply, and translate among mathematical representations to solve problems.
Use representations to model and interpret physical, social, and mathematical
phenomena.
2
Number and Operation
Develop meaning for integers and represent and compare quantities with them.
Understand the meaning and effects of arithmetic operations with fractions, decimals
and integers.
Understand the use of the inverse relationships of addition and subtraction,
multiplication and division, and squaring and finding square roots to simplify
computations and to solve problems.
Develop and analyze algorithms for computing with fractions, decimals, and integers
and develop fluency in their use.
Evaluating Procedure: Walking around and checking student written work, asking students
questions, watching student faces for signs of frustration or accomplishment, using thumbs
up/down to check for understanding.
Evaluation of Lesson Plan:
5-minute check:
Write an equation or expression for each:
1. Six more than one-third of a number
2. seven is eight less than twice a number
3. two-thirds of a number is sixteen
4. three times a number is five more than a number divided by nine
5. Mr. O’Brien is twenty-three years old. The average age in this class is thirteen years
old. How many years older is Mr. O than the average age in the class? Write an
equation and solve.
Focus: Name a place in the world where the weather is really cold. Brrrrr!!!
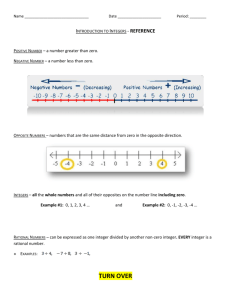
Do it: * * * An integer is any number form the set . . .
{…, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, …}
3
definitions:
1.
positive integers – integers greater than 0.
- integers to the right of 0
a) increase by 3
2.
b) deposit 10 dollars
negative integers – integers less than 0.
- integers to the left of 0.
a) diminish by 7
Examples:
b) loss of four yards
Write an integer for each situation.
a. a loss of $45
b. a gain of 5 pounds
c. 20% above cost
3.
opposites – two numbers represented by points that are the same distance from
0, but on opposite sides of 0.
4.
absolute value – the distance an integer is from 0.
Arithmetic
Absolute value of – 4 = | - 4 | = 4
Algebra
Absolute value of n = | n | =
n
opposite of n
Examples:
a) 4
if n is not negative
if n is negative.
Find the absolute value of each
b) - 22
c) - 243
d) 1,000,000
4
Check for understanding:
Draw a number line that shows 3 and its opposite.
What is the least positive integer?
What is the greatest negative integer?
Handout the Study Guide Worksheet 7-1.
Monitor student work.
Closure:
* * * Think: If the absolute value of an integer is equal to the opposite of the integer, then the
integer is _______________________.
Homework: Practice Worksheet 7-1.