Unit 3-Intergers - Tewksbury Township Schools
advertisement
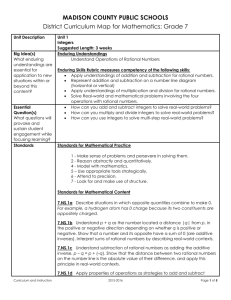
Unit Overview Content Area: Math Unit Title: Integers Unit: 3 Target Course/Grade Level: Seventh Grade Timeline: 3 weeks Unit Summary: Integers provide us with a way to represent situations that involve such concepts as winning/losing, above/below, left/right, and positive/negative. In this chapter, students read and write integers that correspond to positive and negative situations. However, most of their attention focuses on using and justifying the rules for adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing integers. This skill building provides the foundation for students to apply integer rules to all rational numbers in order to solve algebraic equations and real-world problems. Primary interdisciplinary connections: Language Arts and Technology 9.1 21st-Centuries Life & Career Skills Standard 9.1 All students will demonstrate the creative, critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills needed to function successfully as both global citizens and workers in diverse ethnic and organizational cultures. Strand: A. Critical Thinking and Problem Solving B. Creativity and Innovation C. Collaboration, Teamwork and Leadership Content Statement: 9.1.8: A The ability to recognize a problem and apply critical thinking skills and problem solving skills to solve the problem is a lifelong skill that develops over time. 9.1.8: B Gathering and Evaluating knowledge and information from a variety of sources, including global perspective, fosters creativity and innovative thinking. 9.1.8: C Collaboration and team work enable individuals or groups to achieve common goals with greater efficiency. Leadership abilities develop over time through participation in group and or teams that are engaged in challenging or competitive actions. 21st Century themes and skills: Critical Thinking and Problem Solving, Collaboration, Teamwork and Leadership, Creativity and Innovation Mathematical Practices: 7.MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 7.MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 7.MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 7.MP.4 Model with mathematics. 7.MP.6 Attend to precision. 7.MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. 7.MP.8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Learning Targets Domain: The Number System Cluster: Apply and extend previous understandings of numbers to the system of rational numbers Standard # 7.NS.1 7.NS.1a 7.NS.1b 7.NS.1c 7.NS.1d 7.NS.2 7.NS.2a 7.NS.2b 7.NS.2c 7.NS.3 7.EE.3 9.1.8.A.1 Standards Apply and extend previous understandings of addition and subtraction to add and subtract rational numbers; represent addition and subtraction on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram. Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0. For example, a hydrogen atom has 0 charge because its two constituents are oppositely charged. Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. Understand subtraction of rational numbers as adding the additive inverse, p – q = p + (–q). Show that the distance between two rational numbers on the number line is the absolute value of their difference, and apply this principle in real-world contexts. Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. Apply and extend previous understandings of multiplication and division and of fractions to multiply and divide rational numbers. Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (–1)(–1) = 1 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. Understand that integers can be divided, provided that the divisor is not zero, and every quotient of integers (with non-zero divisor) is a rational number. If p and q are integers, then –(p/q) = (–p)/q = p/(–q). Interpret quotients of rational numbers by describing realworld contexts Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational numbers. Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers.1 Solve multi-step real-life and mathematical problems posed with positive and negative rational numbers in any form (whole numbers, fractions, and decimals), using tools strategically. Apply properties of operations to calculate with numbers in any form; convert between forms as appropriate; and assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies. For example: If a woman making $25 an hour gets a 10% raise, she will make an additional 1/10 of her salary an hour, or $2.50, for a new salary of $27.50. If you want to place a towel bar 9 3/4 inches long in the center of a door that is 27 1/2 inches wide, you will need to place the bar about 9 inches from each edge; this estimate can be used as a check on the exact computation. Develop strategies to reinforce positive attitudes and productive behaviors that impact critical thinking and problem-solving skills. 9.1.8.A.2 Implement problem-solving strategies to solve a problem in school or the community. 9.1.8.B.2 Assess data gathered to solve problems for which there are varying perspective (e.g., cross cultural, gender specific, generational, etc.) and determine how the data can best be used to design the multiple solutions. 9.1.8.C.1 Determine an individual’s responsibility for personal actions and contributions to group activities. 9.1.8.C.2 Demonstrate the use of compromise, consensus and community building strategies for carrying out different task, assignments and projects. 9.1.8.C.3 Model leadership skills during classroom and extracurricular activities. Unit Essential Questions Unit Enduring Understandings How can you use numbers to describe concepts such as sea level, losing yardage in a football game, or temperatures that drop below zero? How is adding and subtracting integers like adding and subtracting whole numbers? How is it different? How do positive and negative numbers affect number operations? The set of integers of whole numbers and their opposites When adding two integers with like signs – add and take the sign of the numbers. When adding two integers with different signs, subtract their absolute values and that the sign with the larger absolute value. Subtracting integers can be defined in terms of addition – to subtract integers, add its additive inverse. Unit Learning Targets Students will ... Read and write integers. Add, Subtract, Multiply and Divide Integers. Solve problems looking for a pattern. Evidence of Learning Summative Assessment Use and justify the rules for adding, subtracting, multiplying, dividing integers. Equipment needed: Elmo, Smartboard, graph paper and number lines, dry erase boards/markers Teacher Instructional Resources: Textbook (To be determined) Study Island Khan Academy Videos Formative Assessments Skill sheets Quizzes/Tests Student workbook Homework Math games Study Island Integration of Technology: Smart Board to play online games, utilize online resources, generate models with Smart Software. Kahn Academy Videos Elmo – for demonstration Study Island Technology Resources: http://www.purplemath.com http://www.khanacademy.org – Interactive 2.0 instructional and practice site. Students can view instructional videos and complete practice modules for additional practice/remediation. http://www.studyisland.com/ - Web-based instruction, practice, assessment and reporting built from NJ standards. http://www.ixl.com/math/grade-7 - IXL 7th grade online interactive activities for the students to complete http://www.aaamath.com/grade7.html - AAA math 7th grade – online interactive activities and problems for the student to complete. http://www.adaptedmind.com/Math-Worksheets.html?type=hstb – Grade level material for practice, lessons, games, etc. Opportunities for Differentiation: Decelerate: use positive and negative chips for modeling concepts Accelerated: apply integer rules to fractions and decimals Teacher Notes: