Working with Sets
advertisement

Working with Sets
A.A.29 Use set-builder notation and/or interval notation to illustrate the elements of a set, given the
elements in roster form
A.A.30 Find the complement of a subset of a given set, within a given universe
A.A.31 Find the intersection of sets (no more than three sets) and/or union of sets (no more than three sets)
https://www.khanacademy.org/math/probability/independent-dependentprobability/basic_set_operations/v/intersection-and-union-of-sets
A set is a collection of unique elements. Elements in a set do not "repeat".
Methods of Describing Sets:
Sets may be described in many ways: by roster, by set-builder notation, by interval notation, by
graphing on a number line, and/or by Venn diagrams.
By Roster: A roster is a list of the elements in a set, separated by commas and surrounded by French
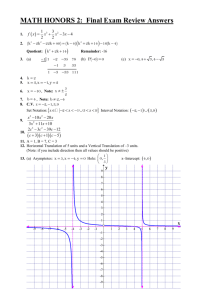
curly braces.
is a roster for the set of integers from 2 to 6, inclusive.
is a roster for the set of positive integers. The three dots indicate that the
numbers continue in the same pattern indefinitely.
Rosters may be awkward to write for certain sets that contain an infinite number of entries.
By Set-builder notation: Set-builder notation is a mathematical shorthand for precisely stating all
numbers of a specific set that possess a specific property.
= real numbers;
= integer numbers;
= natural numbers.
is set-builder notation for the set of integers from 2 to 6, inclusive.
= "is an element of"
Z = the set of integers
| = the words "such that"
The statement is read, "all x that are elements of the set of integers, such
that, x is between 2 and 6 inclusive."
The statement is read, "all x that are elements of the set of integers, such
that, the x values are greater than 0, positive."
(The positive integers can also be indicated as the set Z+.)
It is also possible to use a colon ( : ), instead of the | , to represent the words "such that".
is the same as
1
By interval notation: An interval is a connected subset of numbers. Interval notation is an alternative
to expressing your answer as an inequality. Unless specified otherwise, we will be working with real
numbers.
When using interval notation, the symbol:
(
means "not included" or "open".
[
means "included" or "closed".
as an inequality.
in interval notation.
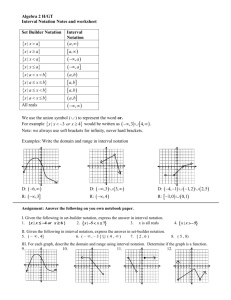
The chart below will show you all of the possible ways of utilizing interval notation.
Interval Notation: (description)
Open Interval: (a, b) is interpreted as a < x < b where the
endpoints are NOT included.
(While this notation resembles an ordered pair, in this context it
refers to the interval upon which you are working.)
Closed Interval: [a, b] is interpreted as a < x < b where the
endpoints are included.
Half-Open Interval: (a, b] is interpreted as a < x < b where a is
not included, but b is included.
Half-Open Interval: [a, b) is interpreted as a < x < b where a is
included, but b is not included.
(diagram)
(1, 5)
[1, 5]
(1, 5]
[1, 5)
Non-ending Interval:
is interpreted as x > a where a is not
included and infinity is always expressed as being "open" (not
included).
Non-ending Interval:
is interpreted as x < b where b is
included and again, infinity is always expressed as being "open"
(not included).
2
Now try these:
1. Which interval notation represents the set of all real numbers greater than 2 and less than or equal to
20?
1)
2)
3)
4)
2. Which notation describes
1)
2)
3)
4)
?
3. Which interval notation represents
1)
2)
3)
4)
Answers: 1. 2
2. 2
?
3. 1
Union and Intersection of Sets
Union of Sets
The union of two sets, denoted AUB ("A union B"), is the set of all members contained in either A or B
or both. We can think of the union of two sets as the entire Venn diagram:
Union of Sets
Union of A and B
Example : What is XUY if X = { -4, 3, 2, 11, -6} and Y = {3, 6, 11, -4, 5}?
The easiest way to write the union of two sets is to write all the members in the first set, and then write
all the members in the second set that haven't been written yet:
XUY = { -4, 3, 2, 11, -6, 6, 5}
Example : What is AUB if A = {2, 3, 4} and B = {5, 6, 7}?
AUB = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
The number of members in AUB should be the total number of members in A plus the total number
of members in B minus the number of members which are in both sets
3
Intersection of Sets
The intersection of two sets, denoted A∩B ("A intersect B") is the set of all members contained in both
A and B. We can think of the intersection of two sets as the overlap in the Venn diagram:
Intersection of Sets
Example: What is X∩Y if X = { -4, 3, 2, 11, -6} and Y = {3, 6, 11, -4, 5}?
X∩Y = { -4, 3, 11}
Example: What is A∩B if A = {2, 3, 4} and B = {5, 6, 7}?
Since A and B have no members in common, A∩B = Ø (the null set).
Now try these:
1. Given:
If set B is a subset of set U, what is the complement of set B?
1)
2)
3)
4)
2. Twelve players make up a high school basketball team. The team jerseys are numbered 1 through
12. The players wearing the jerseys numbered 3, 6, 7, 8, and 11 are the only players who start a
game. Using set notation, list the complement of this subset.
3. Given:
What is the intersection of sets X, Y, and Z?
1)
2)
3)
4)
4. Given:
What is the union of sets A and B?
1)
2)
3)
4)
Answers: 1. 4
2. {1,2,4,5,9,10,12}
3. 1
4. 4
4