Activities for multiplication instruction and practice:
Activities for multiplication instruction and practice:
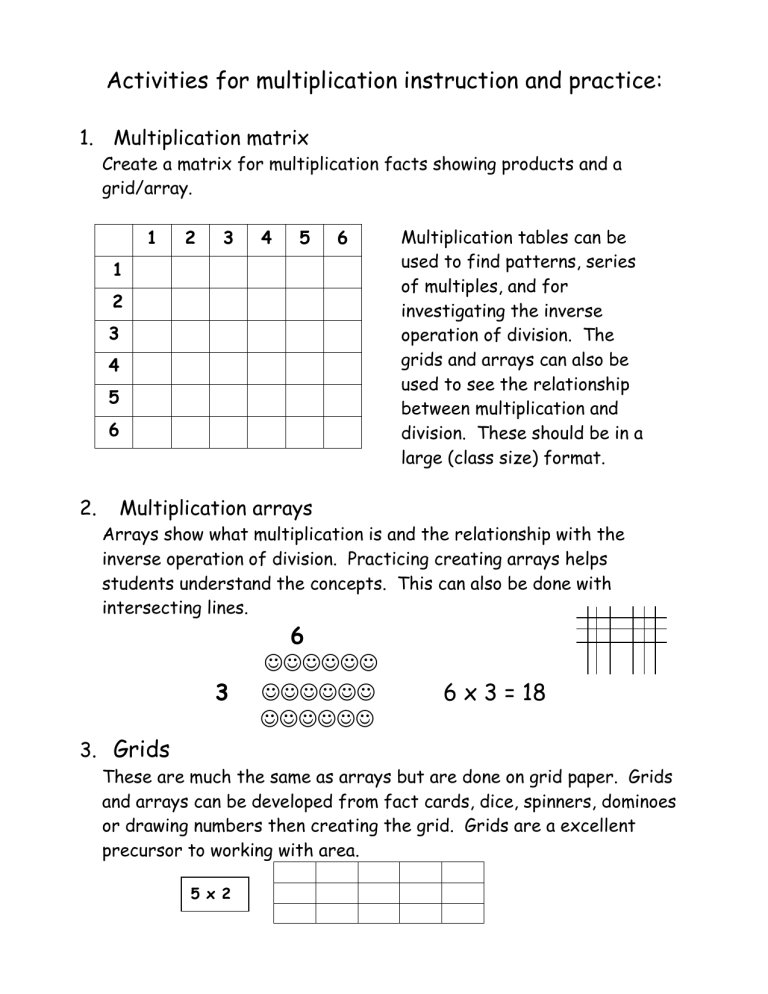
1.
Multiplication matrix
Create a matrix for multiplication facts showing products and a grid/array.
1 2 3 4 5 6
1
2
3
4
5
6
Multiplication tables can be used to find patterns, series of multiples, and for investigating the inverse operation of division. The grids and arrays can also be used to see the relationship between multiplication and division. These should be in a large (class size) format.
2.
Multiplication arrays
Arrays show what multiplication is and the relationship with the inverse operation of division. Practicing creating arrays helps students understand the concepts. This can also be done with intersecting lines.
6
3
6 x 3 = 18
3.
Grids
These are much the same as arrays but are done on grid paper. Grids and arrays can be developed from fact cards, dice, spinners, dominoes or drawing numbers then creating the grid. Grids are a excellent precursor to working with area.
5 x 2
4.
Counting Strips
These connect multiplication to skip counting and help students recognize patterns in multiples. Using the terms multiples helps them build the foundation for future work. Do you see the pattern? Look in the ones column – the numbers repeat every 6 th number.
In the tens the digit changes 000 11 222 33 444 etc.
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
5.
100’s boards
These can be used to illustrate skip counting patterns. Once again these illustrate patterns for students and they see the relationships between the numbers and can identify multiples easily.
Students can cover multiples with counters or color the multiples.
Students should be encouraged to note the patterns
6.
Fact families
Students should be able to identify, create, match equations to form fact families. Dominoes are an excellent source of the numbers for the equations as are triangular flashcards.
7.
Multiplication /division books
Create books for sets of facts; this is especially helpful for fact groups the student is having difficulty with. Books should use fact equations and illustrations.
8.
Power cards
This is played like the card game war. Face cards are removed from the cards and they are divided evenly between 2 players. The players turn their cards over simultaneously. The first player to say the correct answer keeps the cards.
9.
Circles and stars
Students spin or roll a die to determine 1 st number. They then draw that many circles. A second spin or roll determines the number of stars in each circle creating the multiplication problem. 3 x 3 = 9
10.
Tapes, chants, rhymes, songs
Chanting, singing can help some students recall basic facts.
Students can create their own chants, rhymes, songs, or listen/sing with a commercial tape.
11.
Oral Skip counting
Students can regularly practice this as they line up, during transitions or as a warm up before lessons. This is especially helpful for auditory learners.
12.
Building models with counters, unifix cubes, pattern blocks, etc.
Using manipulatives to create models of problems/equations can help students visualize the concept.
13.
Flashcards with a friend
14.
Multiplication bingo
Use cards with problems, products, or a combination. Have students lead the activity.







