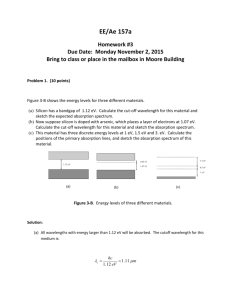
Theoretical Questions

Theoretical questions
I Interaction of light with Matter
1.1
Frequency (Hz), energy (eV), and Wavenumber (cm
-1
)
1.2
Light transmission through material
1.3
Reflection, Transmission , Scattering and Absorption scattering in materials
1.4
Beer -Lambert equation
II AgCl and AgBr crystals their absorption spectra, absorption spectra dependence on composition.
2-1.Urbach-Moser rule
III . Spectral characteristics of activated glasses and crystals:
3.2 Rare earth
3.3 Phonon-assisted optical transitions in solids (Tl
+
-like ions)
IV Equipments for absorption measuring. Two beam spectrometer, Single beam spectrometer.
4-1 Spectrometer calibration: base line, spectral calibration.
References
1.
A. Katzir in Laser and Optical fibers in medicine.
2.
The Theory of Photographic process, Third edition by T. James and A. Kocher.
3.
Biological Spectroscopy: Chapter 2, L. D. Campbell and R. A. Dwek,
(Banjamin/Cumings Publshing. Inc). 1984.
4.
B. Nican, Mc.work
5.
D. Dunn, Urbach’s rule in electron-Phonon Model, Phys Rev.,
174, pp. 855-858
(1968).
1
6.
E. Buhks. On Urbach rule theory for impurity light absorption, J. Phys. C: Solid
State Phys., 8, pp. 1601-1606 (1975).
7.
Laser Crystals, A. Kaminskii, Chapter 2, ( Second Ed., Springer Verlag ) 1975.
8.
L. Nagli, D. Bunimovich, A. Katzir, O. Gorodetsky, V. Molev, The luminescence properties of Dy-doped high silicate glass, J. Non-Crystalline Solids, 217, pp. 208-
214 (1997).
9.
Physics of color centers, Chepter2, (ed by. W.Fowler, NY, Pergamon) 1968 .
10.
UV/VIS Spectrometer, Manuals.
2
Experiments
Objective
1) Spectrometer V-500 calibration a) Base line measurements b) Spectral calibration
2) Absorption spectra for AgBr and AgCl crystal plates a)Calibration curve: wavelength
(nm) at
(cm
-1
) const between 80 -20 cm
-1
as function of chlorine concentration x.
b)Determination of the composition x of Cl – ions in composed AgCl x
Br
1-x
crystals using absorption spectra.
3) Urbach’s parameters determination.
4) Identification of the transition and determination of the absorption cross-sections for
Dy
3+
- ions in borosilicate glass.
5) Gaussian shape of the A band absorption of the In
+
-ions or Eu
2+
- ions in KBr crystals.
0 exp[
( h
m
2 kT h
)
)
2
]
6) Determination of In
+
-ions concentration in KBr: In or KBr:Eu crystals, (Smakula’s relation 2-47 equqtion in [9], ( f c, In
=0.5, n=1.559: f cEu,
=0.03 for KBr:Eu )
3
6.
7.
8.
9.
Procedure
I. Base line correction
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Insert crystal holder in sample chamber torn on spectrometer after 30 min go to spectrum measurements go to measure go to parameters:
Mod.
Response
Scan rate
Scan range start
End
Data pitch
Diapason - 0.005
0.005
Abs
Fasr
1000nm/min
1100nm
200nm
1.0 nm
Ok
Measure
Baseline
Start
II. Wavelength correction
1.
Spectrum measurements Of
2.
In Spectral Manager go to Environment
3.
Wavelength correction
4.
Executive
5.
Executive
6.
If all is OK than close, Stop
III. Absorption spectra measurements
1.
Insert sample
4
2.
In Spectral Manage go to Spectrum measurements
3.
Measure
4.
go to parameters:
Mod.
Response
Scan rate
Scan range
End
Data pitch
Diapason start
0
Abs
Fasr
1000 nm/min
550 nm
380 nm
1.0 nm
2
5.
Ok
6.
start
7.
in after spectrum measuring the Screen Spectrum Analysis appears and save your results in .txt and .jws format
IV. Results
1.
Take you ASCII file to any graphic program (Origin, Exel, etc) trajsform
2.
Transformed Absorption data in optical density to absorption coefficient
α in
(cm
-1
) (using Beer- Lambert equation)
3.
Using fitting subtract reflection and scattering
4.
Put all absorption curves for different AgCl x
Br
1-x
X composition on one screen, fined the wavelength corresponding to the same absorption coefficient α for different composition x and create calibration curve Wavelength = F( x)
5.
Measure absorption spectra for unknown sample and using calibration curve and determine its composition.
6.
Urabch’s parameters determination:
1.
determination using two value of absorption
2.
h
0 and
0
determination using best fit functions.
5
7.
.Dy
3+
ions absorption cross -section estimation in borosilicate glass (0.65 w% concentration)
8.
In
+
concentration estimation in crystal KBr:In crystals ( f
A
= 0.5, n=1.559)
6