IGCSE Physics Mark Scheme (Extended Theory) Nov 1999
advertisement

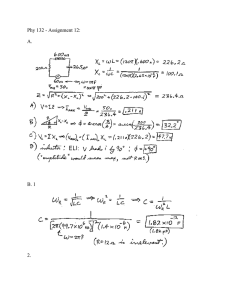
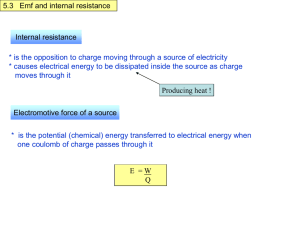
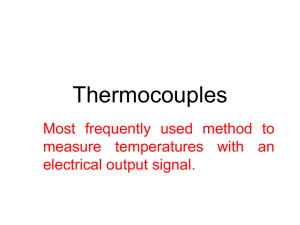
Mark scheme for IGCSE Physics (0625/3) – Extended Theory November 1999 1 (a)(i) PE (for one fall) is mgh = (200 x 10 x 6) = 12 000 J (ii) PE (lost) = KE (on impact) or v = 2gh or s = 2at 12000(J) or answer to (i) = ½ mv or v = 2 x 10 x 6 or t = 1.1 s v = 120 or v = gt v = l0.95 or 11 m/s (b)(i) (Energy to do) work/mechanical energy to move the pile against resistance/ground forces (Energy to) heat (Energy to) sound (energy chains max 1, first answer only considered.)1 At impact kinetic energy/ momentum large After impact kinetic energy/ momentum soon zero Kinetic energy change/ momentum change large Slows to rest in very short distance/time KE lost/work = force x distance the pile moves / rate of change of momentum = force 1 1 1 (c) lifting suspension etc/ pile deeper after each hit need more p.e. each time Rising mass gains k.e. All lost at top Power to stop/brake rising mass All lost as heat Efficiency of motor not 100% Lost as heat 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 (max) (d) Greater mass Fall greater distance Use motor to drive mass down/thinner or pointed pile 1 1 1 3 (a) Take temperatures before and after heating/ temperature difference with thermocouple Take the time that the heater is switched on/ time with stopwatch Find in some way the mass of the block and the power of the heater (ii) 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 7 1 1 1 1 2 8 (max) 1 1 2 3 (max) (b) Heat input of heater = heat gained by the block Heat input of heater =200 x 1 50(J) Heat gained by metal =1 x s x 50(J) s = 600 (J/kgK)/ 0.6 (J/gE) 1 1 1 1 4 (c)(i) Outline e.g. 2 metals to suitable meter Essential parts labelled Temperature difference produces an emf/voltage/current emf/current read by meter as a temperature Temperature rapidly changing/small changes in temperature 1 1 1 1 1 (ii) (iii) 3 measures high/low/wide range of temperatures Not fragile like mercury in glass /can be made recording/remote reading / thermometer not removed 1 (a) Each reflected angle 85o/10o/170o deviation at each reflection Total deviation 20o /160o 1 1 2 (b) (Angle of incidence much) greater than the critical angle So total internal reflection occurs 1 1 2 (c)(i) 1.50 = 1/sin c sin c=0.6667 c = 41.8o / 42o (Angle of incidence is) less than the critical angle Refracted (out into the air)/ not totally internally reflected 1 1 1 1 1 4 (max) Light of one colour/ wavelength Light of one frequency Speed = 4 x l014 x 5 x l0-7 = 2 x l08(m/s) Speed in air/ speed in glass = refractive index Speed in air / speed in glass x 1.50 1 1 1 1 1 1 5 (max) (ii) (d)(i) (ii) (iii) 4 (a)(i) Speed of rotation (of the coil/magnet) is faster The number of turns on the coil / number of coils (not transformer) is greater The strength of the magnet / magnetic field is stronger Any other correct factor identified How factor change relates to the emf (ii) The induced emf/current produced by a conductor cutting a magnetic field induced emf/current also interacts with the magnetic field interaction produces a force which slows/opposes the moving conductor (b)(i) (ii) (iii) (c)(i) 1 6 (max) 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 4 (max) 1 1 1 7 Power input = power output / 400 x 80 = 30 000 x I I = 1.1(A) Reduce voltage to value suitable for consumers / 240 V / 110 V Current in these cables much reduced (because) voltage increased Heat = I 2Rt or Power = I2R or heat in cables less 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 6 (max) 3.1 (A) at X 1 (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) 5 (a) (b)(i) (ii) (c) 0.8 (A) at Y R = 110/any current value R = (110/0.8) = 138 (ohm) Any attempt at use of I/R formula for parallel resistors 1/R = 1/24 + 1/48 R = 16 (ohm) Use of VI or I2R for calculating power = 110 x 4.6/4.62 x 24 = 506/508 (W) Use of energy = I 2 Rt / VIt = 30000 / 31000 (J) Diagram showing radioactive liquid in pipe, weld and detector in correct places three labels Where weld thin reading rises Radiation passes more easily through / less absorbed by thinner metal 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 10 (max) 1 1 1 1 3 (max) Alpha - none passes through steel Beta - some passes through steel Gamma - most/all passes through steel Accept either beta or gamma with some reasoning Beta/gamma with clear reason for the choice 1 1 1 1 1 4 (max) Any 3 standard precautions which apply to this situation (generally shielding/absorbing, distance, monitoring radiation) 3 3