Testing Restrictions
advertisement
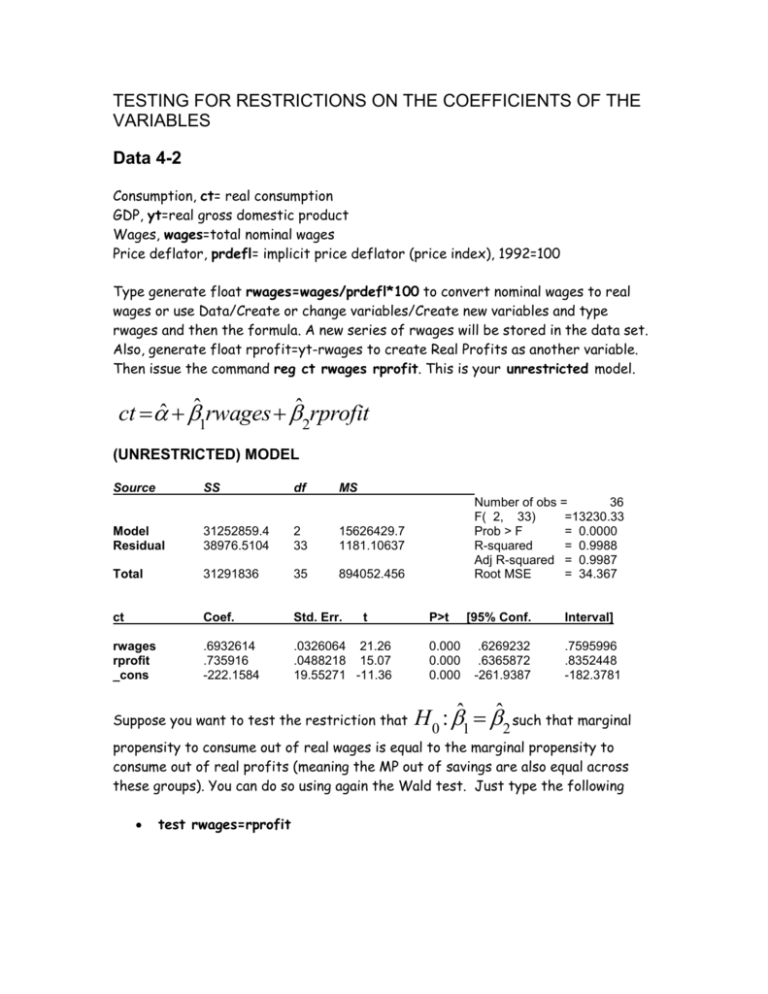
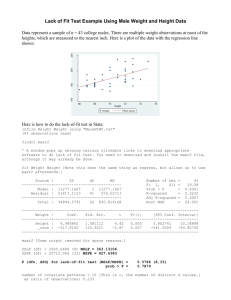
TESTING FOR RESTRICTIONS ON THE COEFFICIENTS OF THE VARIABLES Data 4-2 Consumption, ct= real consumption GDP, yt=real gross domestic product Wages, wages=total nominal wages Price deflator, prdefl= implicit price deflator (price index), 1992=100 Type generate float rwages=wages/prdefl*100 to convert nominal wages to real wages or use Data/Create or change variables/Create new variables and type rwages and then the formula. A new series of rwages will be stored in the data set. Also, generate float rprofit=yt-rwages to create Real Profits as another variable. Then issue the command reg ct rwages rprofit. This is your unrestricted model. ct ˆ ˆ1rwages ˆ2rprofit (UNRESTRICTED) MODEL Source SS df MS Model Residual 31252859.4 38976.5104 2 33 15626429.7 1181.10637 Total 31291836 35 894052.456 ct Coef. Std. Err. rwages rprofit _cons .6932614 .735916 -222.1584 .0326064 21.26 .0488218 15.07 19.55271 -11.36 t Suppose you want to test the restriction that Number of obs = 36 F( 2, 33) =13230.33 Prob > F = 0.0000 R-squared = 0.9988 Adj R-squared = 0.9987 Root MSE = 34.367 P>t 0.000 0.000 0.000 [95% Conf. .6269232 .6365872 -261.9387 Interval] .7595996 .8352448 -182.3781 H 0 : ˆ1 ˆ2 such that marginal propensity to consume out of real wages is equal to the marginal propensity to consume out of real profits (meaning the MP out of savings are also equal across these groups). You can do so using again the Wald test. Just type the following test rwages=rprofit ( 1) rwages - rprofit = 0 F( 1, 33) = Prob > F = 0.28 0.6017 Notice that F-test has a p-value of 0.6017 greater than any alpha. DO NOT REJECT the null hypothesis, H 0 : ˆ1 ˆ2 So, the MPC out of wages and MPC out of profits are equal to each other, refuting an important misconception that saving propensity out of profits are higher than that of wages! Various types of restrictions can be tested using this simple method. METHOD 1: WALD TEST ON RESTRICTIONS Alternatively, you can generate the F-test using the ESSR and ESSUR in the formula described in class. You will get the same value as F=0.277722 in the above table. To get the restricted model, regress ct on yt. This means that restricted model imposes the equality for the coefficients of rwages and rprofit combining them as yt. The output of the restricted model is given below. (RESTRICTED) MODEL reg ct yt Source SS df MS Model Residual 31252531.4 39304.5352 1 34 31252531.4 1156.01574 Total 31291836 35 894052.456 ct Coef. Std. Err. t yt _cons .7102901 -221.4251 .0043199 164.42 19.29488 -11.48 Number of obs = 36 F( 1, 34) =27034.69 Prob > F = 0.0000 R-squared = 0.9987 Adj R-squared = 0.9987 Root MSE = 34 P>t [95% Conf. Interval] 0.000 0.000 .701511 -260.637 7190692 -182.2132 Using the ESSR and ESSUR from these restricted and unrestricted models, you can get the same F statistic and carry out the test as in done in the Wald test output. METHOD 2: Indirect t-test See class notes on the derivation of the model. The output needed for this test is as follows. Regress ct on yt and rprofit. Source SS df Model 31252859.4 Resid 38976.5104 Total 31291836 ct Coef. MS 2 33 15626429.7 1181.10637 35 894052.456 Std. Err. t yt .6932614 .0326064 21.26 rprofit .0426546 .0809389 0.53 _cons -222.1584 19.55271 -11.36 P>t 0.000 0.602 0.000 Number of obs = 36 F( 2, 33) =13230.33 Prob > F = 0.0000 R-squared = 0.9988 Adj R-squared = 0.9987 Root MSE = 34.367 [95% Conf. .6269232 -.1220167 -261.9387 Interval] .7595996 .207326 -182.3781 This method, as explained in class, relies on a t-test on rprofit variable and is based on p-value. We can not reject the null of the equality of coefficients as p-value for rprofit=0.602>0.05 alpha. Same result! METHOD 3: Direct t-test No need for a separate estimation. Use the UR model above and calculate the ttest statistic as will be discussed in class. t ˆ1 ˆ2 s 2 ˆ s 2 ˆ 2Cov( ˆ1, ˆ2 ) 1 2 =(0.693262-0.735916)/sqroot(0.0326062+0.0488222-2(-0.001552))=-0.53 Cov(ˆ1, ˆ2 ) can be calculated as –0.001552 from Covariance Matrix on coefficients using correlate rwages rprofit, covariance _coef option. Based on this tvalue of –0.53, you can not again reject the null! Same result!