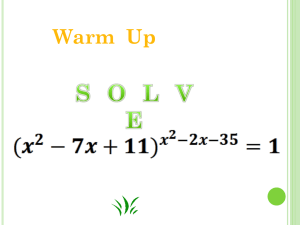ALGEBRA 2 X
advertisement

Name__________________________________________ Syllabus Unit 8: Rational Expressions & Equations We will most likely have a mini-quiz or two this unit. LAST UNIT ‘TIL SPRING BREAK DAY TOPIC 1 8.2 MULTIPLYING AND DIVIDING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS ASSIGNMENT pg. 580: 1-29 ODDS (skip 17) 2 8.3 ADDING AND SUBTRACTING RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS pg. 588 # 7, 9, 10, 22, 26, 34, 35 3 8.3 COMPLEX RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS pg. 588 # 1, 28-30, 43-45 4 5 6 Operations Practice #1 Operations Practice #2 8.5 SOLVING RATIONAL EQUATIONS TBA TBA pg. 605 # 1-9 odd, 10, 11 7 8.1 DIRECT, INVERSE & JOINT VARIATIONS (some hw problems done in class) pg. 573 # 2-8 even, 9-11, 13-15 pg. 573 # 20-23, 31, 40, 41 8 UNIT REVIEW Day #1 Review Worksheet 9 UNIT Review Day #2 TBD Unit 8 Test Enjoy the last day of winter. Spring is almost here. 10 Please be flexible as assignments may change. Page 1 of 24 Day 1: Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions Warm up: Simplify the following 1) 3 6 3 2) x2 2 x x 3) x2 9 x3 4) x 2 25 x2 6 x 5 3) 6 x2 7 x 3 3 x 2 x When simplifying rational expressions… Examples: Simplify and then state the values for x that make the expression undefined. 1) 4 x6 2x 6 x __________ 2) x4 2 3 x 11x 4 x __________ x __________ Multiplying rational expressions is just like simplifying two at a time. Any top can cancel with any ___________________ !! Examples: Multiply. Assume that all expressions are defined. x 2 4x 6 1) 2 x 3 x2 4 x 2 16 x2 2 2) 2 x 4x 4 x 6x 8 3x x 2 9 3) x 3 12 x3 x2 4x 3 x2 6x 8 2 4) x2 4 x 6x 8 Page 2 of 24 Division is just like multiplication, except:_________________________________________________! Examples: Divide. Assume that all expressions are defined. 1) x3 x3 2 x 2x 1 x 1 2) x3 x 5 y 15 y 4 3) x2 2 x 1 x2 1 x 2 3x 18 x 2 7 x 6 Mixed Practice: 1) 4x 8 x2 2x 2) x2 1 x 4 3 x 12 3) x 2 2 x 8 3x 2 10 x 8 9 x 2 16 x 2 16 4) 6 x3 y 2 2 xy 2 7z4 21z 2 5) x 2 36 x 2 12 x 36 6) 4 x 2 3x 2 x 1 4x2 1 x 7) 1 x * x2 1 8) 4 1 4 Page 3 of 24 Day 2: Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions To add or subtract fractions, you must have a ____________________________________. Let’s find a LCD (or LCM) for each of the following. 1) 12 and 18 4) x 2 2) 5x 2 and 25x x 12 and x 4 5) 3) x 2 x 4 and x 3 25 and x 2 10 x 25 Using example #3 from above, let’s add to rational expressions. Also, state x-values that make the expressions undefined. 1) 5 x 3 2x x 4 5 2x x 4 x 3 x 4 x 3 x 3 x 4 To recap, here are the steps to adding rational expressions… Step #1: Identify the __________ Step #2: Multiply each fraction by the _____________ ______________. Step #3: Distribute (or FOIL) on each of the __________ Step #4: Add the tops and keep the bottoms the __________. Step #5: State the values that make the expressions undefined (think ___________ = ____) 2) 7x x2 x2 5x x 5 3) 2 x x 4 x 3 Page 4 of 24 Try on your own… 4) 5) Subtracting is the same process, except you must be careful to ___________________ the negative! 1) 2) 4x 3 2x 3 x2 9 x 3 Mixed Practice: 1. 2. 3. 4. Page 5 of 24 Day 3: Complex Rational Expressions Warm up: Simplify the following 4 problems. Be sure to state restrictions on the variables. 1. 2. Multiply or divide. Write your answer in simplest form. Be sure to state restrictions on the variables. 3. 4. x 2 25 x 5 x 3 x2 9 Complex Fractions: fractions that have a fraction in the numerator, denominator, or BOTH. 1 3 x 1. Simplify the following: 5 4 y 1 1 x y 2. 2 1 y x 3. 3 1 1 2y Page 6 of 24 x 1 4. x 5 x6 x3 x 5. 2 3 x 12 6. x2 3 x 1 x2 1 7. x 5 x 2 x2 8. 3 3x 6 9 Let’s recap all that we have learned so far about rational expressions… 1) Multiplying: 2) Dividing: 3) Adding: 4) Subtracting: 5) Complex: Page 7 of 24 Day 4: Classwork – Operations Practice #1 Page 8 of 24 Page 9 of 24 Day 4: Homework – PSSA Prep Worksheet #1 (Due Monday) Directions: use the formula sheet below to help you with the practice PSSA test on the following 4 pages. There are 22 multiple choice questions to help you prepare for the PSSA (coming up mid April) Page 10 of 24 Page 11 of 24 Page 12 of 24 Page 13 of 24 Page 14 of 24 Day 5: Classwork – Operations Practice #2 Page 15 of 24 Page 16 of 24 Day 6: Solving Rational Equations There are two types of rational equations… 1) 1 7 x 5 2x * use either method 1. 3. x 8 2 x 2) 1 2 17 8 x 8x * Multiply by LCD right away or ** Combine into 1 fraction then cross multiply 2. 5 7 18 2 x 3 x 4 x x 12 k k 2 k 5 k 2 Page 17 of 24 4 x 7 x 1 1 x 6. 5. 12 8 2 x 1 x 6 3x 3 x 2 5 x 66 x 11 Word Problems 7. A kayaker spends an afternoon paddling on a river. She travels 3 miles upstream and 3 miles downstream in a total of 4 hours. In still water, the kayaker can travel at an average speed of 2 miles per hour. Based on this information, what is the average speed of the river’s current? Distance Rate Time Upstream Downstream 8. Jason can clean a large tank at an aquarium in about 6 hours. When Jason and Lacy work together, they can clean the tank in about 3.5 hours. About how long would it take Lacy to clean the tank if she worked alone? Time Jason Lacy Together Work 1 1 1 Rate Page 18 of 24 Day 7: Unit Review Simplify and state the restrictions on x. 1. x3 3x 2 18 x x 2 36 x ____________ 2. 15 x 2 240 25 x 2 200 x 400 x ____________ Simplify. You do not need to state restrictions. 3. x 2 x 12 2 x 2 9 x 18 2 x 2 11x 12 4 x 12 3 1 5. 2 x 1 x 3x x x 7. 5 1 x2 x x6 4. 5 x 35 x 2 9 x 14 9 x2 1 30 x 10 6. x3 x3 2 x 2 x 4x 4 8. 5 x3 2 x 3 x 8 x 15 Page 19 of 24 Solve the following equations. Don’t forget to check! 9. 5 2 1 5 2x 3 x 6 10. 11. 12 8 2 x 1 x 12. x 7 x 1 1 x 6 3x 3 x 5 x 66 x 11 2 Write an equation and solve it to find the solution to each problem. 13. John can mow a lawn in 4 hours. When Melissa helps him, they can mow the lawn in 2 12 hours. How long would it take Melissa to mow the lawn? Time John Melissa Together Work 1 1 1 Rate 14. A boat travels 6 miles upstream in the same amount of time it can travel 10 miles downstream. In still water the speed of the boat is 5 miles per hour. What is the speed of the current? Distance Upstream Downstream Rate 5-x 5+x Time Let x = the current of the water. 15. A water tank is filled by pipes from 2 wells. The first pipe can fill the tank in 4 days. The second pipe can fill the tank in 6 days. How long will it take to fill the tank using both pipes? Time Pipe A Pipe B Together Work 1 1 1 Rate Page 20 of 24 Day 8: Homework – PSSA Prep Worksheet #2 (After the Test) Directions: Use your formula sheet (if appropriate) to help you answer the following 11 questions. Page 21 of 24 Page 22 of 24 Day 9: Direct, Inverse, & Joint Variations Type of Variation Equation Form y kx k Direct y Inverse Ratio Form y x k xy k x Example y 45 x 5 y 3 x 8 Questions from HW: 2) If y varies directly as x, find an equation when y = 6 and x = 3. 9) If y varies inversely as x, find an equation when y = 2 and x = 7. 13) Determine whether each data set represents a direct variation, an inverse variation or neither. x y 2 3 5 6 9 4 A ______________________ variation is a relationship that contains both direct and inverse variation in one problem. Directly will be in the ________________ and inversely will be in the _________________. 20) Medicine: The dosage d of a drug that a physician prescribes varies directly as the patient’s mass m, and d = 100 mg when m = 55 kg. Find d to the nearest milligram when m = 70 kg. 22) Agriculture: The number of bags of soybean seeds N that a farmer needs varies jointly as the number of acres a to be planted and the pounds of seed needed per acre p, and N = 980 when a = 700 acres and p = 70 lb/acre. Find N when a = 1000 acres and p = 75 lb/acre. Page 23 of 24 40) Complete the table if y varies jointly as x and z. x 2 5 y 1.5 52.5 z 4 7 -36 1.38 23 1. y varies directly with x, and x = 18 when y = 3. Find y when x = 66. 2. y varies jointly with x and z, and y = 200 when x = 4 and z = 20. Find x when y = 500 and z = 25. 3. Speed is inversely proportional to time. If I can reach my destination travelling at 50 mph for 2 hours, how long would it take me at 65 mph? 4. The volume of a gas varies inversely with the pressure of the gas and directly with the temperature of the gas. A certain gas has a volume of 10 L at a temperature of 300 K (“Kelvin,” an important unit of temp. in Chemistry), and a pressure of 1.5 atmospheres (a unit of pressure). If the volume changes to 7.5 L and the temperature increases to 350 K, what will the new pressure be? 5. Fill in the chart, given that y varies jointly with x and z. x y z 2 120 5 10 25 2400 144 6 15 Answers! 1 1. y kx, k ; y 11 6 4. V 2. y kxz, k 2.5; x 8 5. k = 12 k 20 1.54 hours 3. s , k 100 miles; t t 13 x y z kT 7 , k .05; P 2.33 atmospheres. P 3 2 120 5 10 1800 15 25 2400 8 2 144 6 Page 24 of 24