Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Monomial: a number, variable
advertisement

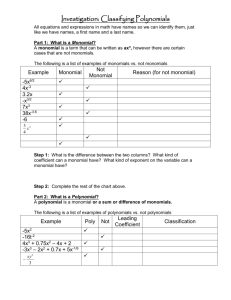
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials Monomial: a number, variable, or product of a number and variable. Binomial: The sum or difference of two monomials. Trinomials: The sum of difference of three monomials Polynomial: A monomial or sum of monomials. Degree of Monomial: The sum of the exponents on its variables. Degree of Polynomial: The greatest degree of its monomials. Polynomials are normally written in descending order. Example: x 3 5x 2 1. The exponents go 3, 2, 0 so it is in descending order. Leading Coefficient The coefficient of the largest number in the polynomial. In the example, 1 is the leading coefficient because of x 3 . Like Terms: Same variable, same exponent. Identifying if something is a monomial. Monomial 10 3x 1 ab 2 1.8m 5 Degree 0 1 1+2=3 Not a Monomial 5+x Reason A sum is not a monomial 2 A monomial cannot have a n variable in the 5 denominator a A monomial 4 cannot have a variable exponent 1 The variable must x have a whole number exponent. Example: Identifying and Classifying Polynomials: Tell whether the expression is a polynomial. If it is a polynomial, find its degree and classify it by the number of its terms. Otherwise, tell why it is not a polynomial. Expression Is a Polynomial? 9 2x 2 x 5 6n 4 8 n n 2 3 7bc 3 4b 4 c Yes Yes No; Variable Exponent No; Negative Exponent Yes Classify by Degree and Number of Terms 0 degree monomial 2nd degree trinomial 5th degree binomial Adding Polynomials To add polynomials, add like terms. You can us a vertical or horizontal format. Example: Add Polynomials Find the Sum a) Solve using vertical format: 2x 3 5x 2 x 2x 2 x 3 1 Solution: Align like terms in vertical columns and add. 2x 3 5x 2 x + x 3 2x 2 -1 3 2 3x 3x x 1 b) Solve using horizontal format: 3x 2 x 6 x 2 4x 10 Solution: Group Like Terms and Simplify 2 3x x 6 x 2 4 x 10 3x 2 x 2 x 4 x 6 10 4 x 2 5x 4 Try This: 3 2 3 Find the sum: 5x 4x 2x 4x 3x 6 Subtracting Polynomials To subtract a polynomial, add its opposite. To find the opposite of a polynomial, multiply each of its terms by -1. Example: Subtract Polynomials Find the Difference a) Solve using the vertical format: 4n 2 5 2n 2 2n 4 Solution: 4n +5 - 2n 2 2n 4 2 b) Solve using the horizontal format: 2 2 4x 3x 5 3x x 8 4n 2 +5 + 2n 2 2n 4 6n 2 2n 9 Solution: 2 2 4 x 3x 5 3x x 8 4 x 2 3x 5 3x 2 x 8 4 x 2 3x 2 3x x 5 8 x 2 2x 13 Try This: 4x 2 7x 5x 2 4x 9