Mathematics Graphmatica Folio Piece 1
advertisement

Melbourne High School
Mathematics Faculty
Year 9 Mathematics
Semester 2 Project: Graphmatica
Introduction to Graphmatica
Description
Graphmatica is an interactive algebraic equation grapher that can be used as an aide to plotting
mathematical curves. While it is designed to be extremely simple to use, its advanced features may not
be readily apparent to the first-time user. Please take a moment to acquaint yourself with them:
The screen layout includes the familiar menu bar, followed by the tool bar with icon symbols and then
The Redraw Queue. In the redraw queue Graphmatica remembers the last 25 equations you typed in or
loaded from a file. You can access these equations with the drop down arrow symbol on the right side
of the box. You can save your work for use in a later session or with any text editor including Word.
In the following example the graph of the line y=x is shown:
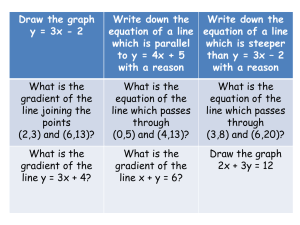
Linear Graphs
Linear graphs are formed by plotting a series of points according to some rule (an equation like y=x) on
the cartesian plane (x-y graph) and then joining them with a straight line. See Exercise 7E page 218
Linear Graphs always form straight lines. Every straight line has five things you must understand:
General Form
m = Gradient
c = y-intercept
x-intercept
Distance between
two points
The equation of a straight line
The gradient is the slope of the line.
A positive slope goes up hill.
A negative slope goes down hill.
The point where the straight line crosses the y axis
The point where the straight line crosses the x axis
Use Pythagoras’ Theorem to find the distance
between two points on the cartesian plane.
y mx c
m
rise y 2 y1
run x 2 x1
dAB
( y 2 y1 ) ( x 2 x1 )
2
2
Saturday, February 06, 2016
D:\687320737.doc
Melbourne High School
Mathematics Faculty
Activity 1 A Family of Straight Linear Graphs
To Draw the Graphs
Open Graphmatica and sketch a family of straight lines which have different m values.
Method 1: individually sketch each line by typing them in and press enter each time
Step
1
2
3
4
In the redraw queue Type
y mx c
yx
y 2x
y 3x
y 4x
Method 2: Use the menu bar to choose Point then Variables panel and make “a” go from 1 to 4 step 1
If you then type in y a * x and then press enter. All the graphs should appear.
There are a number of things that you can change with this presentation. The graph paper can clutter
the diagram. To remove the background use the menu bar to choose View, then Graph Paper and then
select none on “Select grid level detail”.
If you want to change the axes of the graph that appear on the screen use the menu to choose View then
Grid Range and type in the parts that you want to see. However, if you wish to restrict the domain of
the graph to show only 0 x 5 type {0,5} after the equation, for example: y a * x {0,5}
To Paste into Word
Open word and type appropriate headings to identify the graph.
Use the menu bar to choose Edit then Copy Graphs WMF then Monochrome.
Open Microsoft Word and choose Edit then Paste and these graphs will appear.
Tasks to hand in
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Draw the following sets of straight line graphs in Graphmatica using the set of x values
{x : 3 x 3} , and then copy each set into Word
In Word, describe the effect of the gradient on each graph when compared to the graph y x
In Word, describe the effect of the y-intercept on each graph when compared to y x
For each line state the range (the set of y values) in your Word document and then print your
document with headings using the conventions you have been taught.
Clearly label each line on the set of axes by hand.
SET A
y 2x 5
y 2x 3
y 2x
y 2x 3
y 2x 5
SET B
y x/5
yx/4
yx/3
yx/2
yx
SET C
y 3 x 5
y 3 x 3
y 3 x
y 3 x 3
y 3 x 5
Saturday, February 06, 2016
D:\687320737.doc
Melbourne High School
Mathematics Faculty
Activity 2: Patterns
Open Graphmatica and reproduce the following patterns:
Pattern 1 Square and Diagonal
Pattern 2: Sparkler
y
y
6
8
4
6
2
x
0
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
4
-2
2
-4
-6
x
0
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Pattern 3: Curve Stitching
y
8
6
4
2
x
0
-7
-6
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
Pattern 4: Your design
Design and draw your own pattern and clearly label the equation of each of the lines you have used.
Task to hand in
6.
For each of the patterns above, create a table in Word and enter the details in the columns:
Line
Equation
Gradient
y intercept
x intercept
1
2 etc
Saturday, February 06, 2016
D:\687320737.doc
Melbourne High School
Mathematics Faculty
Activity 3: Intersection of lines
Task to hand in
Open Graphmatica and plot the following pairs of lines onto a set of axes:
PAIR A
2 x y 1
x y4
7.
8.
9.
PAIR B
3x y 1
2 x y 4
PAIR C
y x 2
y
x
8
2
Copy the graph of each pair into Word
State the point of intersection of each pair of lines. Then print your Word document and clearly
label the lines
Solve each pair of simultaneous equations using the elimination method to confirm the solution.
Task to hand in
Open Graphmatica and plot each of the following on separate axes
a) A line which intersects the line y x 1 at the point (1,2) with a gradient of 2
b) A line which intersects the line y x at the point (-2,2) with a gradient of 1
c) A line which intersects the line y 2 x 2 at the point (4,6) with a gradient of -1
d) Make up your own question using your own lines.
10. Copy each graph into Word
11. Print your Word document and clearly label the lines
Submission of Work:
All tasks are to be completed in Word or on the printed word document
There are 11 numbered tasks with a marking scheme as follows
Saturday, February 06, 2016
D:\687320737.doc
Melbourne High School
Mathematics Faculty
Submission of Work:
All tasks are to be completed in Word or on the printed word document
There are 11 numbered tasks with a marking scheme as follows
Marking and Information Sheet
Student Name: _________________________________________Form: _______________
Overall Indicators
Marks allocated
Use of Word conventions
Presentation of Graphs
/5
/5
Marks =_______/10
Activity 1 Family of Curves
Task
Required information
1
2
3
4
5
6
Graph of SET A
Graph of SET B
Graph of SET C
Effect of Gradient
Effect of y intercept
Range of values
Print document
Correct labelling of each line
Marks allocated
/5
/5
/5
/5
/5
/3
No marks
/3
Marks =_______/31
Activity 2 Patterns
Task
Required information
7
Pattern 1
Pattern 2
Pattern 3
Pattern 4
Marks allocated
/6
/6
/7
/10
Marks =_______/29
Activity 3 Intersection of lines
8
Pair A
Pair B
Pair C
9
Point of intersection
10
Print document
11
Algebraic solution
12
13
Graphs of lines
Correct labelling of each line
/2
/2
/2
/3
No marks
/9
/8
/4
Marks =_______/30
Total Marks =_______/100
Saturday, February 06, 2016
D:\687320737.doc