Linear Relations and Functions Unit Test 1
advertisement
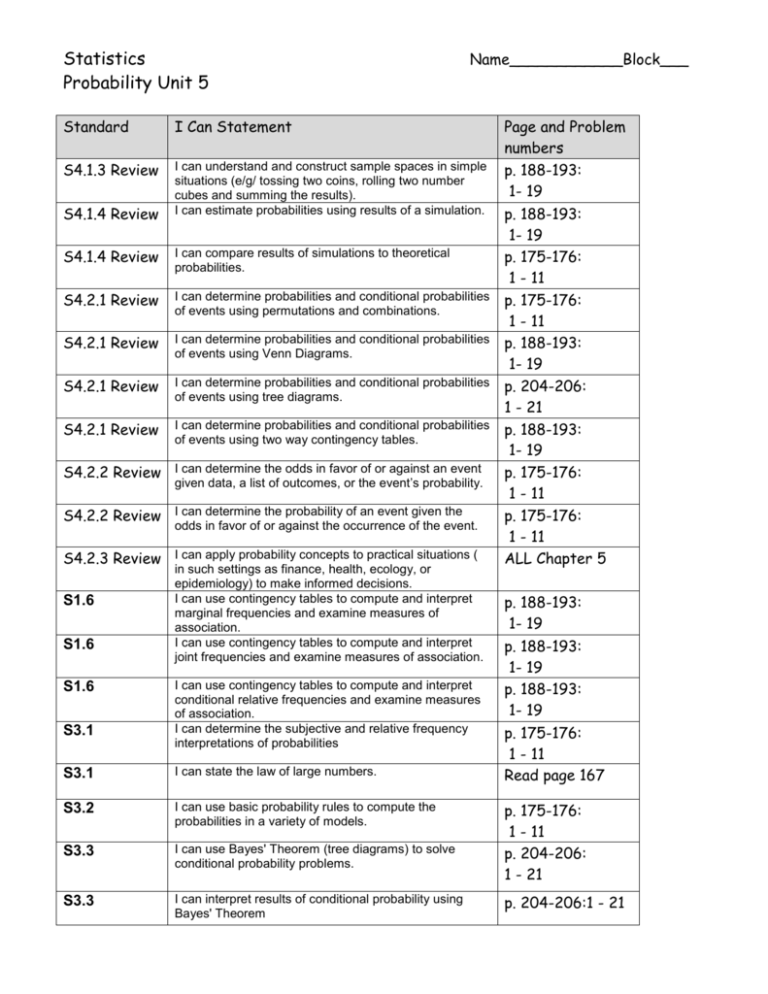
Statistics Probability Unit 5 Name____________Block___ Standard I Can Statement S4.1.3 Review I can understand and construct sample spaces in simple situations (e/g/ tossing two coins, rolling two number cubes and summing the results). I can estimate probabilities using results of a simulation. S4.1.4 Review S4.1.4 Review I can compare results of simulations to theoretical probabilities. S4.2.1 Review I can determine probabilities and conditional probabilities of events using permutations and combinations. S4.2.1 Review I can determine probabilities and conditional probabilities of events using Venn Diagrams. S4.2.1 Review I can determine probabilities and conditional probabilities of events using tree diagrams. S4.2.1 Review I can determine probabilities and conditional probabilities of events using two way contingency tables. S4.2.2 Review I can determine the odds in favor of or against an event given data, a list of outcomes, or the event’s probability. S4.2.2 Review I can determine the probability of an event given the odds in favor of or against the occurrence of the event. S4.2.3 Review I can apply probability concepts to practical situations ( S1.6 S1.6 S1.6 S3.1 in such settings as finance, health, ecology, or epidemiology) to make informed decisions. I can use contingency tables to compute and interpret marginal frequencies and examine measures of association. I can use contingency tables to compute and interpret joint frequencies and examine measures of association. I can use contingency tables to compute and interpret conditional relative frequencies and examine measures of association. I can determine the subjective and relative frequency interpretations of probabilities S3.1 I can state the law of large numbers. S3.2 I can use basic probability rules to compute the probabilities in a variety of models. S3.3 I can use Bayes' Theorem (tree diagrams) to solve conditional probability problems. S3.3 I can interpret results of conditional probability using Bayes' Theorem Page and Problem numbers p. 188-193: 1- 19 p. 188-193: 1- 19 p. 175-176: 1 - 11 p. 175-176: 1 - 11 p. 188-193: 1- 19 p. 204-206: 1 - 21 p. 188-193: 1- 19 p. 175-176: 1 - 11 p. 175-176: 1 - 11 ALL Chapter 5 p. 188-193: 1- 19 p. 188-193: 1- 19 p. 188-193: 1- 19 p. 175-176: 1 - 11 Read page 167 p. 175-176: 1 - 11 p. 204-206: 1 - 21 p. 204-206:1 - 21 S3.7 I can know and use the definition of independence of two discrete random variables S3.7 w.s. 3 S3.7 I can use joint distribution to determine whether two discrete random variables are independent. S3.7 w.s. 3 Statistics Chapter 5 Fri 10/24 to Wed 10/29 – Mini project #2 Thurs. Oct 30 5.1 What is Probability? #21 p. 175-176: 1 – 11 Fri. Oct 31 5.2 Some Probability Rules – Compound Events #23 p. 188-193: 1 -15 odd Mon. Nov 3 Tues Nov 4 5.2 Continue – #24 p. 188-193: 17-20 no school Wed. Nov 5 Venn Diagram w.s. Thurs. Nov 6 5.3 Trees and Counting Techniques – Bayes Theorem #24 p. 204-206: 1 – 21 odd Fri. Nov 7 Review #25 Practice worksheets 14-1, 14-2, and 14-3 Mon. Nov 10 Bayes Theorem w.s. Tues. Nov 11 Review Practice Worksheets 14-4, 14-5, 14-6, 14-7 Wed. Nov 12 Chapter 5 review #25 p. 207-208: 1-14 Thurs. Nov 13 More review Fri. Nov 14 Chapter 5 Test